J Korean Soc Med Inform.
2009 Sep;15(3):303-312.
Technical Considerations for Successful Implementation of a Barcode-based Medication System in Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Industrial and Information Systems Engineering, Soongsil University, Korea. dskim@ssu.ac.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To identify the technical considerations in implementing a barcode-based medication system and propose practical solutions for successful implementation of the system. In order to reduce medical errors related to medication and blood transfusion, we analyze various factors that hinder the successful implementation of the barcode-based medication system and discuss issues involved in the effective adoption of such a system.
METHODS
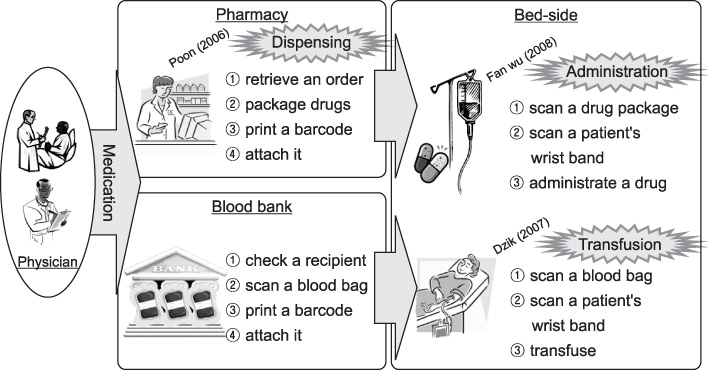
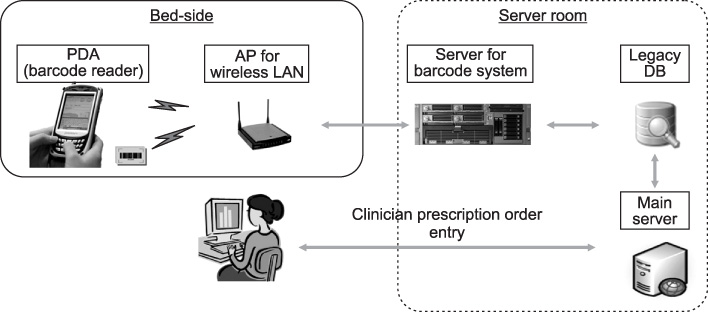
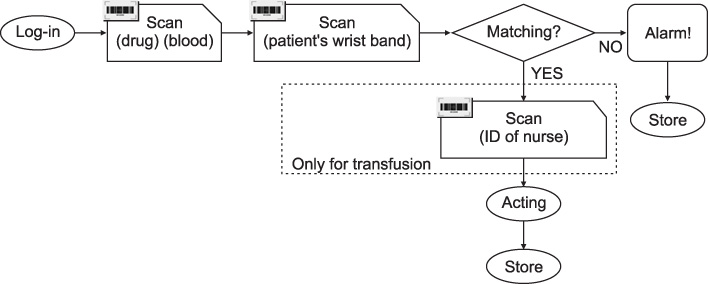
The barcode-based medication system of this research uses one-dimensional, barcode bands on patients' wrists and two-dimensional barcodes attached to drug bags and blood bags. PDAs with barcode reading capability and wireless networking function are used, which enables Point of Care. The business process for applying the developed system and the current status of the system usage are analyzed.
RESULTS
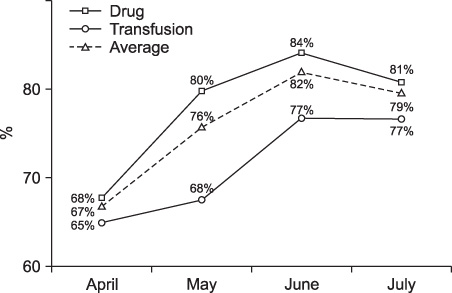
The factors causing a variety of system failures in the demonstration and pilot periods were identified and categorized as including PDA malfunction, PDA battery discharge due to users' carelessness, confusion in reading barcodes and so on.
CONCLUSIONS
It is expected that the analyzed obstructive factors and the proposed technical considerations addressed in this paper can help other hospitals implement similar barcode-based medication systems successfully. Ultimately, this research will contribute to reducing medical errors and improving quality of patient care.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huang HH, Ku CY. A RFID grouping proof protocol for medication safety of inpatient. J Med Syst. 2008. DOI 10.1007/s10916-008-9207-z.
Article2. Poon EG, Cina JL, Churchill W, Patel N, Featherstone E, Rothschild JM, et al. Medication dispensing errors and potential adverse drug events before and after implementing bar code technology in the pharmacy. Ann Intern Med. 2006. 145(6):426–434.
Article3. Chassin MR, Becher EC. The wrong patient. Ann Intern Med. 2002. 136(11):826–833.
Article4. Flynn EA. A brief History of medication errors. Accessed August 29 2009. Available at: http://www.medaccuracy.com/Papers%20and%20Publications/A%20Brief%20History%20of%20Medication%20Errors.pdf.5. Kaushal R, Bates DW. Information technology and medication safety: what is the benefit? Qual Saf Health Care. 2002. 11:261–265.
Article6. Dzik WH. New technology for transfusion safety. Brit J Haematol. 2007. 136(2):181–190.
Article7. Bernard F, Brian M, Aziz S. Reducing medication-related adverse events in elderly patients. Rev Clin Gerontol. 2006. 16:79–87.
Article8. Sun PR, Wang BH, Wu F. A new method to guard inpatient medication safety by the implementation of RFID. J Med Syst. 2008. 32(4):327–332.
Article9. Lee SY. A study on medication error among nurses and prevention strategy [dissertation]. 2008. Daejeon: Eulji University;35.10. Cho WS. A study on the types and causes of medication errors and related drugs. J Korea Community Health Nurs Acad Soc. 2002. 16(1):176–189.11. A study on the introduction methodology of RFID. National Computerization Agency. Accessed August 29, 2009. Available at: http://www.nia.or.kr/open_content/board/fileDownload.jsp?tn=LC_0000047&id=51912&seq=1&fl=7http://www.nia.or.kr/open_content/board/fileDownload.jsp?tn=LC_0000047&id=51912&seq=1&fl=7.12. Choi KA, Jung IS, Yu HS, Yoon ES, Lee YH, Kang UG. A study on RFID recognition rate for pharmaceutical storage management. J Korea Soc Comput Inform. 2008. 16(2):249–254.13. Ji KY, Kim D, Kim MC, Lee YH, Kim SB, Lee SK, et al. Ubiquitous health. 2006. 1st ed. Seoul, Korea: Jinhan M&B;196.14. Park SD. Mobile authentication system and it's application based on 2-dimensional barcode and OTP [dissertation]. 2009. Seoul: Hanyang University;3.15. Poon EG, Keobane CA, Bane A, Featherstone E, Hays BS, Dervan AD, et al. Impact of barcode medication administration technology on how nurses spend their time providing patient care. J Nurs Admin. 2008. 38(12):541–549.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and Application of Direct Data Capture for Monitoring Medication Compliance in Clinical Trials
- LAN Based Hospital Information System (II): Computerization of Blood Collection Room to Reduce Clinical Order Turnaround Time
- Technology and Policy Challenges in the Adoption and Operation of Health Information Exchange Systems
- Technical Consideration of Endovascular Treatment for Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease Based on a 10-Year Tertiary Hospital Experience: A Retrospective Study
- A survey for Management of Drug Safety Evaluation System for Investigational Product