J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Dec;55(12):1860-1867. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1860.
ILM Peeling Size and Postoperative Foveal Tissue Elongation in Macular Hole Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Busan Sungmo Eye Hospital, Busan, Korea. heesyoon@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2338977
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1860
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the relationship between the size of internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and the elongation of foveal tissue after macular hole (MH) surgery.
METHODS
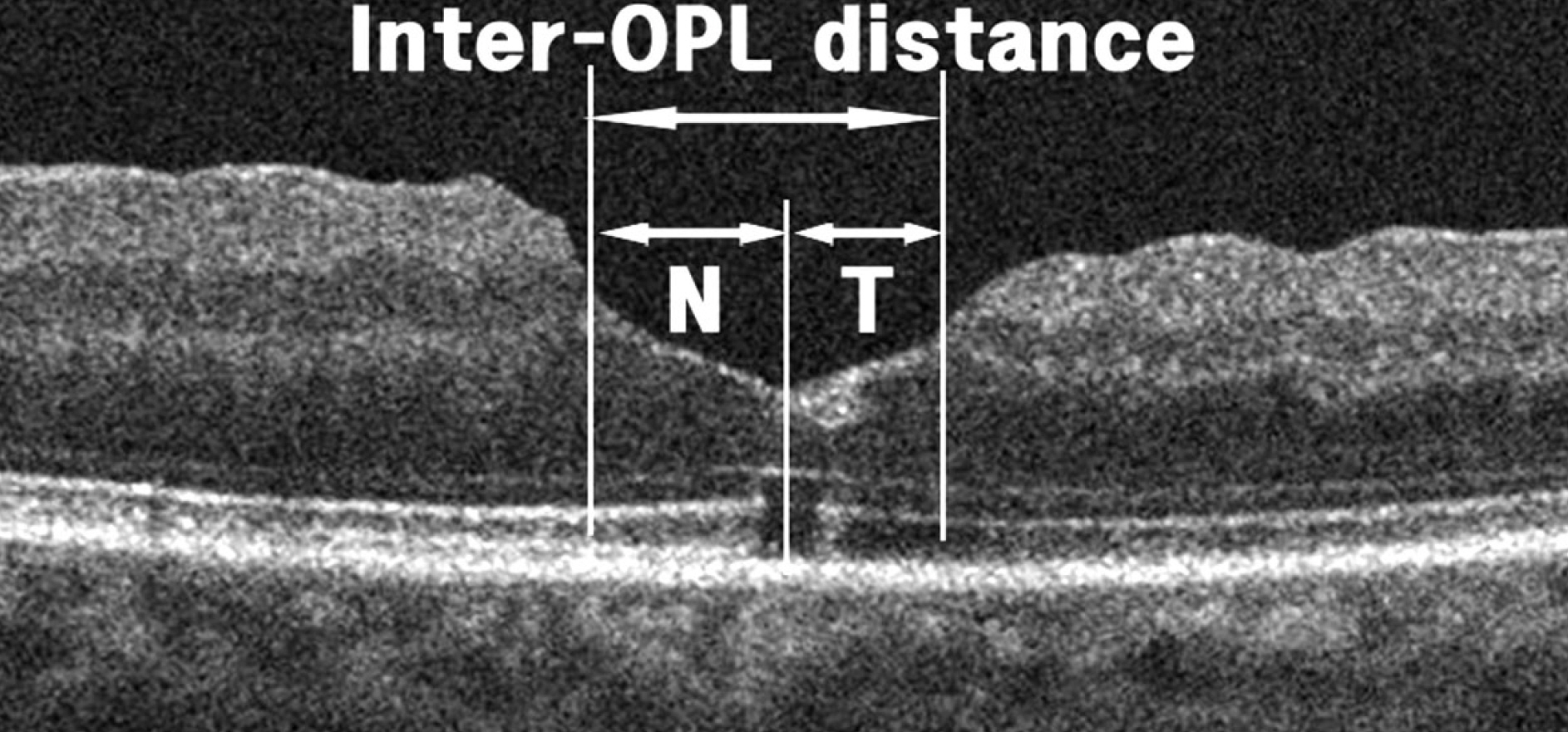
The medical records of 29 patients (29 eyes) who developed elongation of foveal tissue on spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) after vitrectomy with ILM peeling and gas tamponade for idiopathic MH were retrospectively reviewed. These eyes were classified into 3 subgroups by the size of ILM peeling: group A (9 eyes), smaller than 2 disc diameter (DD); group B (12 eyes), larger than 2 DD and within the major temporal vascular arcade, and group C (8 eyes), till the edge of the major temporal vascular arcade. Inter-outer plexiform layer (OPL) distance, representing elongation of foveal tissue, was measured 1, 3, and 6-8 months (only 18 eyes) postoperatively. 'Asymmetric elongation' was defined as non-uniform elongation of the foveal tissue in certain directions.
RESULTS
Horizontal/vertical inter-OPL distances 1 month postoperative, in descending order, were: group B, 436.58 +/- 88.54 / 404.92 +/- 78.55 microm; group A, 421.33 +/- 109.97 / 404.14 +/- 120.9 microm; and C group, 389.25 +/- 48.75 / 400 +/- 52.23 microm. Variations in the horizontal/vertical inter-OPL distance 3 months after MH surgery were: group B, 136.83 +/- 65.64 / 103.92 +/- 73.37 microm; group A, 88.11 +/- 41.57 / 75.89 +/- 53.18 microm; and group C, 140.25 +/- 68.51 / 83.63 +/- 56.62 microm. There were no significant differences in inter-OPL distance, variation in inter-OPL distance, or percent asymmetry in both horizontal and vertical directions among these groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Elongation of the foveal tissue and asymmetric elongation after MH surgery were not associated with the size of ILM peeling.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Benson WE, Cruickshanks KC, Fong DS, et al. Surgical management of macular holes: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:1328–35.2. Tognetto D, Grandin R, Sanguinetti G, et al. Internal limiting membrane removal during macular hole surgery: results of a multicenter retrospective study. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1401–10.3. Haritoglou C, Reiniger IW, Schaumberger M, et al. Five-year follow-up of macular hole surgery with peeling of the internal limiting membrane: update of a prospective study. Retina. 2006; 26:618–22.4. Tranos PG, Ghazi-Nouri SM, Rubin GS, et al. Visual function and subjective perception of visual ability after macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:995–1002.
Article5. Sjaarda RN, Frank DA, Glaser BM, et al. Resolution of an absolute scotoma and improvement of relative scotomata after successful macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 116:129–39.
Article6. Bottoni F, De Angelis S, Luccarelli S, et al. The dynamic healing process of idiopathic macular holes after surgical repair: a spectral-domain optical coherence tomography study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:4439–46.
Article7. Wakabayashi T, Fujiwara M, Sakaguchi H, et al. Foveal micro-structure and visual acuity in surgically closed macular holes: spectral-domain optical coherence tomographic analysis. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:1815–24.
Article8. Christensen UC, Kr⊘yer K, Sander B, et al. Prognostic significance of delayed structural recovery after macular hole surgery. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2430–6.
Article9. Kang SW, Lim JW, Chung SE, Yi CH. Outer foveolar defect after surgery for idiopathic macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 150:551–7.
Article10. Sano M, Shimoda Y, Hashimoto H, Kishi S. Restored photoreceptor outer segment and visual recovery after macular hole closure. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:313–8.e1.
Article11. Imai M, Iijima H, Gotoh T, Tsukahara S. Optical coherence tomography of successfully repaired idiopathic macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 128:621–7.
Article12. Oh J, Smiddy WE, Flynn HW Jr, et al. Photoreceptor inner/outer segment defect imaging by spectral domain OCT and visual prognosis after macular hole surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:1651–8.
Article13. Itoh Y, Inoue M, Rii T, et al. Correlation between length of foveal cone outer segment tips line defect and visual acuity after macular hole closure. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1438–46.
Article14. Kim JH, Kang SW, Park DY, et al. Asymmetric elongation of foveal tissue after macular hole surgery and its impact on metamorphopsia. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2133–40.
Article15. Jeong SH, Kim JH, Kim JW, et al. Long-term changes in foveal microstructure after macular hole surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1731–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of the Macular Curvature on Foveal Migration after Macular Hole Surgery
- Idiopathic Macular Hole Surgery with or without Indocyanine Green-Stained Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling
- Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling with or without Indocyanine Green in Macular Hole Surgery
- Macular Hole Surgery with or without Indocyanine Green-Assisted Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling
- The Effect of Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling in Epiretinal Membrane Including Pseudolamellar Macular Hole