J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Apr;44(2):271-274.
Partial Paralysis of the Posterior Interosseous Nerve: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. ospjy1222@empas.coms
Abstract
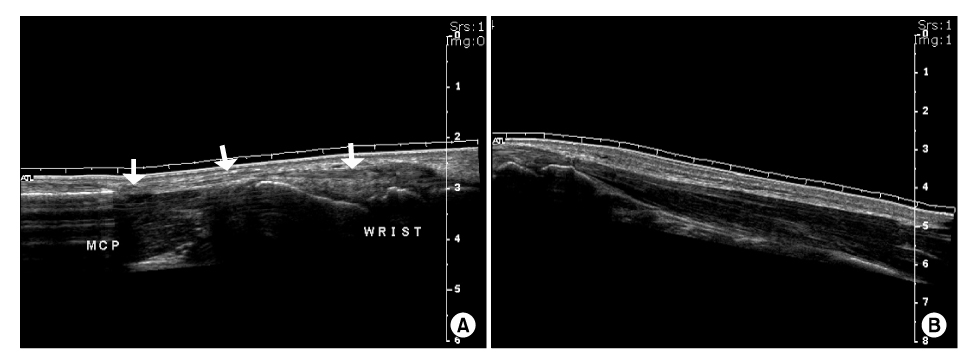
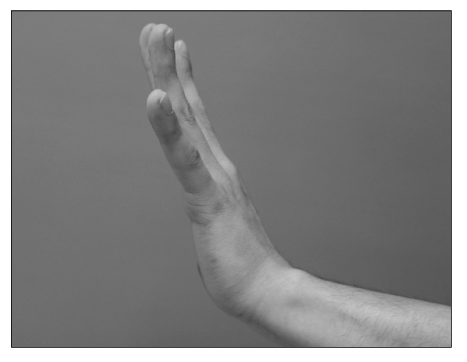
- Partial paralysis of the posterior interosseous nerve at the forearm region has been rarely reported. We report our patients. After closed crushing injury at the forearm region, the patients showed "Sign of horns" which means disability of extension at the third and fourth metacarpo-phalangeal joint because of partial paralysis of the posterior interosseous nerve. We treated the patients as conservative treatment and the patients was completely recovered. So the autors report this case.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cravens G, Kline DG. Posterior interosseous nerve palsies. Neurosurgery. 1990. 27:397–402.
Article2. Elgafy H, Ebraheim NA, Rezcallah AT, Yeasting RA. Posterior interosseous nerve terminal branches. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 376:242–251.
Article3. Erdem S, Demirci M, Tan E. Focal myopathy mimicking posterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2001. 24:969–972.
Article4. Hirachi K, Kato H, Minami A, Kasashima T, Kaneda K. Clinical features and management of traumatic posterior interosseous nerve palsy. J Hand Surg Br. 1998. 23:413–417.
Article5. Hirayama T, Takemitsu Y. Isolated paralysis of the descending branch of the posterior interosseous nerve. Report of a case. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:1402–1403.
Article6. Seradge H, Tian W, Baer C, Seradge A. Anatomical variation of the posterior interosseous nerve: a cadaver dissection study. Orthopedics. 2000. 23:1195–1196.
Article7. Spiner M. Injuries to the major branches of the peripheral nerve of the forearm. 1978. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;80–157.8. Spinner RJ, Berger RA, Carmichael SW, Dyck PJ, Nunley JA. Isolated paralysis of the extensor digitorum communis associated with the posterior (Thompson) approach to the proximal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1998. 23:135–141.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed palsy of Posterior Interosseous Nerve due to compression of the Arcade of Frohse and old anterior dislocation of the radial head
- The Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome
- Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Case of Report
- Incomplete Compressive Neuropathy of Posterior Interosseous Nerve Caused by Ganglion : A Case Report
- Incomplete Anterior Interosseous Nerve Palsy That Accompanied a Monteggia Fracture