Korean J Clin Neurophysiol.
2016 Jun;18(1):14-17. 10.14253/kjcn.2016.18.1.14.
Pulmonary Thromboembolism after Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dongguk University, School of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 2Divison of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jinforeva@gmail.com
- KMID: 2328823
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/kjcn.2016.18.1.14
Abstract
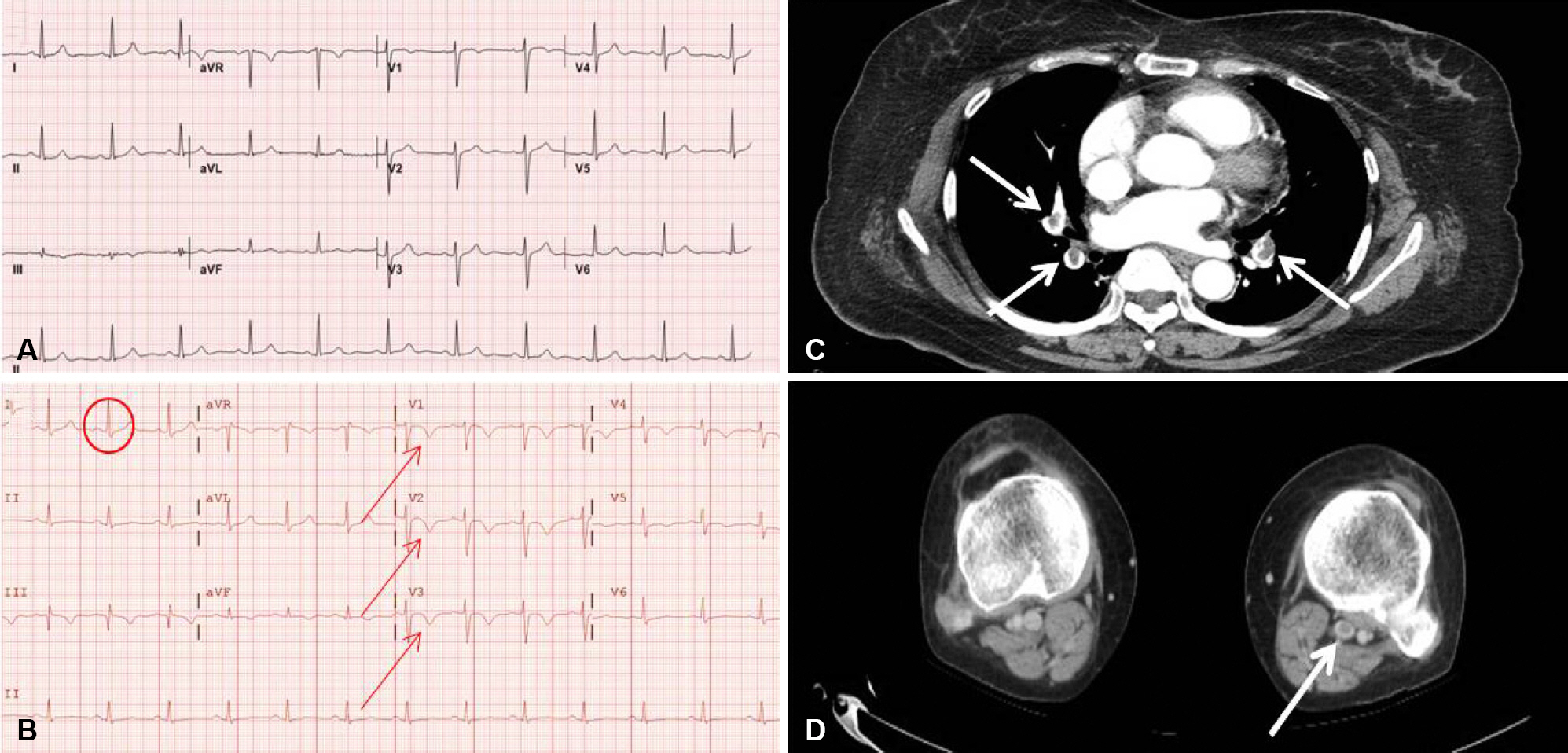
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is a safe treatment to treat various neurological disorders, but fatal thrombotic events as rare complications have been reported. A 54-year-old woman with Guillain-Barre syndrome complained of dyspnea during IVIG treatment. She was finally diagnosed with pulmonary thromboembolism. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of pulmonary thromboembolism associated with IVIG treatment in a Korean patient with Guillain-Barre syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Willison HJ., Jacobs BC., van Doorn PA. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet. 2016 Feb 19. [Epub].http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00339-1.
Article2.Brannagan TH 3rd., Nagle KJ., Lange DJ., Rowland LP. Complications of intravenous immune globulin treatment in neurologic disease. Neurology. 1996. 47:674–677.
Article3.Marie I., Maurey G., Herve F., Hellot MF., Levesque H. Intravenous immunoglobulin-associated arterial and venous thrombosis; report of a series and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol. 2006. 155:714–721.
Article4.Stangel M., Kiefer R., Pette M., Smolka MN., Marx P., Gold R. Side effects of intravenous immunoglobulins in neurological autoimmune disorders- a prospective study. J Neurol. 2003. 250:818–821.5.Wolberg AS., Kon RH., Monroe DM., Hoffman M. Coagulation factor XI is a contaminant in intravenous immunoglobulin preparations. Am J Hematol. 2000. 65:30–34.
Article6.Voltz R., Rosen FV., Yousry T., Beck J., Hohlfeld R. Reversible encephalopathy with cerebral vasospasm in a Guillain-Barré syndrome patient treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Neurology. 1996. 46:250–251.7.Paran D., Herishanu Y., Elkayam O., Shopin L., Ben-Ami R. Venous and arterial thrombosis following administration of intravenous immunoglobulins. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2005. 16:313–318.
Article8.Rajabally YA., Kearney DA. Thromboembolic complications of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in patients with neuropathy: A two-year study. J Neurol Sci. 2011. 308:124–127.
Article9.Lee YJ., Shin JU., Lee J., Kim K., Kim WS., Ahn JS, et al. A case of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:758–761.
Article10.Kang SY., Kang JH., Kim JS. A case of cerebral infarction following intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in a patient with Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2003. 21:217–219.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Rapid Improvement of Symptoms in Severe Guillain-Barre Syndrome after Additional Use of Intravenous Immunoglobulin
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Following Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in a Patient with Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- A Case of Pompholyx Following Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- Pseudohyponatremia After Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in a Patient With Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- SIADH and Guillain-Barre Syndrome Associated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis