J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2011 Apr;46(2):162-166.
Kimura's Disease of the Trunk
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. insoooh@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
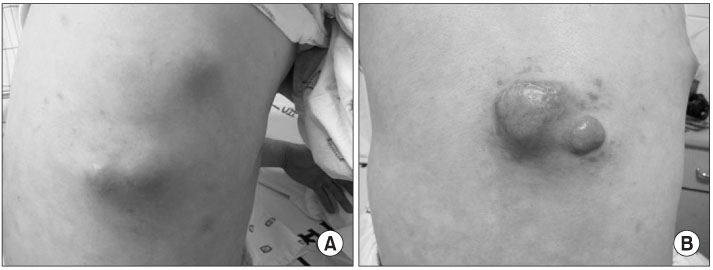
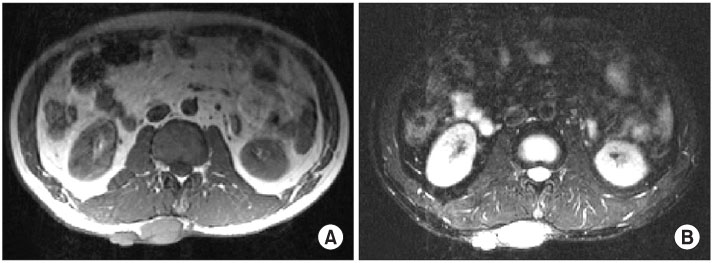
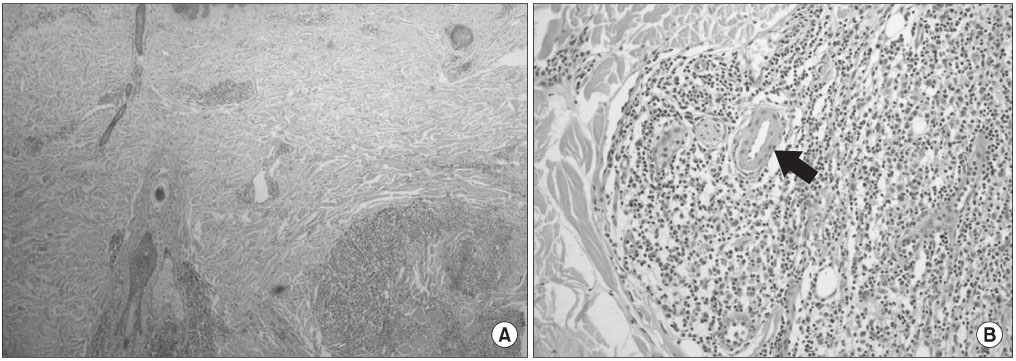
- Kimura's disease is a very rare, benign, lymphoproliferative inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology. A 48 year-old man had multiple soft tissue masses in his trunk, which was diagnosed as Kimura's disease by histopathologic evaluation. Here, we report the case with a review of the literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Googe PB, Harris NL, Mihm MC Jr. Kimura's disease and angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia: two distinct histopathological entities. J Cutan Pathol. 1987. 14:263–271.
Article2. Kimura T, Yoshimura S, Ishikawa E. On the unusual granulation combined with hyperplastic changes of lymphatic tissue. Trans Soc Pathol Jpn. 1948. 37:179–180.3. Yuen HW, Goh YH, Low WK, Lim-Tan SK. Kimura's disease: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Singapore Med J. 2005. 46:179–183.4. Kim KJ, Kim HY, Kim SK, Choy WS, Kim SH. Kimura's disease on upper arm - a report of 2 cases -. J Korean Bone Joint Tumor Soc. 2006. 12:78–82.5. Kim H, Szeto C. Eosinophilic hyperplastic lymphogranuloma, comparison with mikulicz's disease. Chin Med J. 1937. 23:699–700.6. Kuo TT, Shih LY, Chan HL. Kimura's disease. Involvement of regional lymph nodes and distinction from angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988. 12:843–854.7. Ohta N, Okazaki S, Fukase S, Akatsuka N, Aoyagi M, Yamakawa M. Serum concentrations of eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophils of patients with Kimura's disease. Allergol Int. 2007. 56:45–49.
Article8. Katagiri K, Itami S, Hatano Y, Yamaguchi T, Takayasu S. In vivo expression of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 and IFN-gamma mRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and effect of cyclosporin A in a patient with Kimura's disease. Br J Dermatol. 1997. 137:972–977.9. Birol A, Bozdogan O, Keleş H, et al. Kimura's disease in a Caucasian male treated with cyclosporine. Int J Dermatol. 2005. 44:1059–1060.
Article10. Chang AR, Kim K, Kim HJ, Kim IH, Park CI, Jun YK. Outcomes of Kimura's disease after radiotherapy or nonradiotherapeutic treatment modalities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:1233–1239.
Article