J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Mar;56(3):420-426. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.3.420.
Dose-Effect Relationship of Unilateral Medial Rectus Resection for Recurrent Exotropia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yclee@cmcnu.or.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2339049
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.3.420
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the dose-effect relationship of unilateral medial rectus resection for recurrent exotropia after bilateral lateral rectus recession.
METHODS
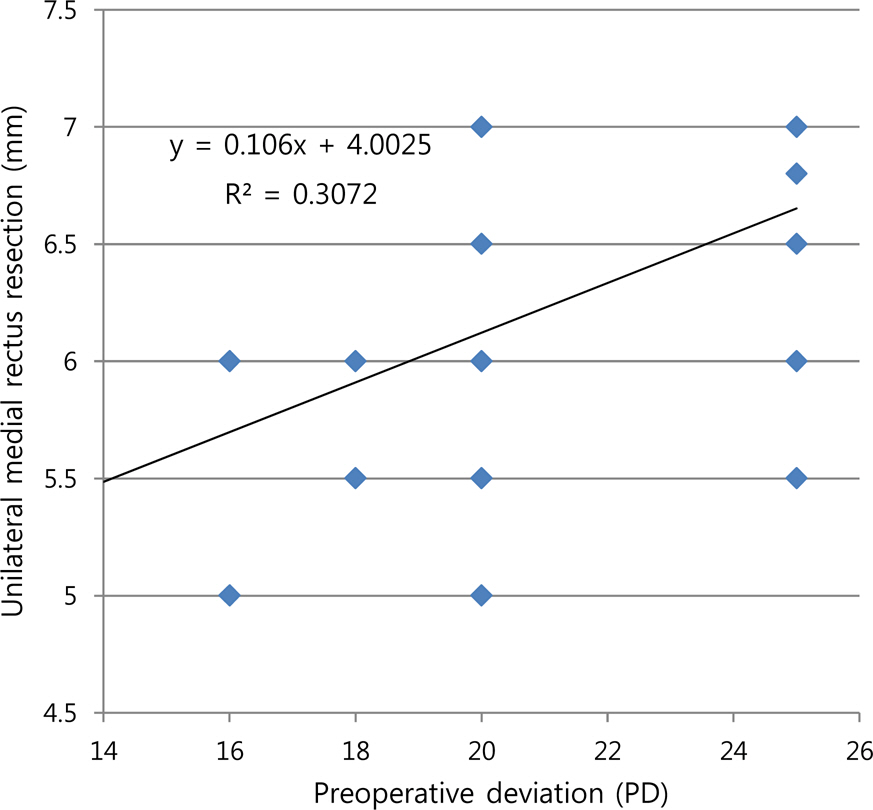
This study comprised 39 patients who underwent unilateral medial rectus resection for recurrent exotropia under 25 PD and bilateral rectus recession for prior surgery of exotropia. The medial rectus was resected from 5.0 to 7.0 mm according to angle deviation at a distance. The postoperative deviated angle was checked at one week, 3 months and 6 months postoperatively to investigate the amount of corrected deviation per resected muscle.
RESULTS
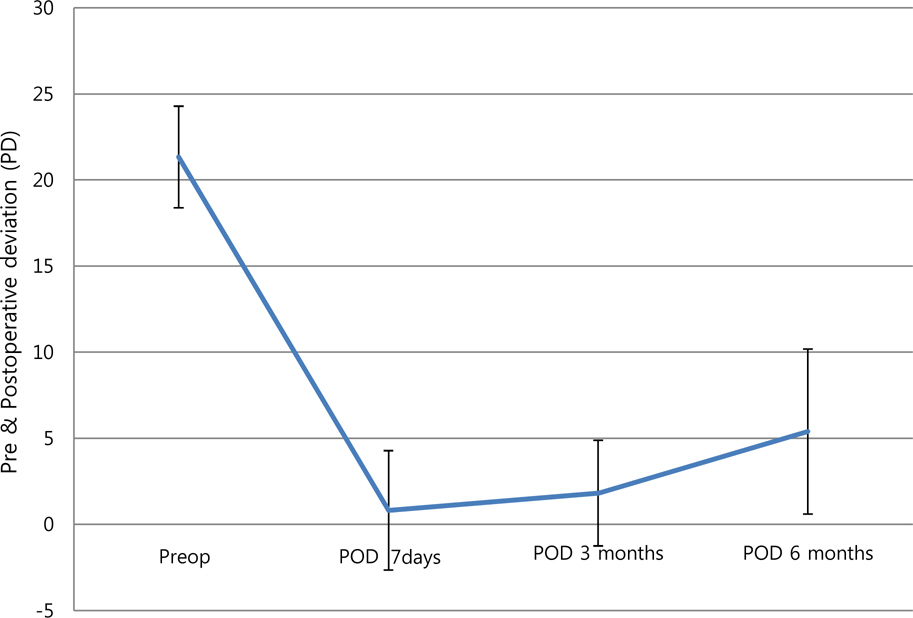
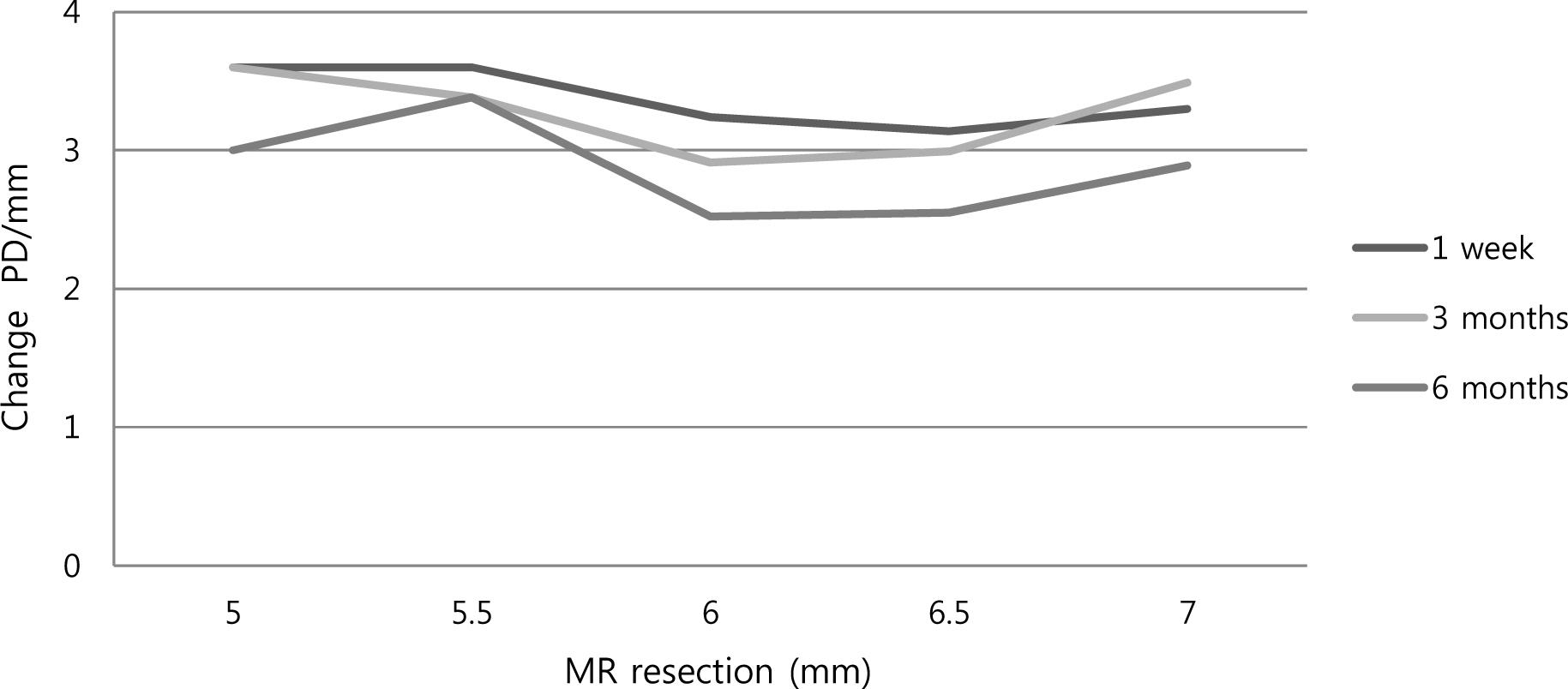
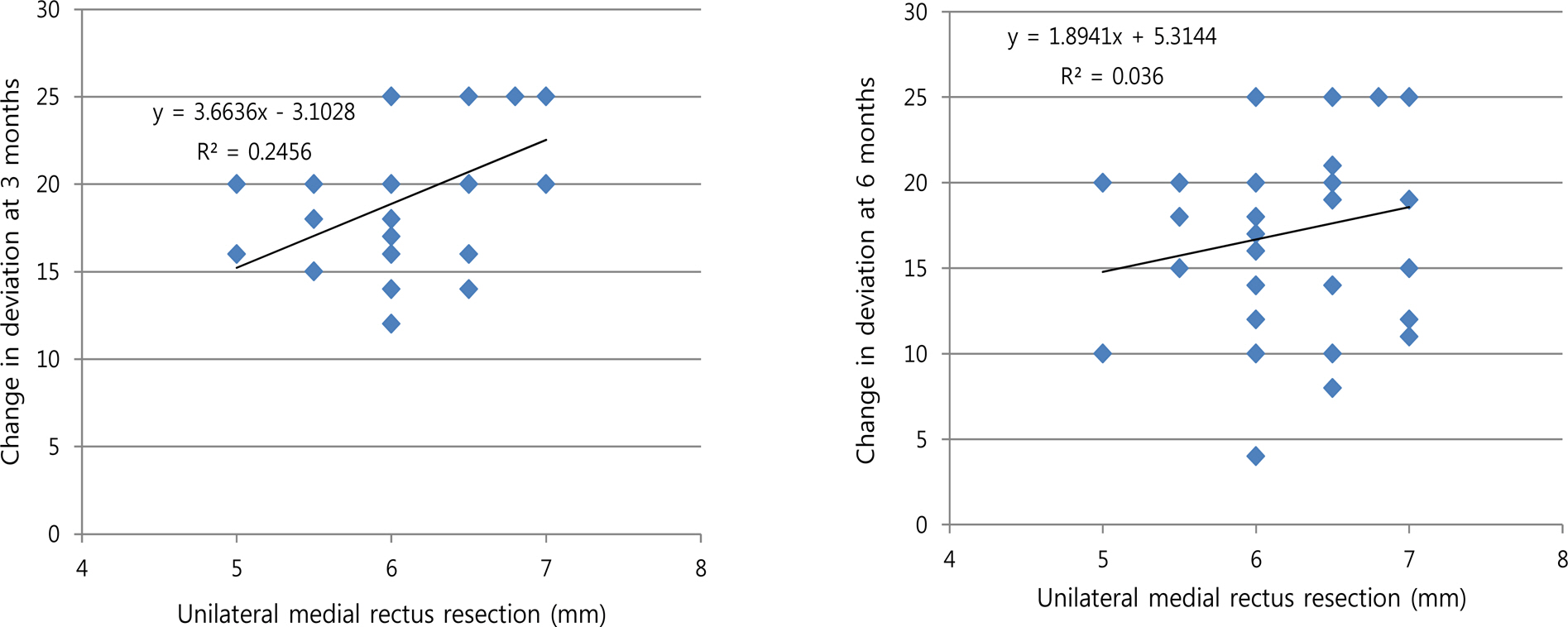
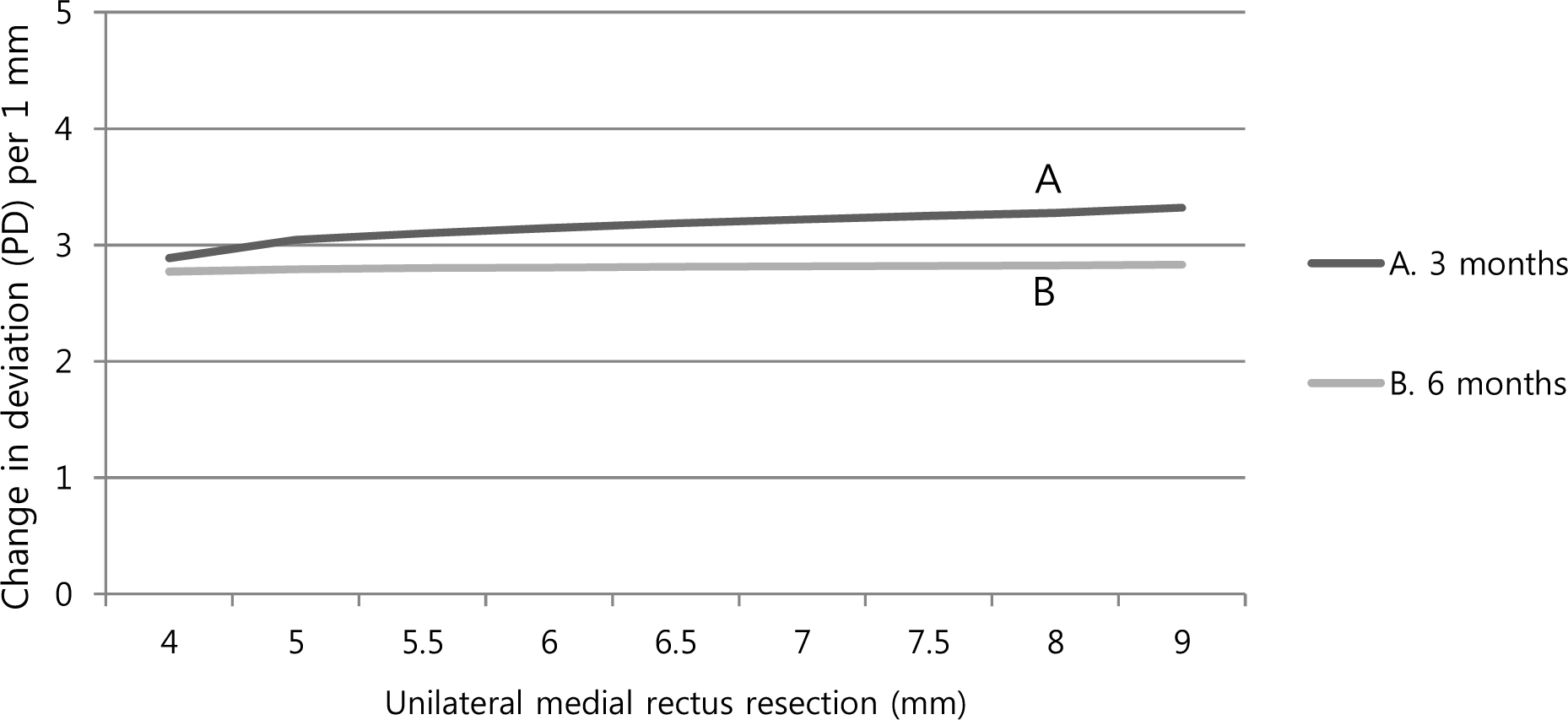
The average preoperative deviation was 21.33 +/- 2.96 PD. We resected mean 6.26 +/- 0.57 mm of the medial rectus muscle. The postoperative deviated angle was 0.82 +/- 3.47, 1.87 +/- 3.10 and 5.40 +/- 4.79 PD at 1 week, 3 months and 6 months after surgery, respectively. The corrected deviated angle per millimeter (mm) was 3.29 +/- 0.68, 3.17 +/- 0.58 and 2.75 +/- 0.89 PD at 1 week, 3 months and 6 months after surgery. There were no significant differences among the changes of postoperative deviation per millimeter according to the amount of medial rectus (MR) resection (p-value = 0.423, 0.382) The success rate was 89.75%, 92.31% and 87.18% at 1 week, 3 months and 6 months after surgery, respectively. The expected corrected angle according to the amount of resection remained constant and was 3.04-3.22 PD/mm at 3 months after surgery and 2.79-2.82 PD/mm at 6 months after surgery.
CONCLUSIONS
The dose-effect per millimeter was decreased as time passed. There was no statistical difference among the corrected deviation angles per millimeter according to the amount of MR resection. We expect that the calculated dose-effect relationship may be a useful guideline for unilateral medial rectus resection for recurrent exotropia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Effect of Bilateral Medial Rectus Resection for Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
Sae Rom Chung, Tae Eun Lee, In Cheon You, Nam Chun Cho, Min Ahn
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(6):577-581. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.6.577.Surgical Outcomes of Modified Medial Rectus Resections in Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
Kwang Hyun Kim, Joo Yeon Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2019;60(11):1098-1104. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.11.1098.
Reference
-
References
1. Olitsky SE, Kelly C, Lee H, Nelson LB. Unilateral rectus resection in the treatment of undercorrected or recurrent strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2001; 38:349–53.
Article2. Lee JY, Choi DG. The clinical analysis of recurrence after surgical correction of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2220–6.3. Kim SC, Kim MM. The efficacy of unilateral rectus resection in the reoperation of strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:904–10.4. Ryu JW, Lee SY, Lee YC. Result analysis according to surgical am-out after unilateral lateral rectus recession in patients with exodeviation under 25 PD. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:593–9.5. Chae SH, Chun BY, Kwon JY. The effect of unilateral medial rectus muscle resection in patients with recurrent exotropia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2008; 22:174–7.
Article6. Yang HK, Hwang JM. Bilateral vs unilateral medial rectus resection for recurrent exotropia after bilateral lateral rectus recession. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 148:459–65.
Article7. Cho WK, Lee SY, Lee YC. The effect of medial rectus resection in reccurent exotropia after lateral rectus recession. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1093–7.
Article8. Suh YW, Seo IH, Cho YA, Kim SH. Analysis of the effects of medial rectus muscle resection for recurrent exotropia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:341–3.
Article9. Kim JY, Chang BL. The effect of unilateral lateral rectus recession in recurrent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:2261–5.10. Chun KI, Rah SH. The Comparison of outcomes between lateral rectus muscles re-recession and medial rectus muscles resection in recurrent exotropia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2008; 22:111–4.11. Mims JL 3rd. Outcome of 5 mm resection of one medial rectus ex-traocular muscle for recurrent exotropia. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 2003; 18:143–50.12. Wright KW. Color atlas of strabismus surgery: strategies and techniques. 2nd ed.Republic of Panama: Wright publishing;2000. p. 249–50.13. Wang L, Nelson LB. One muscle strabismus surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2010; 21:335–40.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Unilateral Medial Rectus Muscle Resection in Patients with Recurrent Exotropia
- The Clinical Analysis after Reoperation for Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
- The Effect of Medial Rectus Resection in Reccurent Exotropia After Lateral Rectus Recession
- Unilateral Recession-Resection Versus Re-resection of Medial Rectus in Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Unilateral Recession-Resection and Bilateral Resections in Recurrent Exotropia