J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2007 Aug;48(8):1082-1087.
Clinical Course of Bimatoprost-induced Periocular Skin Hyperpigmentation after Stopping Bimatoprost Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonbuk National University, Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. ldw@chonbuk.ac.kr
Abstract
-
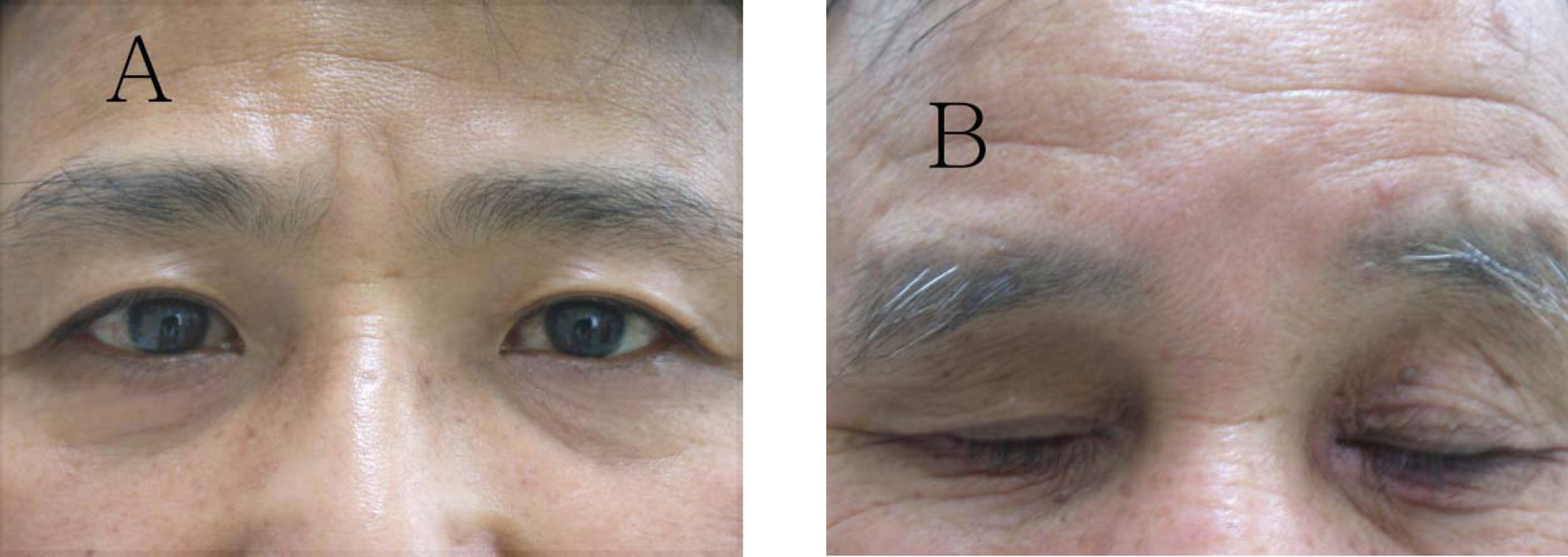
PURPOSE: To evaluate the demographic and clinical characteristics of bimatoprost-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation.
METHODS
The chart analyses of 16 patients in whom cosmetically noticeable periocular skin hyperpigmentation developed after starting bimatoprost therapy were reviewed. Data collated included age, medication history, dates of starting and stopping bimatoprost treatment, and the subjective assessment of the periocular hyperpigmentation at initial detection as well as follow-up visits. Periocular hyperpigmentation was graded using an arbitrary scale from 0 to 3. The number of days to the onset of hyperpigmentation and to pigment resolution was determined and their associations to demographic and other clinical parameters were analyzed.
RESULTS
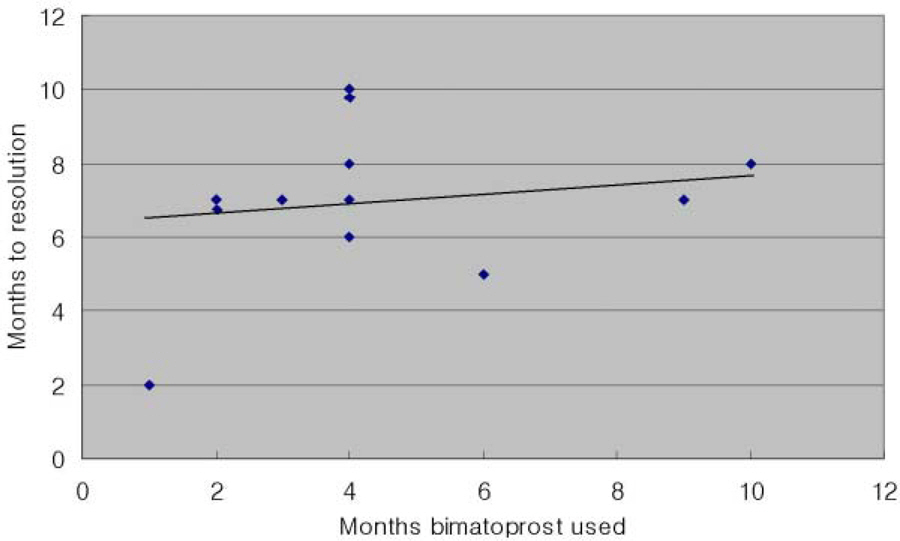
Patients had variable grades of periocular hyperpigmentation at presentation (mean, 1.53+/-0.66). Bimatoprost-induced periocular hyperpigmentation appeared 1-10 (mean, 4.3+/-2.6) months after initiation of bimatoprost therapy. Resolution of skin hyperpigmentation was noted 2-10(mean 6.8+/-1.9) months after stopping bimatoprost treatment. There was a minor correlation(R=+0.19) between the number of days to resolution of hyperpigmentation and the number of days when bimatoprost was used. At 12 months after stopping bimatoprost treatment, 12 of the 13 patients had complete resolution of periocular hyperpigmentation. However, weak hyperpigmentation remained in one patient.
CONCLUSIONS
Bimatoprost-induced hyperpigmentation is benign and reversible.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Woodward DF, Krauss AHP, Chen J, et al. Pharmacological characterization of a novel antiglaucoma agent, bimatoprost (AGN 192024). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003; 305:772–85.
Article2. Johnstone MA, Albert DM. Prostaglandin-induced hair growth. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002; 47:185–202.
Article3. Wand M, Ritch R, Isbey EK Jr, Zimmerman TJ. Latanoprost and periocular skin color changes. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:614–5.4. Lee JW, Kim DY, Lee YK. Two Cases of Deepening of the Upper Lid Sulcus from Topical Bimatoprost Therapy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:332–6.5. Johnstone MA. Hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of eyelashes and adjacent hair in the region of the ipsilateral eyelids of patients treated with unilateral topical latanoprost. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 124:544–7.
Article6. Herndon LW, Williams RD, Wand M, Asrani S. Increased periocular pigmentation with ocular hypotensive lipid use in African Americans. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:713–5.
Article7. Grierson I, Jonsson M, Cracknell K. Latanoprost and Pigmentation. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2004; 48:602–12.
Article8. Woodward DF, Krauss AH, Chen J, et al. The pharmacology of bimatoprost (Lumigan). Surv Ophthalmol. 2001; 45:337–45.
Article9. Tomita Y, Maeda K, Tagami H. Mechanisms for hyperpigmentation in postinflammatory pigmentation, urticaria pigmentosa and sunburn. Dermatologica. 1989; 179:49–53.
Article10. Seiberg M. Keratinocyte-melanocyte interactions during melanosome transfer. Pigment Cell Res. 2001; 14:236–42.
Article11. Kapur R, Osmanovic S, Toyran S, Edward DP. Bimatoprost induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation: histopathological study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:1541–6.12. Kim EC, Kim JW. Effect of Latanoprost on the Cultured Human Uveal Melanocytes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:893–97.13. Marco C, Francesco O, Sergio C, Lucia T. Prevention of dermatologic side effects of bimatoprost 0.03% topical therapy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:1059–60.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Deepening of the Upper Lid Sulcus from Topical Bimatoprost Therapy
- Effect of Bimatoprost on the Permeability of Trabecular Meshwork Cell Monolayer
- The Short Term Effects of Bimatoprost on Optic Nerve Head and Peripapillary Retinal Blood Flow
- Add-on Effect of Prostaglandin Analogues in Dorzolamide/Timolol Fixed Combination Treated Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Patients
- Comparing the Efficacy of Latanoprost (0.005%), Bimatoprost (0.03%), Travoprost (0.004%), and Timolol (0.5%) in the Treatment of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma