J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Apr;55(4):473-479.
Clinical Outcomes of Browlift Using Various Methods
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The present study investigated the outcomes of browlift using various surgical methods including direct browplasty, endoscopic browlift and transblepharoplasty browlift.
METHODS
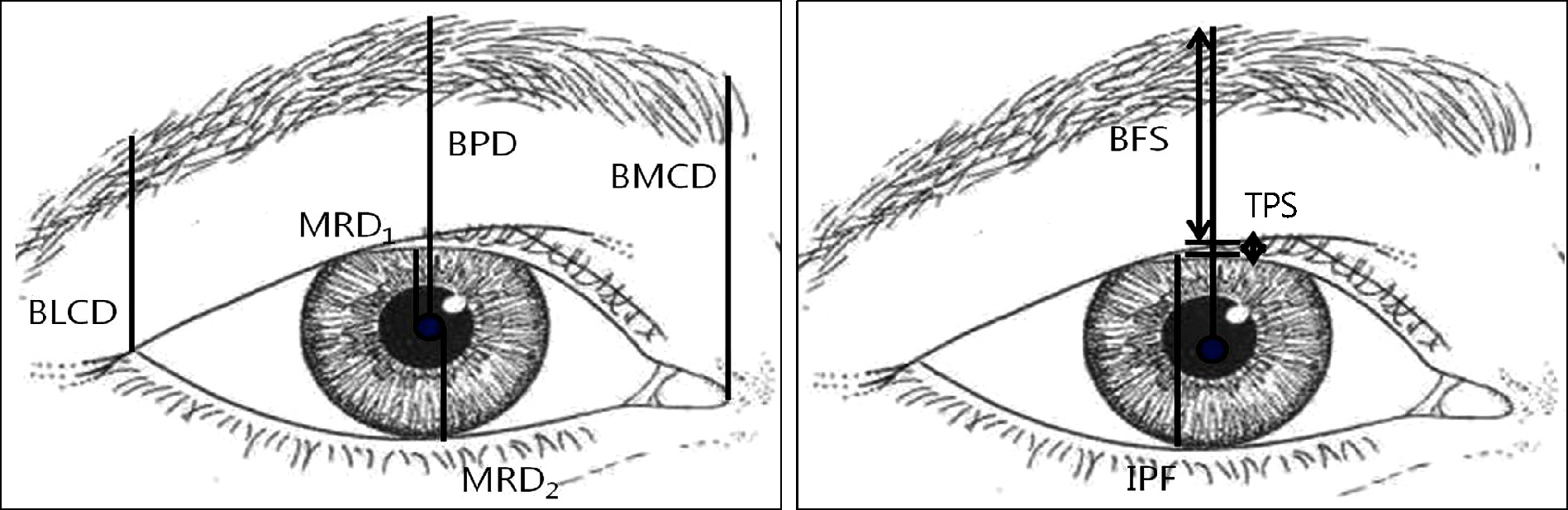
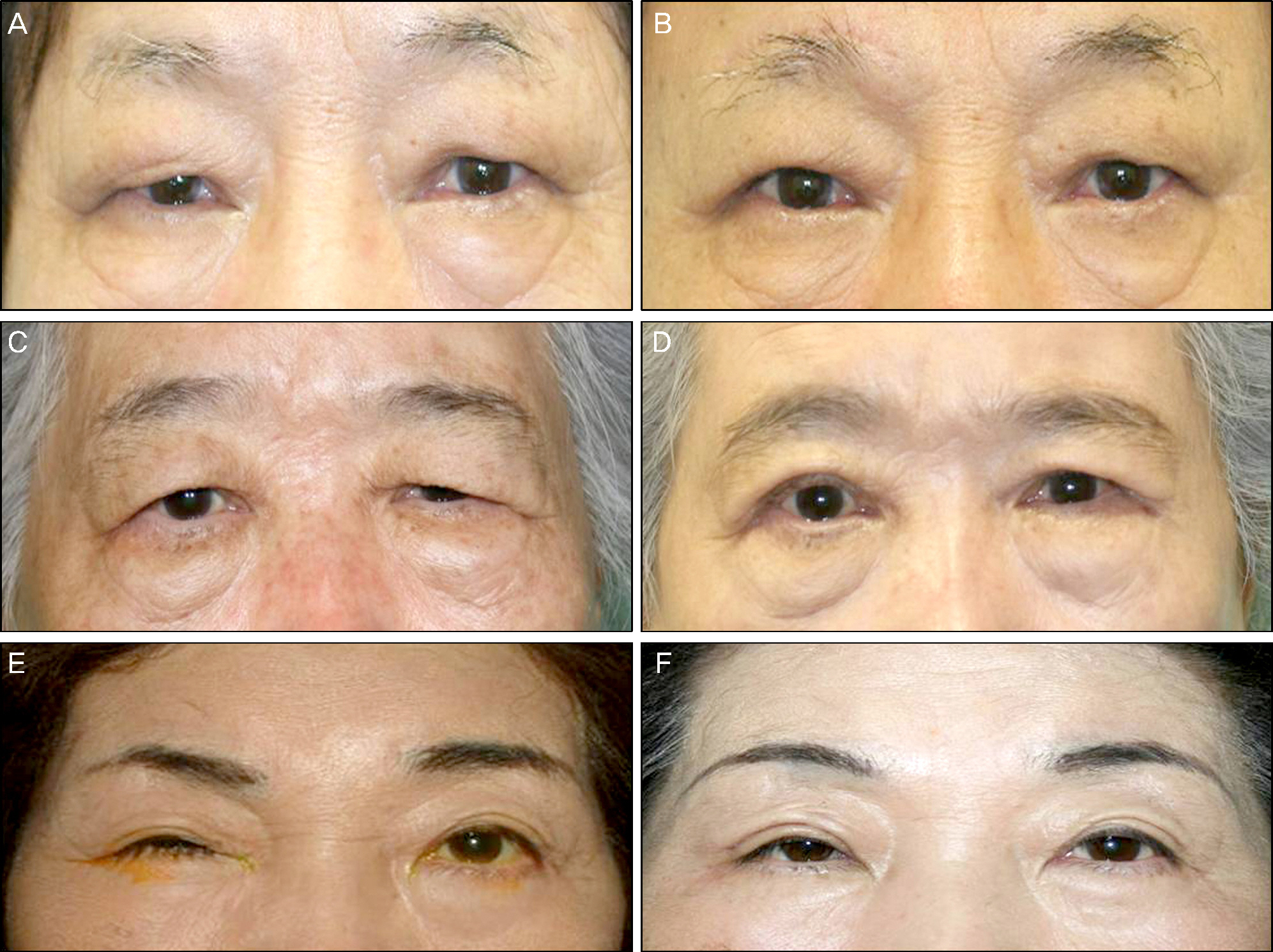
Twenty-eight brow ptosis cases in 19 patients were treated in the present study. The mean patient age was 67.9 +/- 9.7 years, and the mean observation period was 9.0 +/- 3.8 months. Nine cases were treated with direct browplasty, eight cases with endoscopic browlift and 11 cases with transblepharoplasty browlift. Photographs of patients were taken before surgery and two months, six months and on the final follow-up after surgery. The brow-to-pupil distance (BPD), brow-to-medial canthus distance (BMCD), and brow-to-lateral canthus distance (BLCD) were analyzed by the Image J Program.
RESULTS
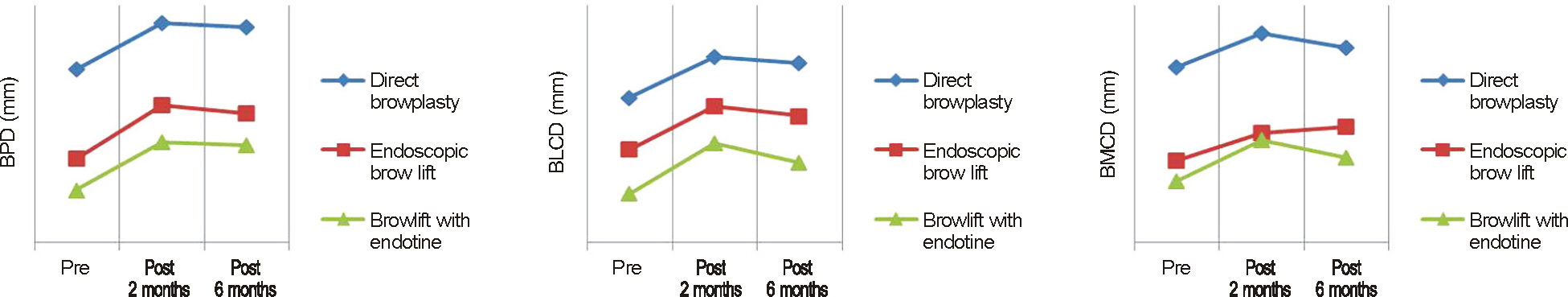
BPD increased 1.88 +/- 0.99 mm, BMCD increased 1.06 +/- 1.21 mm and BLCD increased 1.36 +/- 1.17 mm in all patients six months after surgery. Regarding the change in BPD, direct browplasty increased 1.79 +/- 1.29 mm, endoscopic browlift increased 1.94 +/- 0.80 mm and transblepharoplasty browlift increased 1.90 +/- 0.94 mm without significant difference among the groups on the final follow-up. In terms of brow shape, direct browplasty effectively elevated the lateral brow and endoscopic browlift effectively elevated the medial brow compared to other procedures. No significant complications were observed in any patient.
CONCLUSIONS
Browlift techniques such as direct browplasty, endoscopic browlift and transblepharoplasty browlift are safe and effective surgical methods to correct brow height and shape in patients with brow ptosis without any significant complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Knize DM. Anatomic concepts for brow lift procedures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 124:2118–26.
Article2. Goldberg RA, Lew H. Cosmetic outcome of posterior approach ptosis surgery (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 109:157–67.3. Czyz CN, Hill RH, Foster JA. Preoperative evaluation of the brow-lid continuum. Clin Plast Surg. 2013; 40:43–53.
Article4. Nahai FR. The varied options in brow lifting. Clin Plastic Surg. 2013; 40:101–4.
Article5. Terella AM, Wang TD. Technical considerations in endoscopic brow lift. Clin Plast Surg. 2013; 40:105–15.
Article6. Costantino PD, Hiltzik DH, Moche J, Preminger A. Minimally invasive brow suspension for facial paralysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2003; 5:171–4.
Article7. Rohrich RJ, Beran SJ. Evolving fixation methods in endoscopi-cally assisted forehead rejuvenation: controversies and rationale. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997; 100:1575–82.
Article8. Sclafani AP. Comprehensive periorbital rejuvenation with resorb-able endotine implants for trans-lid brow and midface elevation. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2007; 15:255–64.
Article9. Niamtu J 3rd. The Subcutaneous Brow- and Forehead-Lift: a face-lift for the forehead and brow. Dermatol Surg. 2008; 34:1350–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periorbital changes in patients with Poly(Lactic Acid/ Caprolactone) threads for brow augmentation
- Forehead, temporal augmentation and lateral browlift with Ellanse M
- Demographic review of aesthetic surgery for patients with facial palsy
- Clinical features of adolescents with suicide attempt and the factors associated with their outcomes: poisoning versus non-poisoning
- Glucose-Lowering Agents and COVID-19