Korean J Clin Neurophysiol.
2016 Jun;18(1):25-27. 10.14253/kjcn.2016.18.1.25.
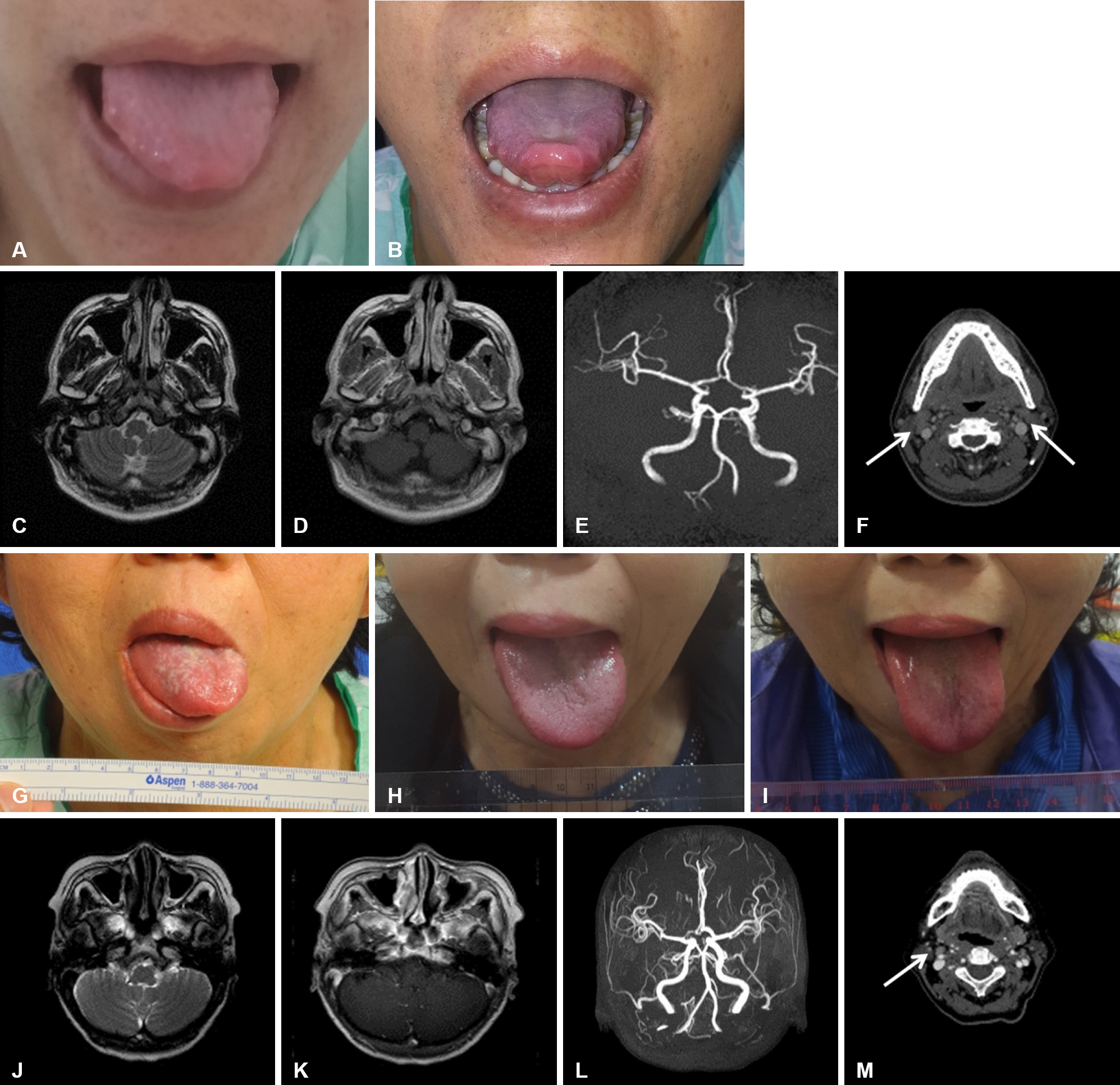
Different Clinical Courses of Idiopathic Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shheo73@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2328826
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/kjcn.2016.18.1.25
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Combarros O., Alvarez de Arcaya A., Berciano J. Isolated unilateral hypoglossal nerve palsy: Nine cases. J Neurol. 1998. 245:98–100.
Article2.Lee SS., Wang SJ., Fuh JL., Liu HC. Transient unilateral hypoglossal nerve palsy: a case report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1994. 96:148–151.
Article3.Freedman M., Jayasundara H., Stassen LF. Idiopathic isolated unilateral hypoglossal nerve palsy: a diagnosis of exclusion. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008. 106:e22–e26.
Article4.Ho MW., Fardy MJ., Crean SJ. Persistent idiopathic unilateral isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy: a case report. Br Dent J. 2004. 196:205–207.
Article5.Thompson EO., Smoker WR. Hypoglossal nerve palsy: a segmental approach. Radiographics. 1994. 14:939–958.
Article6.Choi JY., Moon SY. Idiopathic isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy after upper respiratory infection. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2009. 27:192–193.7.Keeling D., Mackie I., Moore GW., Greer IA., Greaves M. Guidelines on the investigation and management of antiphospholipid syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2012. 157:47–58.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Improved Idiopathic Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy without Use of Steroid
- Idiopathic Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy After Upper Respiratory Infection
- A Case of Idiopathic Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy
- Delayed Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy after Submandibular Gland Surgery
- A Case of Oropharyngeal Carotid Space Mass Presenting with Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy