J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Dec;14(4):340-344.
Clinical Significance of Autoantibodies to Glucose-6-phosphate Isomerase in Serum of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwanju, Korea. mdkim9111@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI) antibody (Ab) is known to be arthritogenic in K/BxN mice. Anti-GPI Ab is present in some patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but their clinical manifestations are not clearly elucidated. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether GPI serves as a specific autoantigen in patients with RA and to investigate the relationship of anti-GPI Ab with clinical parameters of RA.
METHODS
Sera were collected from 54 patients with RA, 15 patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and 28 healthy controls. The samples were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using human recombinant GPI as antigen. Patients with RA were classified according to rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity, the presence of RA shared epitope (SE), the presence of extraarticular manifestations, and evidence of bony erosive changes.
RESULTS
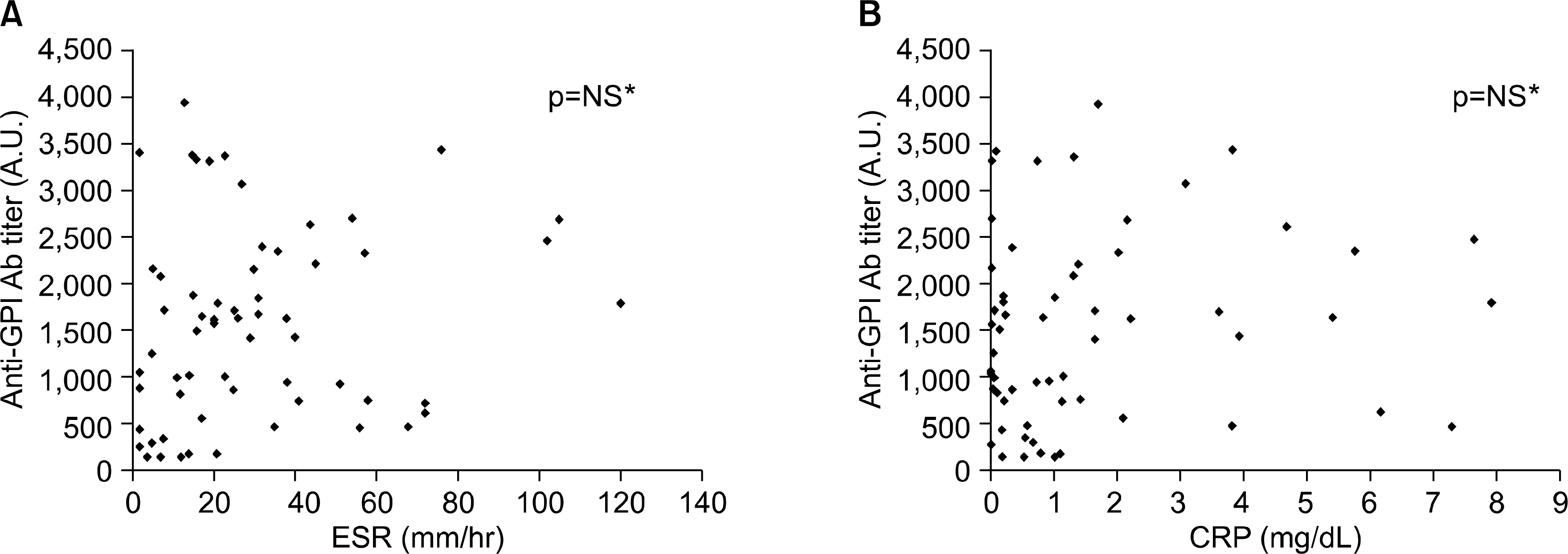
Serum levels of anti-GPI Ab were higher in patients with RA than controls (1599.46+/-1022.48 versus 344.82+/-223.16 AU, p<0.001), and the levels of patients with OA were also higher than controls (1161.47+/-917.44 versus 344.82+/-223.16 AU, p<0.01). In RA, there were no significant difference in anti-GPI Ab levels according to RF positivity, the presence of RA SE, the presence of extraarticular manifestations, and evidence of bony erosive changes.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that anti-GPI Ab may not be RA specific Ab and not related to the severity of RA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Feldmann M., Brennan FM., Maini RN. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996. 85:307–10.
Article2). Herve CA., Wait R., Venables PJ. Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase is not a specific autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003. 42:986–8.
Article3). Schaller M., Burton DR., Ditzel HJ. Autoantibodies to GPI in rheumatoid arthritis: linkage between an animal model and human disease. Nat Immunol. 2001. 2:746–53.
Article4). Matsumoto I., Lee DM., Goldbach-Mansky R., Sumida T., Hitchon CA., Schur PH, et al. Low prevalence of antibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a spectrum of other chronic autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:944–54.
Article5). Hayashi T., Matsumoto I., Muraki Y., Takahashi R., Chino Y., Goto D. Clinical characteristics of anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase antibody-positive Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2005. 15:258–63.
Article6). Cha HS., Kim TJ., Kim JY., Lee MH., Jeon CH., Kim J, et al. Autoantibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase are elevated in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004. 33:179–84.
Article7). 김상현: 김성동: 김해림: 박성환: 김호연. 류마티스관절염환자의활액내항GPI 항체의임상적유용성. 대한류마티스학회지. 2005. 12:12–7.8). Kim HY., Min JK., Yang HI., Park SH., Hong YS., Jee WH, et al. The impact of HLA-DRB10405 on disease severity in Korean patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1997. 36:440–3.
Article9). Kouskoff V., Korganow AS., Duchatelle V., Degott C., Benoist C., Mathis D. Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell. 1996. 87:811–22.
Article10). Maccioni M., Zeder-Lutz G., Huang H., Ebel C., Gerber P., Hergueux J, et al. Arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies from K/BxN mice. J Exp Med. 2002. 195:1071–7.
Article11). Ji H., Pettit A., Ohmura K., Ortiz-Lopez A., Duchatelle V., Degott C, et al. Critical roles for interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in antibody-induced arthritis. J Exp Med. 2002. 196:77–85.12). Schaller M., Stohl W., Tan SM., Benoit VM., Hilbert DM., Ditzel HJ. Raised levels of anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase IgG in serum and synovial fluid from patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:743–9.
Article13). van Gaalen FA., Toes RE., Ditzel HJ., Schaller M., Breedveld FC., Verweij CL, et al. Association of autoantibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase with extraarticular complications in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:395–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A New Paradigm for Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Clinical Significance of Autoantibodies to Glucose-6-Phosphate Isomerase in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Potential Role of Bacterial Infection in Autoimmune Diseases: A New Aspect of Molecular Mimicry
- Detection of antibodies against glucose 6-phosphate isomerase in synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis using surface plasmon resonance (BIAcore)
- Clinical significance of rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis