J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Oct;51(10):1392-1397.
Pattern VEP in Adult Amblyopic Patients Requested From Military Service
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. yjm@nongae.gsnu.ac.kr
- 2Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the pattern VEP in adult amblyopic patients seen in consultation for ophthalmic evaluation as a past of physical examinations for conscription.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed, 67 men, 20-year-old or older, who had pattern VEP done for the diagnosis of amblyopia from January 2004 to May 2009. P100 latency and P100 amplitude were analyzed.
RESULTS
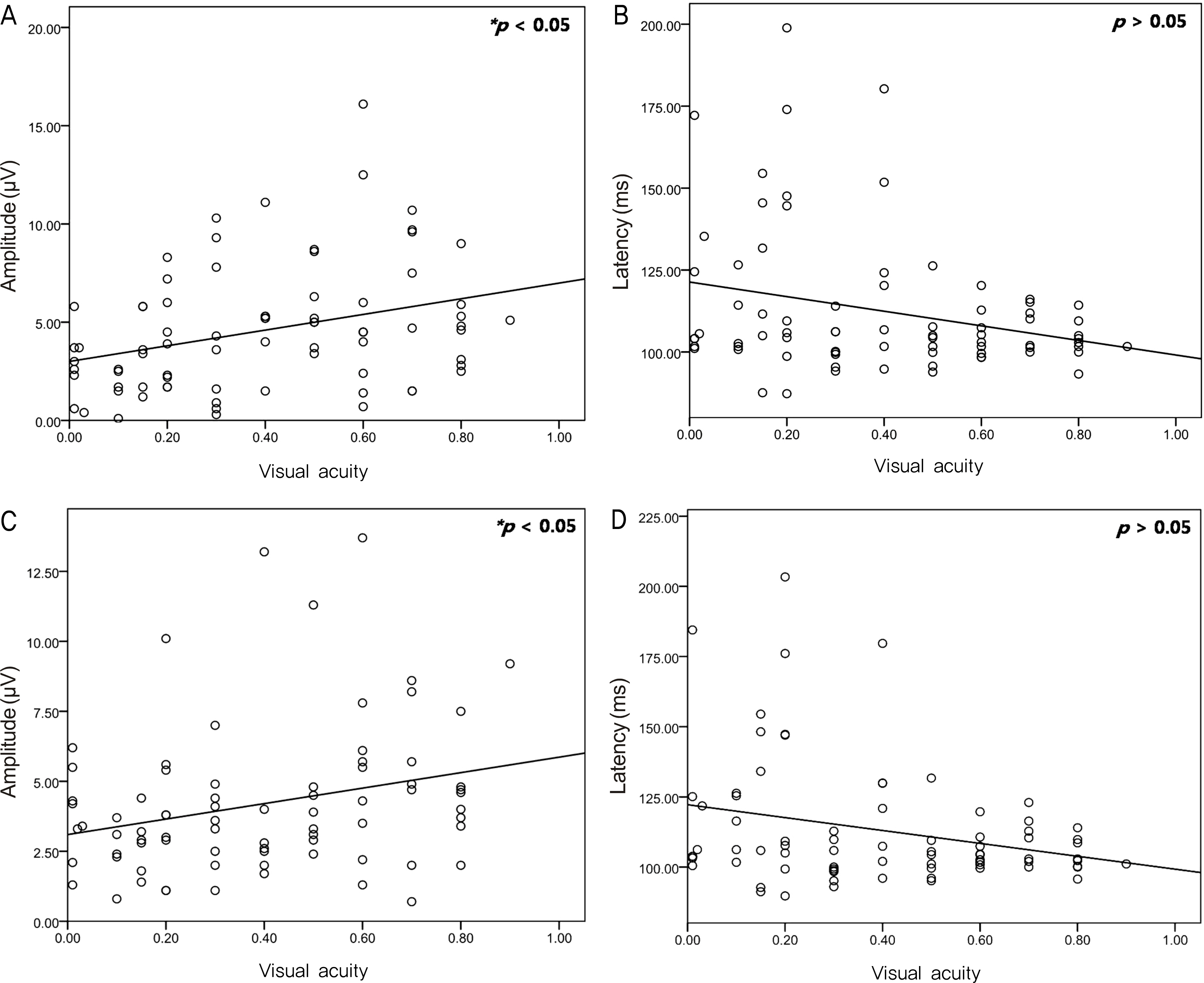
Thirteen patients were non-amblyopic, and 54 patients had amblyopia. Binocular amblyopia and monocular amblyopia were found in 23 and 31 patients, respectively. In the binocular amblyopic patients, four patients were hyperopic, seven patients were myopic, and 12 patients were astigmatic amblyopia. In the monocular amblyopic patients, 15 patients were anisometropic, 12 patients were strabismic, and four patients had organic amblyopia. The value of P100 latency and P100 amplitude were statistically significantly different between non-amblyopic and amblyopic eyes, with check size of 32x32. However, the types of amblyopia among the patients were not different at a statistically significant level. Visual acuity and P100 amplitude were significantly positively correlated.
CONCLUSIONS
VEP might be a useful tool for diagnosis of adult amblyopia, especially using a 32x32 check size. This tool may impart the ability to decide relationship between amblyopia and visual acuity by analyzing P100 latency and amplitude values.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Binocular vision and ocular motility. 6th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 246.2. Wanger P, Nilson BY. Visual evoked response to pattern reversal stimulation in patients with amblyopia and/or defective binocular functions. Acta Ophthalmol. 1978; 56:617–27.3. Chung W, Hong S, Lee JB, Han SH. Pattern visual evoked potential as a predictor of occlusion therapy for amblyopia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2008; 22:251–4.
Article4. Lee SJ, Park S, Shin H. Pattern-VEP in child amblyopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:924–9.5. Kriss A, Thompson D, Lloyd I, et al. Pattern VEP findings in young children treated for unilateral congenital cataract. Cottlier E, editor. Congenital cataract. Austin: Laudes;1994. p. 79–88.6. Sokol S. Abnormal evoked potential latencies in amblyopia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983; 67:310–4.
Article7. Hoe JW, Kim CW, Kim SM. VEP and pattern ERG in adult amblyopes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1481–8.8. Wanger P, Persson HE. Visual evoked response to pattern-reversal stimulation in childhood amblyopia. Acta Ophthalmol. 1980; 58:697–706.9. Sokol S, Fishman GA. Electrophysiologic testing in disorders of the retina, optic nerve, and visual pathway. In electrophysiologic testing. San Francisco: American academy of ophthalmology;1990. p. 123–5.10. Park HK, Kim MM, Hahn DK. Evaluation of VEP in optic nerve diseases and amblyopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1568–73.11. Feinsod M, Hoyt WF, Wilson WB, Spire JP. Visually evoked response: use in neurologic evaluation of posttraumatic subjective visual complaint. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976; 94:237–40.12. Kramer KK, La Piana FG, Appleton B. Ocular malingering and hysteria: diagnosis and management. Surv Ophthalmol. 1979; 24:89–96.
Article13. Saitoh E, Usami EA, Mizota A, Fujimoto N. Comparison of visual evoked potentials in patients with psychogenic visual disturbance and malingering. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2001; 38:21–6.
Article