J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Aug;44(4):408-413.
Radiographic Examination at Lateral Decubitus Position for Reducing the Variability of Cup Inclination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kangwon National University College of Medicine and The Clinical Research Institute of Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea. hkyljh@kangwon.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
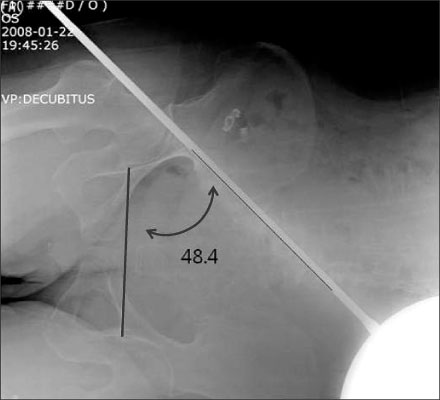
This study analyzed the factors related to a variable inclination angle in patients who have undergone total hip arthroplasty by taking pelvis AP X-rays in the lateral decubitus position with a 45degrees targeted goniometer. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We recruited 100 adults (50 men and 50 women) who were without a history of hip joint disease. The mean age was 30.1 years for the men and 33.7 years for the women. The circumferences of the shoulder and pelvis, the shoulder to pelvis ratio, and the body mass index were checked. We examined the radiographs with using a goniometer, which was targeted to 45degrees for allowing a rod to be across the center of the acetabulum. The cross angle between the rod and the interteardrop line was checked. RESULTS: On the comparison of the gender groups, the shoulder to pelvis ratio was on average 1.18 in men and it was 1.08 in women. The mean cross angle was 45.3degrees in men and 48.1degrees in women. As the ratio was increased, the cross angle decreased. CONCLUSION: For men, there was little pelvic tilt in the lateral decubitus position. But for women, if inserting the acetabular cup with the acetabular orientation at 45degrees is done without considering the pelvic tilt inclination at the lateral decubitus position, then the inclination angle could be lower than expected.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harkess WJ. Crenshaw AH, editor. Arthroplasty of the hip: dislocation and subluxation. Campbell's orthopaedics. 1992. 8th ed. Mosby;54.2. Hwang SK. Ceramic on ceramic bearing surfaces. J Korean Hip Soc. 2004. 16:106–114.3. Daly PJ, Morrey BF. Operative correction of an unstable total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:1334–1343.
Article4. DiGioia AM, Jaramaz B, Blackwell M, et al. The Otto Aufranc Award. Image guided navigation system to measure intraoperatively acetabular implant alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 355:8–22.5. Sarmiento A, Ebramzadeh E, Gogan WJ, McKellop HA. Cup containment and orientation in cemented total hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:996–1002.
Article6. Gibson RS. Evaluation of anthropometric indices. Principles of nutritional assessment. 1990. Oxford University Press;247–262.7. Crowninshield RD, Maloney WJ, Wentz DH, Humphrey SM, Blanchard CR. Biomechanics of large femoral heads?: What they do and don't do. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 429:102–107.8. Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, Sullivan RJ, Griffen DG, Sheehan LJ. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998. 13:530–534.
Article9. Livermore J, Ilstrup D, Morrey B. Effect of femoral head size on wear of the polyethylene acetabular component. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:518–528.
Article10. Bader R, Willmann G. Willmann G, Zweymuller K, editors. Einschrankung der Range of Motion von Hultendoprothesen durch Design, Position und Pfannenabrieb. Bioceramics in Hip Joint Replacement. 2000. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme;66–74.11. DiGioia AM 3rd, Plakseychuk AY, Levison TJ, Jaramaz B. Mini-incision technique for total hip arthroplasty with navigation. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:123–128.
Article12. Nogler M, Kessler O, Prassl A, et al. Reduced variability of acetabular cup positioning with use of an imageless navigation system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 426:159–163.
Article13. Kim YL, Shin SI, Nam KW, Yoo JJ, Kim YM, Kim HJ. Total hip arthroplasty for bilaterally ankylosed hips. J Arthroplasty. 2007. 22:1037–1041.
Article14. McCollum DE, Gray WJ. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: Causes and prevention. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. 261:159–170.
Article15. Parratte S, Kilian P, Pauly V, Champsaur P, Argenson JN. The use of ultrasound in acquisition of the anterior pelvic plane in computer-assisted total hip replacement: A cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008. 90:258–263.16. Najarian BC, Kilgore JE, Markel DC. Evaluation of component positioning in primary total hip arthroplasty using an imageless navigation device compared with traditional methods. J Arthroplasty. 2009. 24:15–21.
Article17. Nakamura S, Matsuda K, Arai N, Kobayashi M, Wakimoto N, Matsushita T. Method to reduce variations of inclination angle of the acetabular component during mini-incision hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2006. 11:254–258.
Article18. Lee CM, Sung HK, Kim JR. The 5th Korean physical data research report. 2004. Ergonomic Society of Korea.19. Chung YK, Park YW, Ryoo JG, Lee EC. Radiographic assessment of acetabular cup angle after the total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1995. 30:33–41.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness of a Pre-Operative Lateral Decubitus Position Radiologic Examination Using a Goniometer and Rod in THRA
- Change of Sacral Slope according to the Surgical Position in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- The Usefulness of Left Subcostal Transverse Ultrasound Scan with a Right Lateral Decubitus Position for Pancreas Tail Lesions
- Left Lateral Decubitus Position of Gallbladder Ultrasound: Is It Always Necessary in Detection of Gallbladder Lesion?
- Radiographic Assessment of Acetabular Cup angle after the Total Hip Arthroplasty