J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Jan;51(1):81-87.
Analysis of Factors Affecting the Change in Axial Length of Premature Infant's Eye
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, CHA University, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. swha@chamc.co.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the effect of presence with or absent of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and its stage, birth weight, conceptual age and associated diseases on the axial length of premature infants' eye.
METHODS
A total of 102 eyes of 51 premature infants less than 36 weeks of conceptual age were evaluated in this study. Fundus examination for ROP and axial length measurement were conducted at 40, 52 and 64 weeks of postconceptual age. The medical records were reviewed retrospectively. Independent t-test analysis, simple regression analysis, and one-way ANOVA were performed to assess the influence of each factor on axial length.
RESULTS
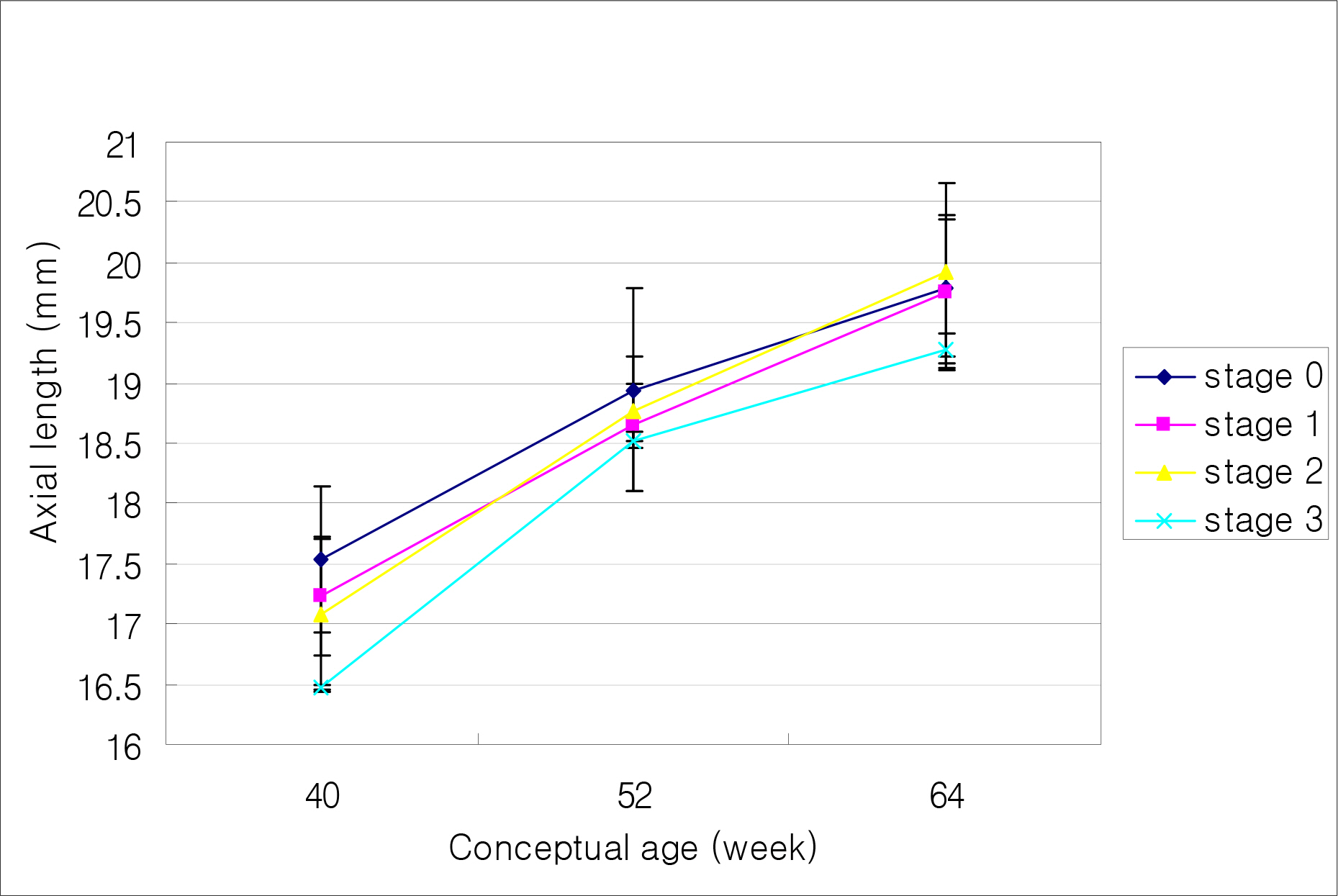
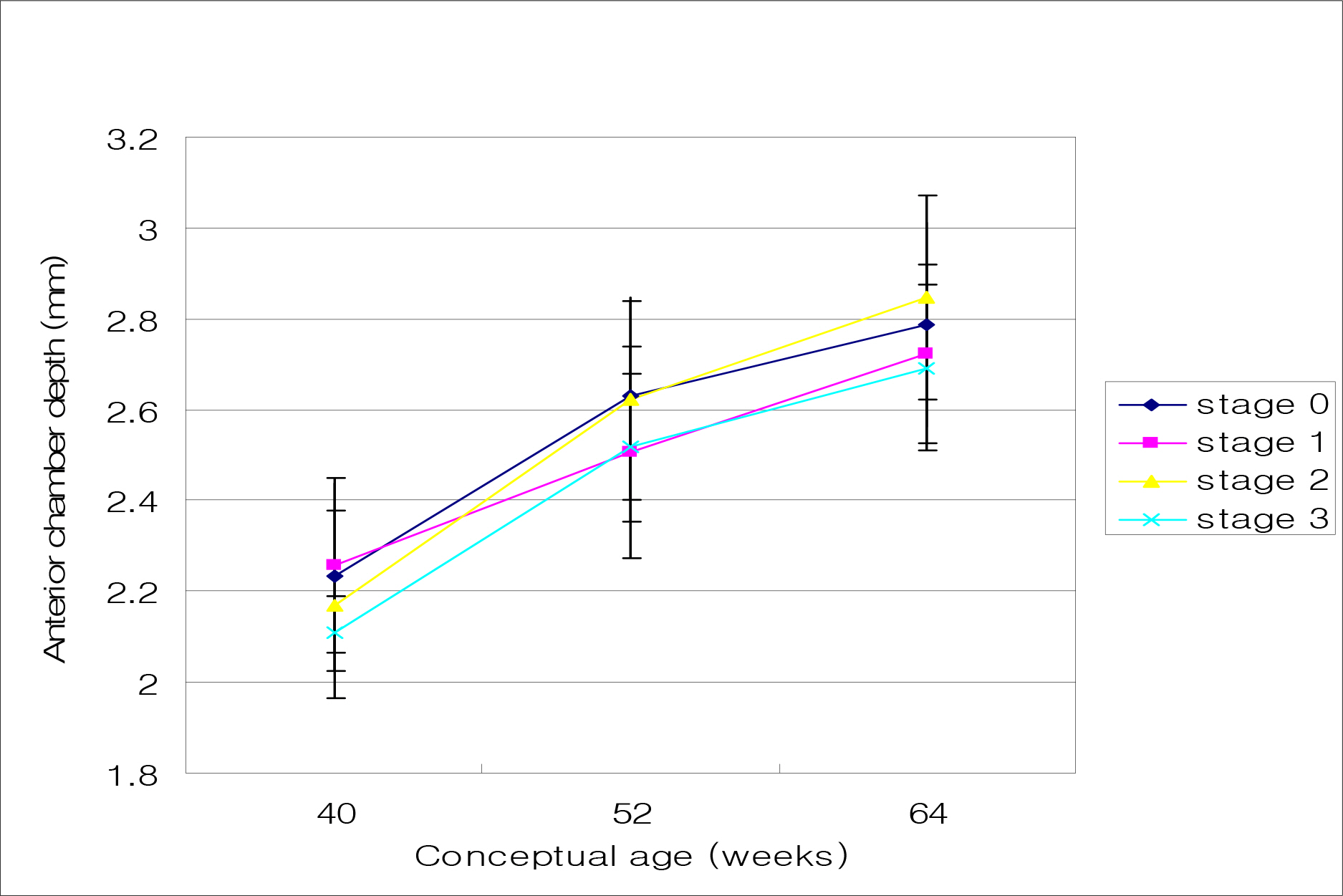
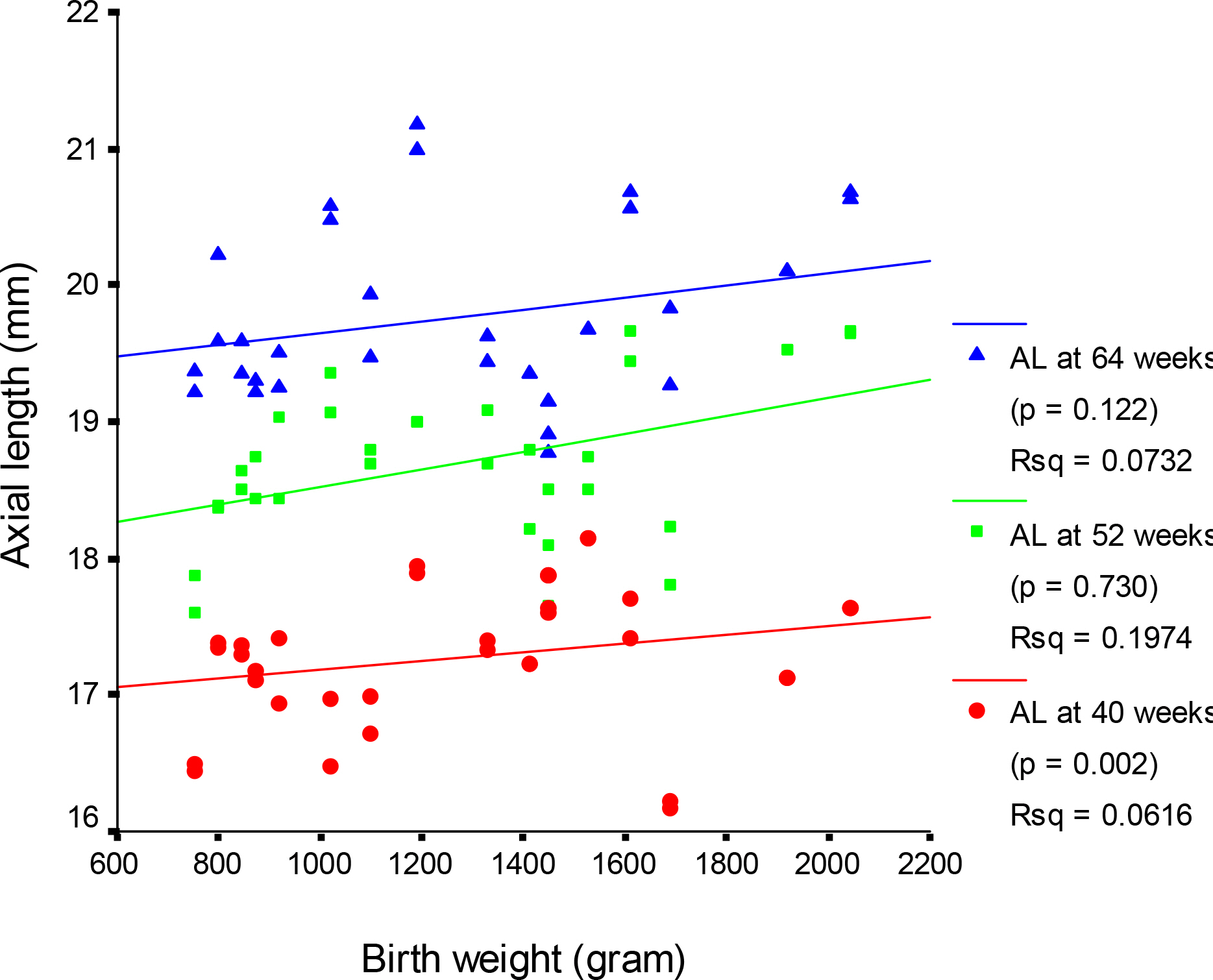
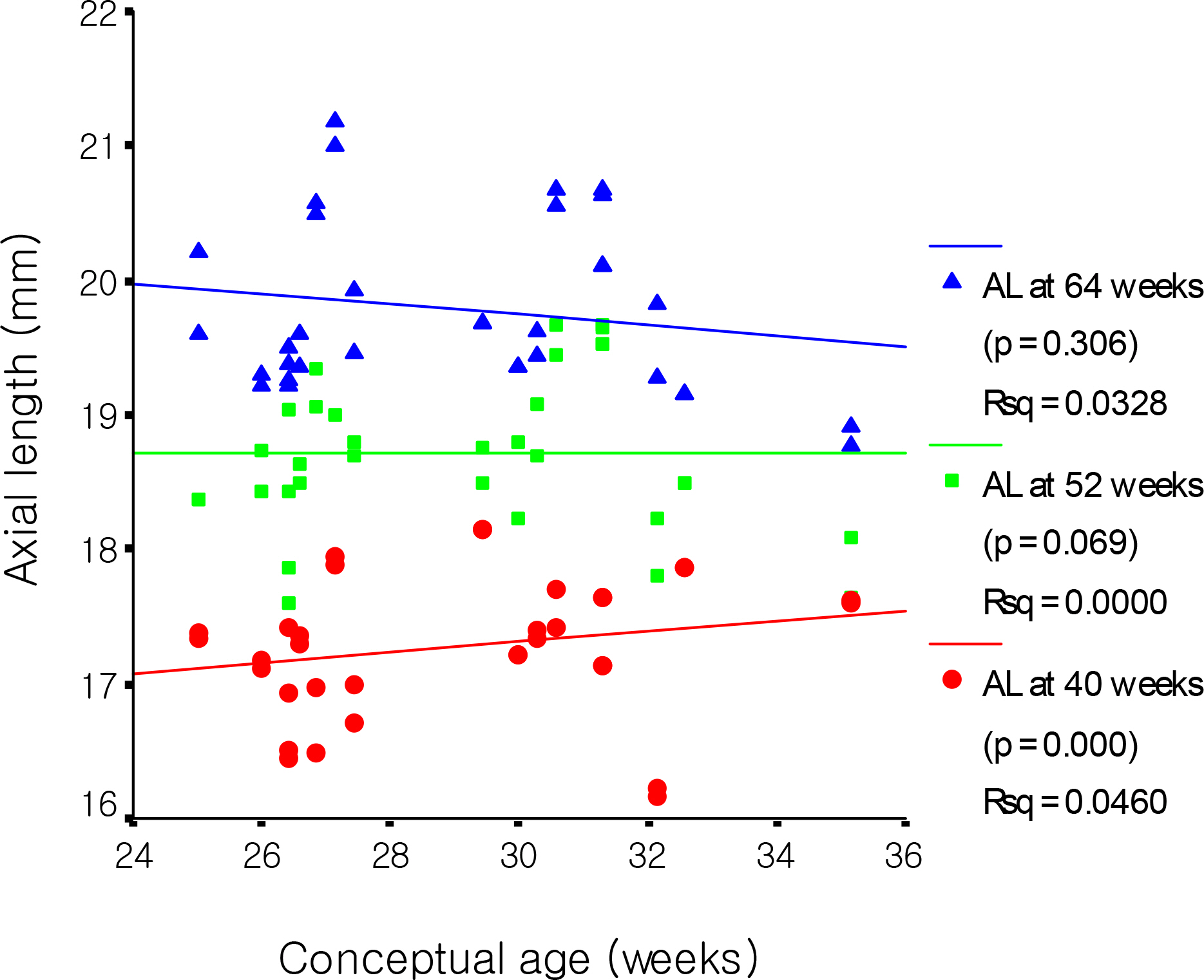
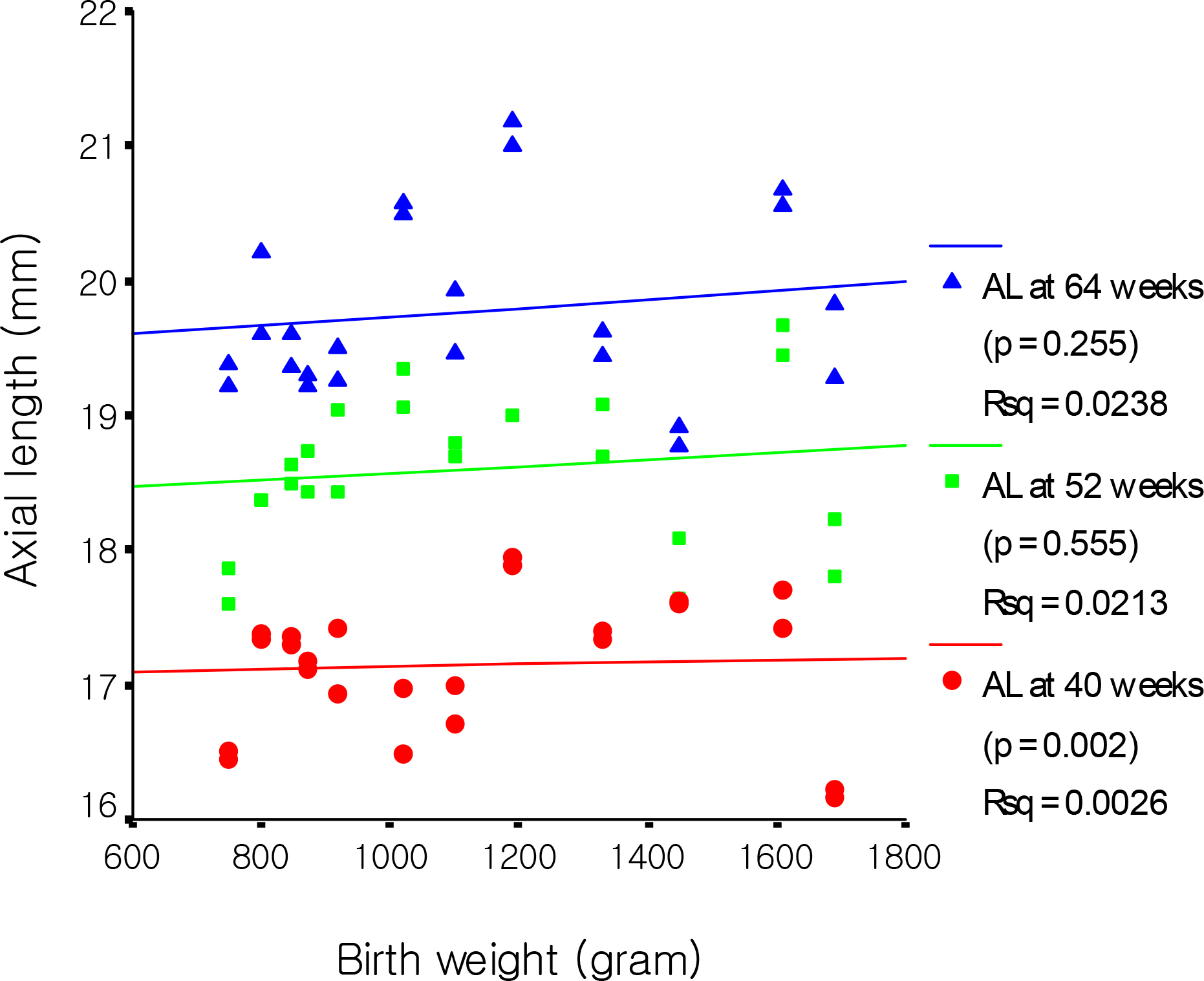
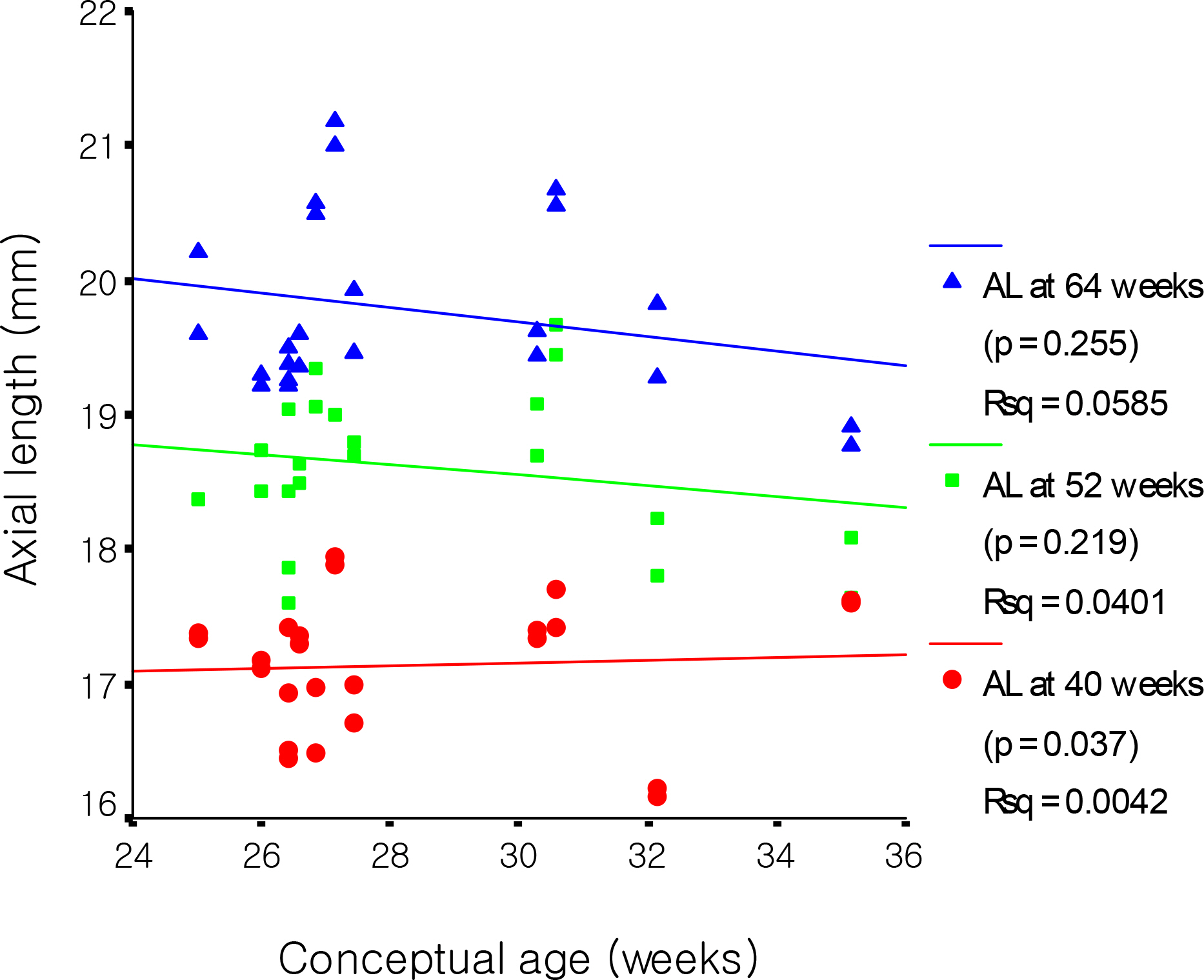
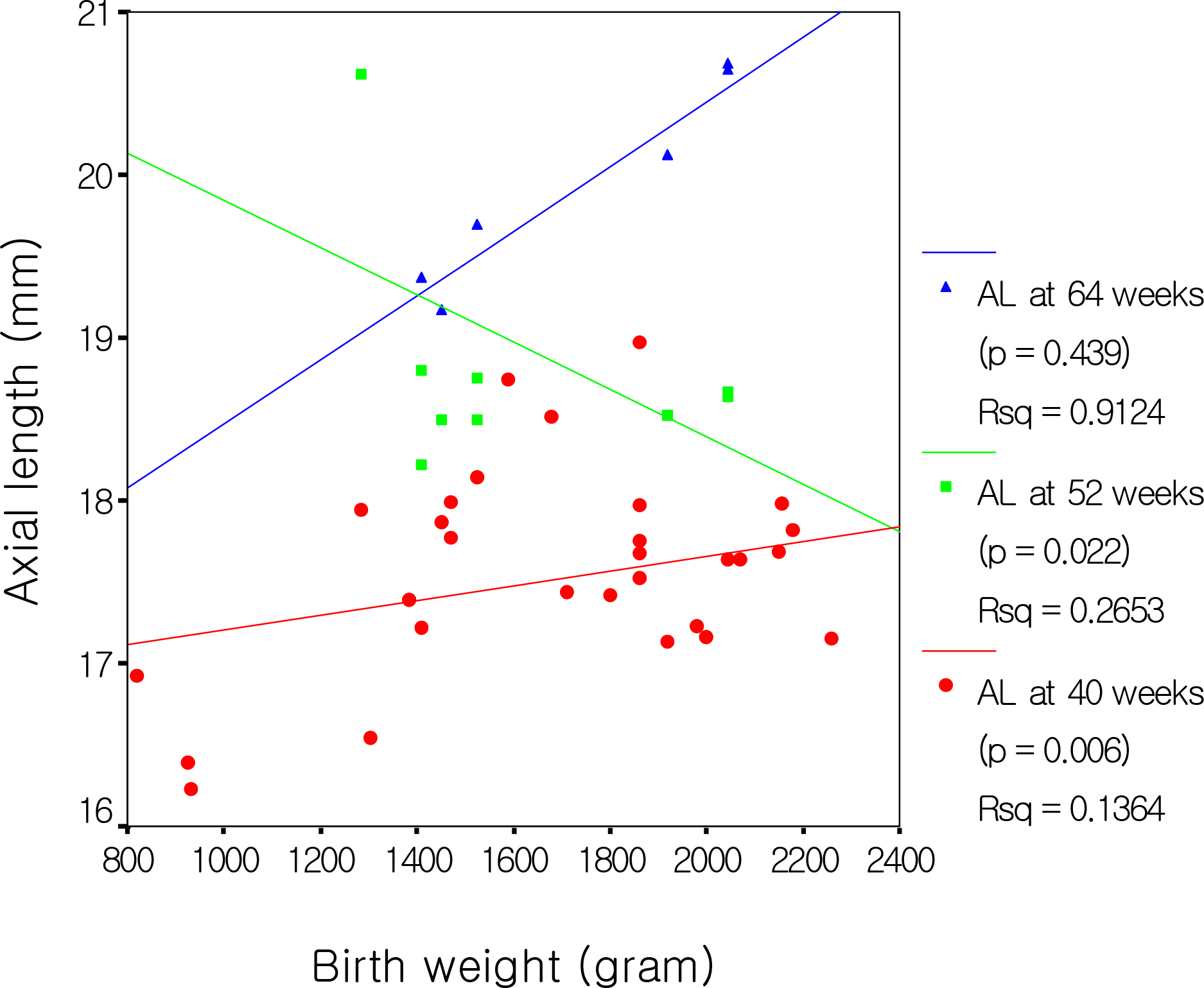
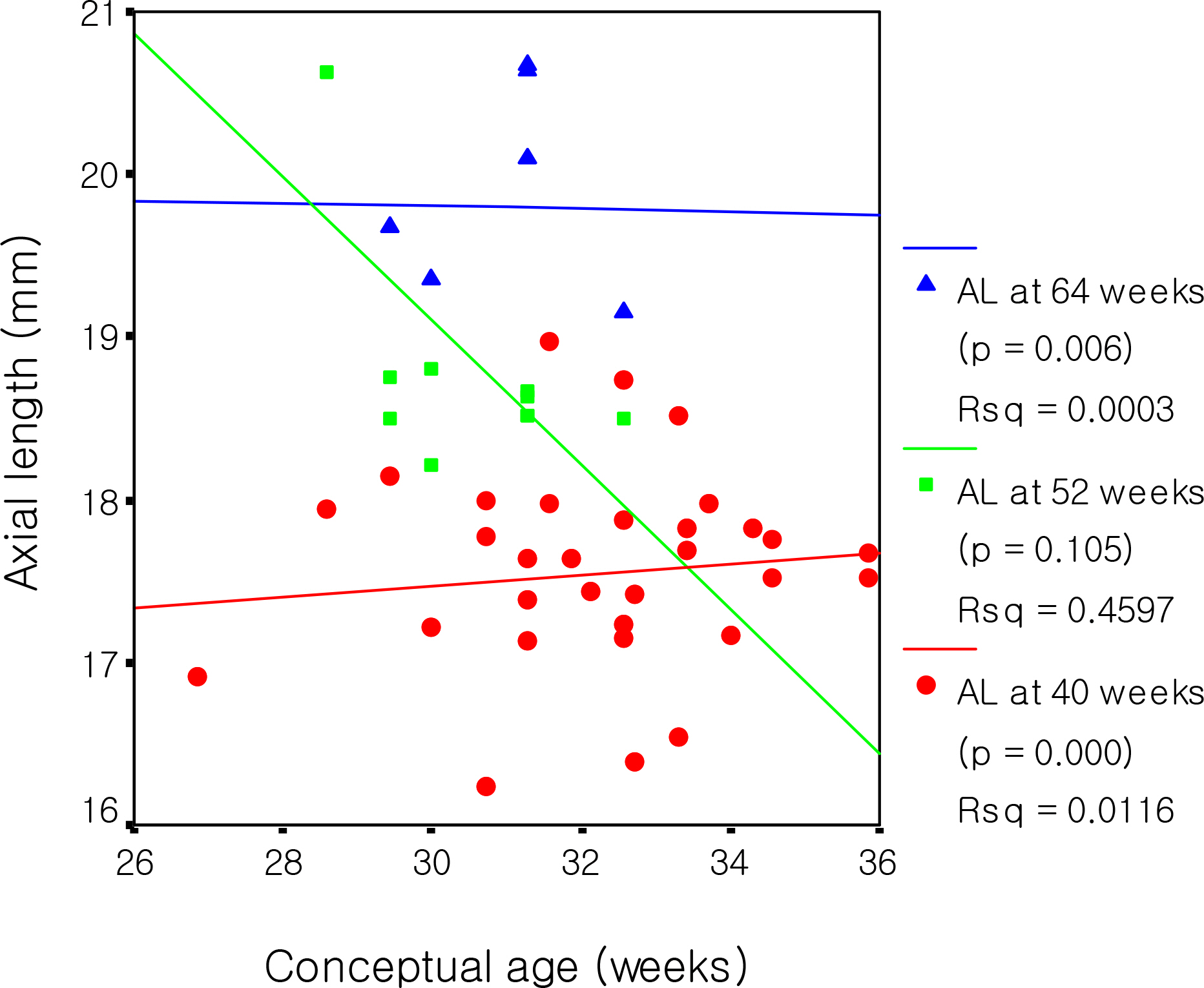
The mean axial length at 40, 52 and 64 weeks were 17.35, 18.80 and 19.78 mm, respectively. The mean axial length with and without ROP at 40 weeks were 17.10 mm and 17.54 mm, respectively, which were statistically significant (p=0.000). There was a significant decrease in axial length at 40 weeks in the higher ROP stage (p<0.05). Axial length and birth weight showed positive correlation with statistical significance at 40 weeks, while these parameters showed no significant correlation at 64 weeks. Axial length and conceptual age showed a positive correlation with statistical significance at 40 weeks (p=0.000), yet a negative correlation at 64 weeks with no statistical significance (p=0.306). A significant difference was not observed between sex and the associated diseases.
CONCLUSIONS
The factors that affect the axial length of an infants'eye at 40 weeks were ROP and its stage, birth weight, and conceptual age. Additionally, there was no significant relationship between sex and the associated diseases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yamamoto Y. A new study on the measurement of ocular axial length by ultrasound echography. Acta Soc Ophthalmol Jpn. 1960; 64:1333–41.2. Sorsby A, Leary GA, Richards MJ, Chaston J. A aberrations measurement of the components of ocular refraction in life. Vision Res. 1963; 3:499–506.3. Larsen JS. The sagittal growth of the eye. I. Ultrasonic measurement of the depth of the anterior chamber from birth to puberty. Acta Ophthalmol. 1971; 49:239–62.4. Larsen JS. The sagittal growth of the eye. IV. Ultrasonic measurement of axial length of the eye from birth to puberty. Acta Ophthalmol. 1971; 49:873–86.5. Coleman DJ, Carlin B. A new system for visual axis measurements in the human eye using ultrasound. Arch Ophthalmol. 1967; 77:124–7.
Article6. Duke-Elder S. System of Ophthalmolgy. 2:The Anatomy of visual System. St. Louis: CV Mosby;1961. p. 80–1.7. Villada JR, Raj PS, Akingbehin T. Calculation of the power of anterior chamber implants. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992; 76:303–306.
Article8. Youn DH, Yu YS, Park IW. Intraocular pressure and axial length in children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:397–401.
Article9. Woo JM, Kim SJ, Jeong SK, Park YG. The influence of axial aberrations on the response to strabismus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:680–6.10. Park HY, Park SW, Park YG. The study of axial length and functional equator in strabismus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:827–36.11. Tarkkanen A, Uusitalo T, Mianowicz J. Ultrasonographic biometry in congenital glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 1983; 61:618–23.
Article12. Page J, Schneeweissm Whyte H, Harvey P. Ocular sequelae in premature infants. Pediatrics. 1993; 92:787–90.
Article13. Choi MY, Park IK, Yu YS. Long term refractive outcome in eyes of preterm infants with and without retinopathy of prematurity: comparison of keratometric value, axial length, anterior chamber depth, and lens thickness. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:138–43.
Article14. American Academy of Pediatrics. Section on Ophthalmology. Screening examination of premature infants for retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics. 2001; 108:809–811.15. Blomdahl S. Ultrasonic measurement of eye in the newborn infant. Acta Ophthalmol. 1979; 57:1048–56.16. Gordon RA, Donzis PB. Refractive development of the human eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:785–91.
Article17. Cho KS, Shim YB, Kim BC. Interrelationship between axial length and refractive states, and anterior chamber depth in the newborn. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:215–9.18. Harayama K, Amemiya T, Nishimura H. Development of the eyeball during fetal life. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1981; 18:37–40.
Article19. Kim WJ, Park SH, Shin HH. The change f axial length according to age in the eyeball of premature infants by ultrasonic biometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1993; 34:667–671.20. Cook A, White S, Batterbury M, Clark D. Ocular growth and refractive error development in premature infants with or without retinopathy of prematurity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:5199–207.
Article21. Fledelius HC, Jamsen EC, Thorn J. Refractive change during hyperbaric oxygen therapy. A clinical trial including ultrasound oculometry, Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002; 80:188–90.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Change of Axial Length According to Age in the Eyeball of Premature infants by Ultrasonic Biometry
- Corneal Curvatures of the Infants
- Comparison of the Phakic and Pseudophakic Axial Length
- The Study of the Correlation between Axial Length and Refractive Error in Korean Children
- The Influence of Axial Myopia on Diabetic Retinopathy