J Korean Soc Med Inform.
2009 Dec;15(4):403-410.
Simulation of a Multiversion Medical Data Management System for Medical Information Security
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hospital Information Management, Gwangju Health College University, Korea. hcjeong@ghc.ac.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
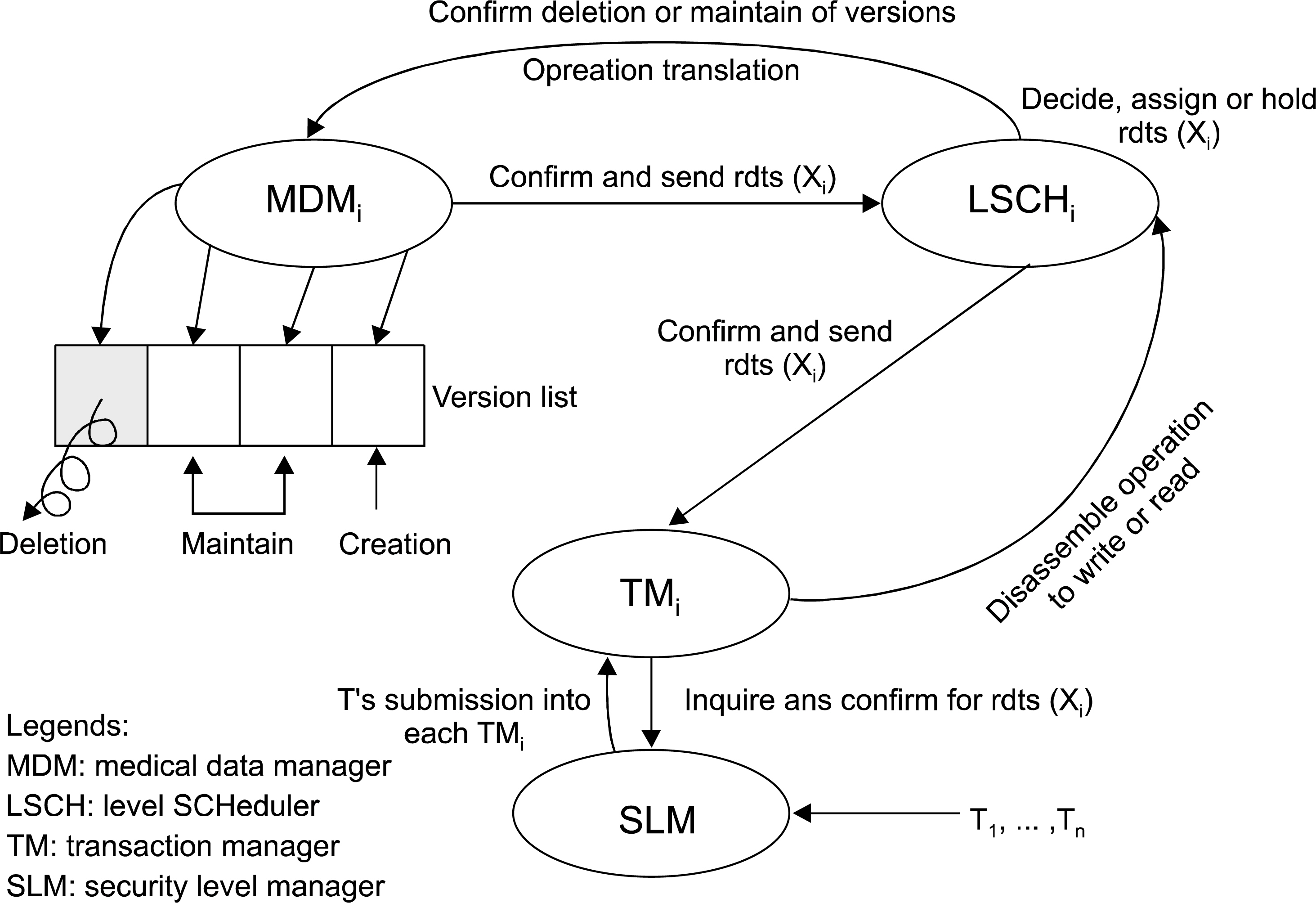
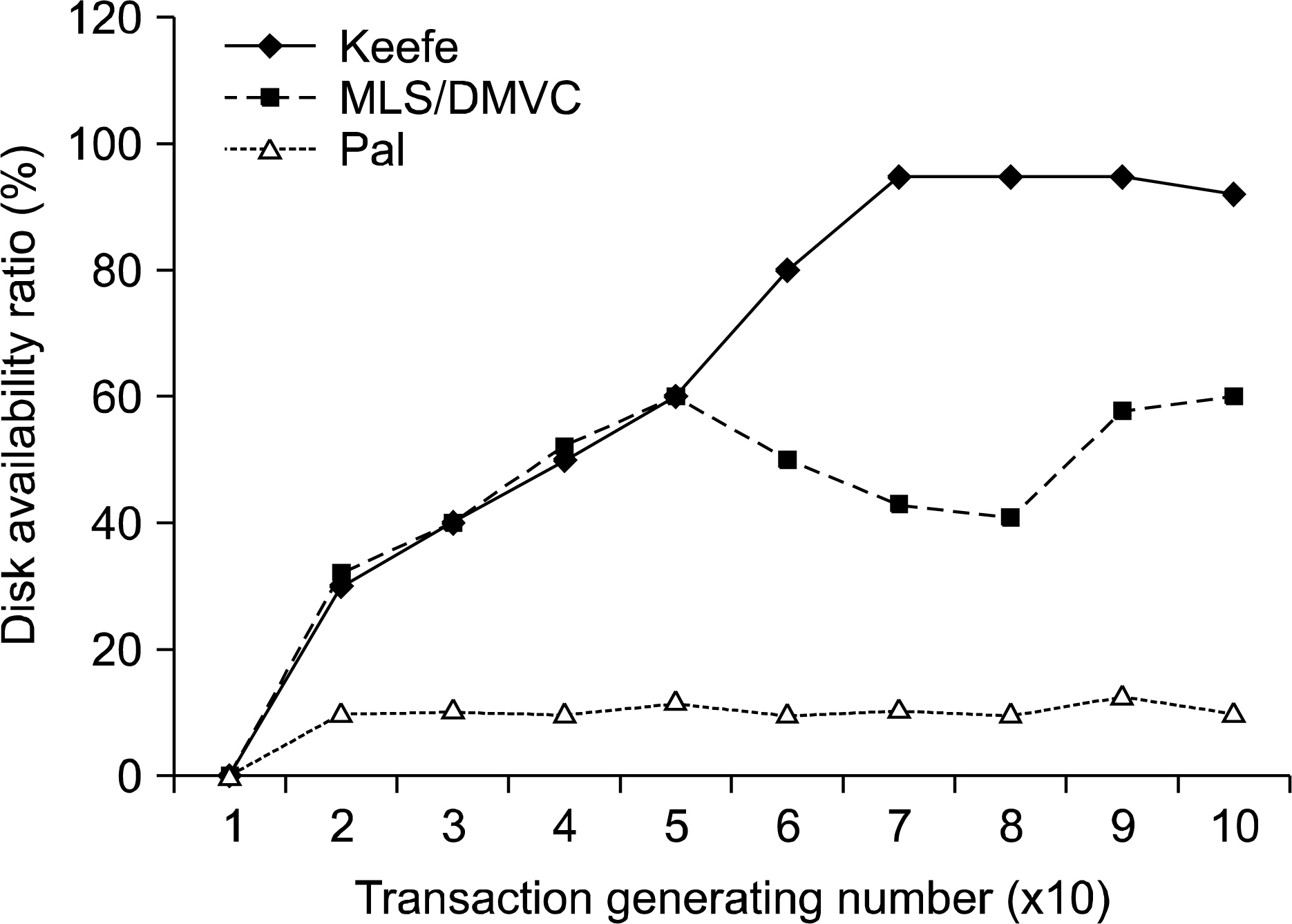
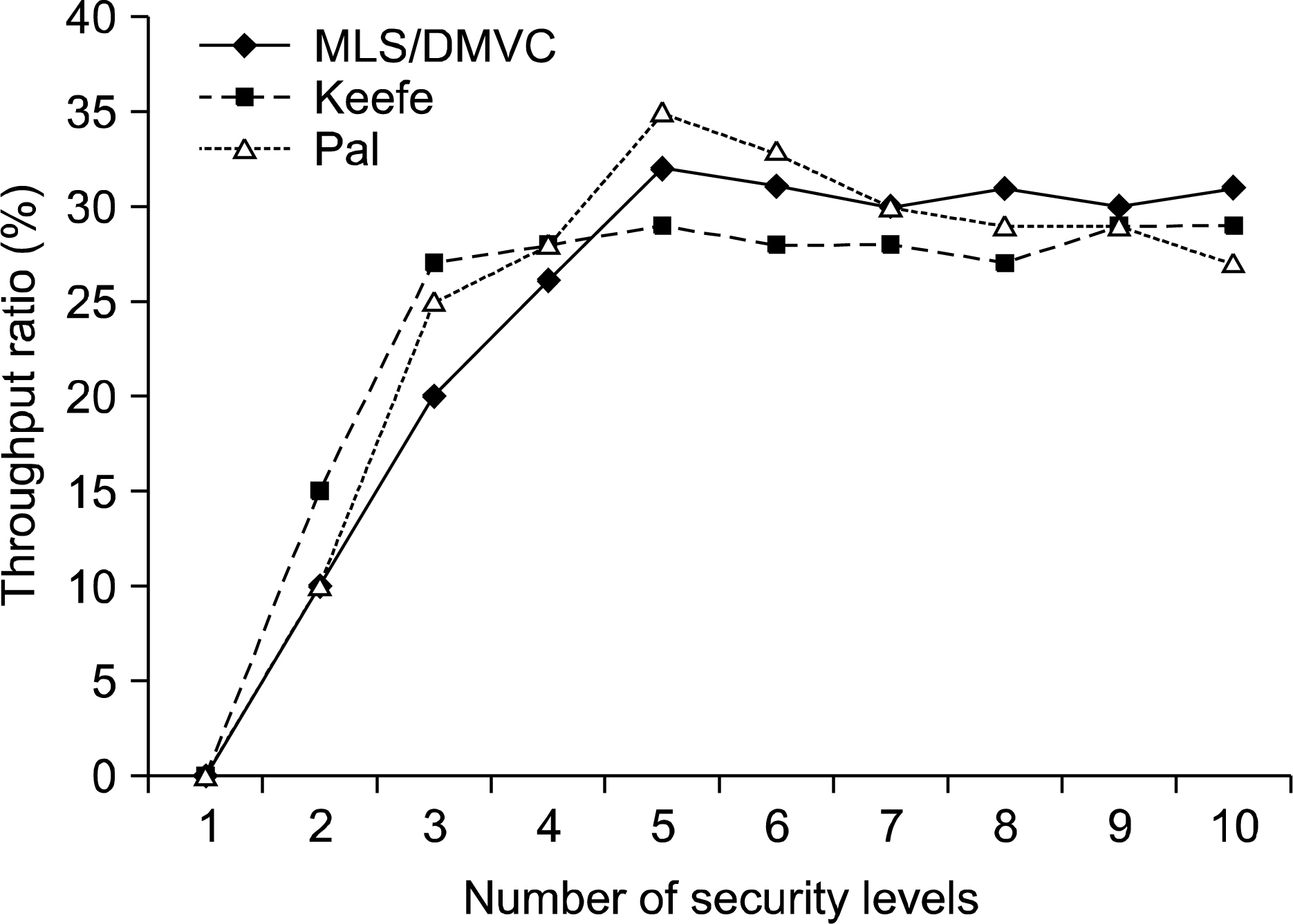
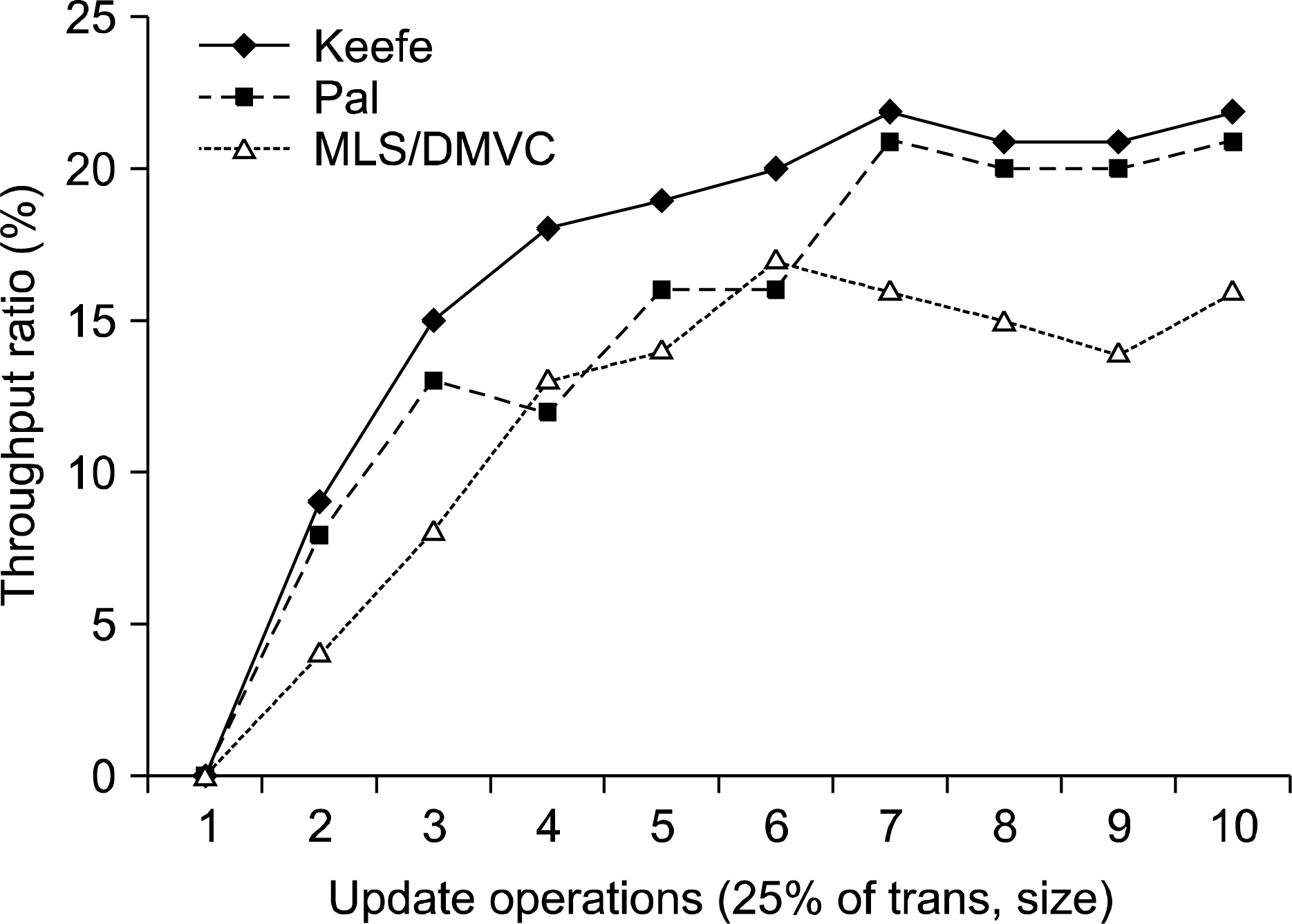
If medical information is integrated for management purposes, the efficiency of the system may increase. In addition, diagnostic abilities of physicians may be improved through the increased speed and accuracy of information processing. Medical databases must ensure high performance in terms of speed and reliability. In addition, access to medical information must be restricted to persons with proper authorization to ensure the privacy of patients. METHODS: Thus, the security of medical database systems with multiversion data requires both the existing management system and security policies. RESULTS: This study simulates the performance of a dynamic multiversion data management system in terms of security levels and update operations. CONCLUSION: The results show that a dynamic multiversion data management system increases disk availability more than a double version system. In addition, if the number of security levels is small, throughput will be improved because the security overhead will be low. However, frequent update operations will decrease throughput whenever versions are created at each interval.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jeong HC. The security of medical information system. KISS. 1998; 16(12):141–145.2. Bell DE, LaPadula LJ. Secure computer systems: unified exposition and multics interpretation. Technical Report MTR-2997 Mitre Corp. 1976.3. Castano S. Database security. Addison-Wesley;1994. p. 82–96.4. Pfleeger CP. Security in computing. Prentice Hall;1989. p. 249–250.5. Jeong HC. Dynamic multiversion control in multilevel security environments. KIPS. 1997; 3(4):123–130.6. Keefe TF, Tsai WT. Multiversion concurrency control for multilevel secure database systems. IEEE:Security and Privacy;1990. p. 369–383.7. Jajodia S, Atluri V. Alternative correctness criteria for concurrent execution of transactions in multilevel secure databases. IEEE:Security and Privacy;1992.8. Atluri V, Bertino E, Jajodia S. Providing different degrees of recency options to transactions in multilevel secure databases. IFIP:WG 11.3. Database Security;1995. p. 199–221.9. Pal S. A locking protocol for multilevel secure databases providing support for long transactions. IFIP:WG 11.3. Database Security;1995. p. 119–121.10. Graubart R. A comparison of three secure DBMS architectures. IFIP:WG 11.3. Database Security;1989. p. 130–135.11. Care M, Stonebraker M. The performance of concurrency control algorithm for database management systems. IEEE:10th VLDB. 1984; 107–118.12. Agrawel D, Abbadi A, Lang A. Performance characteristics of protocols with ordered shared locks. IEEE: 7th Data Engineering;1991. p. 592–601.13. Choi YG. The performance of concurrency control in multilevel secure database management system. MS thesis. Kaist;1995.14. Jeong HC, Lim CG. Transaction serializability with security in heterogeneous medical database systems. J of KOSMI. 1999; 5(3):109–118.
Article15. Jeong HC. Multilevle secure recovery management of medical databases in hospital information system. J of KOSMI. 2000; 6(2):17–25.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multilevel Secure Recovery Management of Medical Databases in Hospital Information System
- Trends in Research on the Security of Medical Information in Korea: Focused on Information Privacy Security in Hospitals
- Transaction Serializability with Security in Heterogeneous Medical Database Systems
- Analysis of Information Security Management Systems at 5 Domestic Hospitals with More than 500 Beds
- Personal Privacy Protection of Electronic Medical Record in Health Information System