Prog Med Phys.
2016 Jun;27(2):98-104. 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.2.98.
Changes of Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dosimeter Sensitivity with High Dose
- Affiliations
-
- 1Radiological & Medico-Oncological Sciences, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea. jyh328@kirams.re.kr
- 2Division of Medical Radiation Equipment, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2328195
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.2.98
Abstract
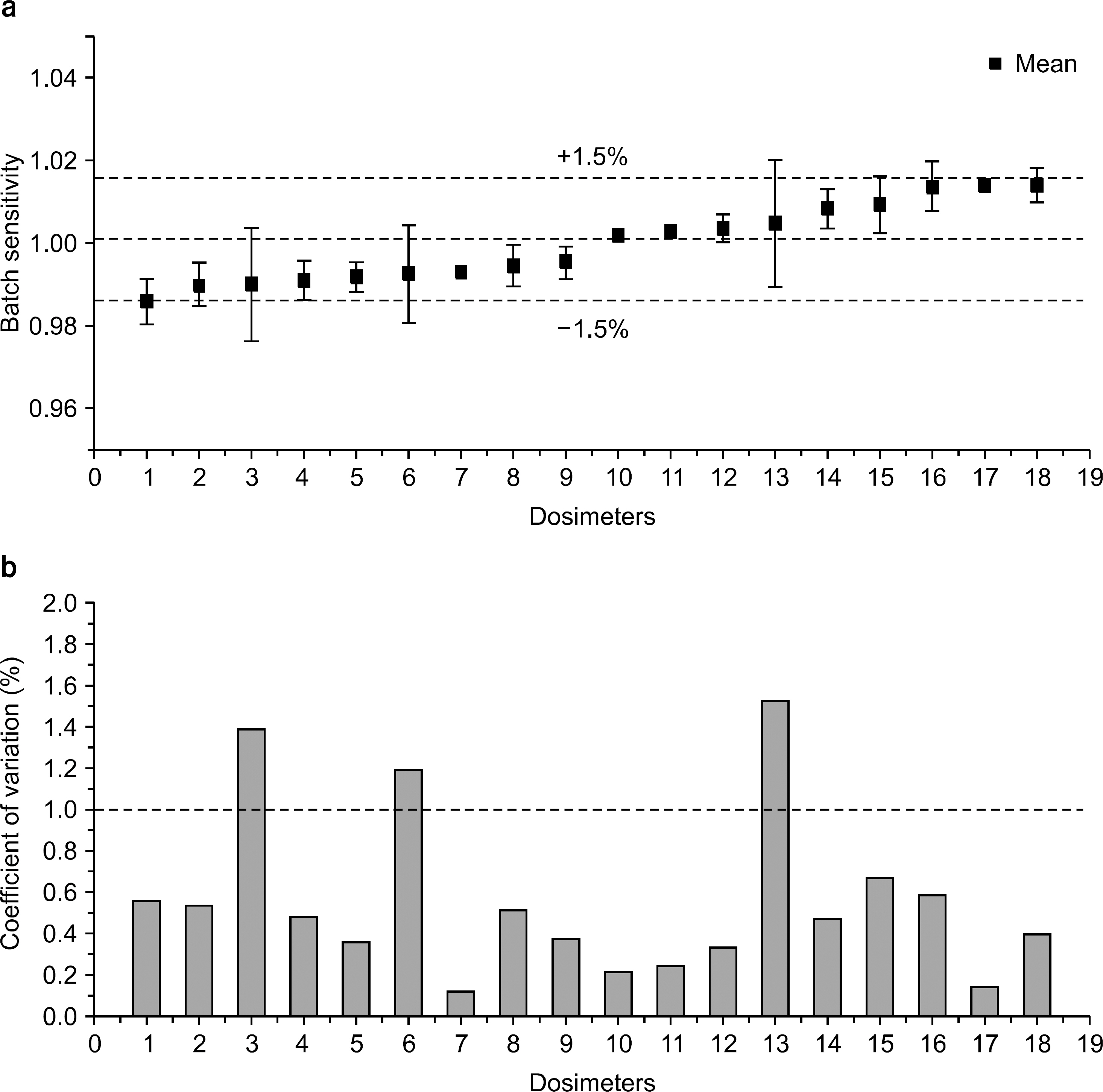
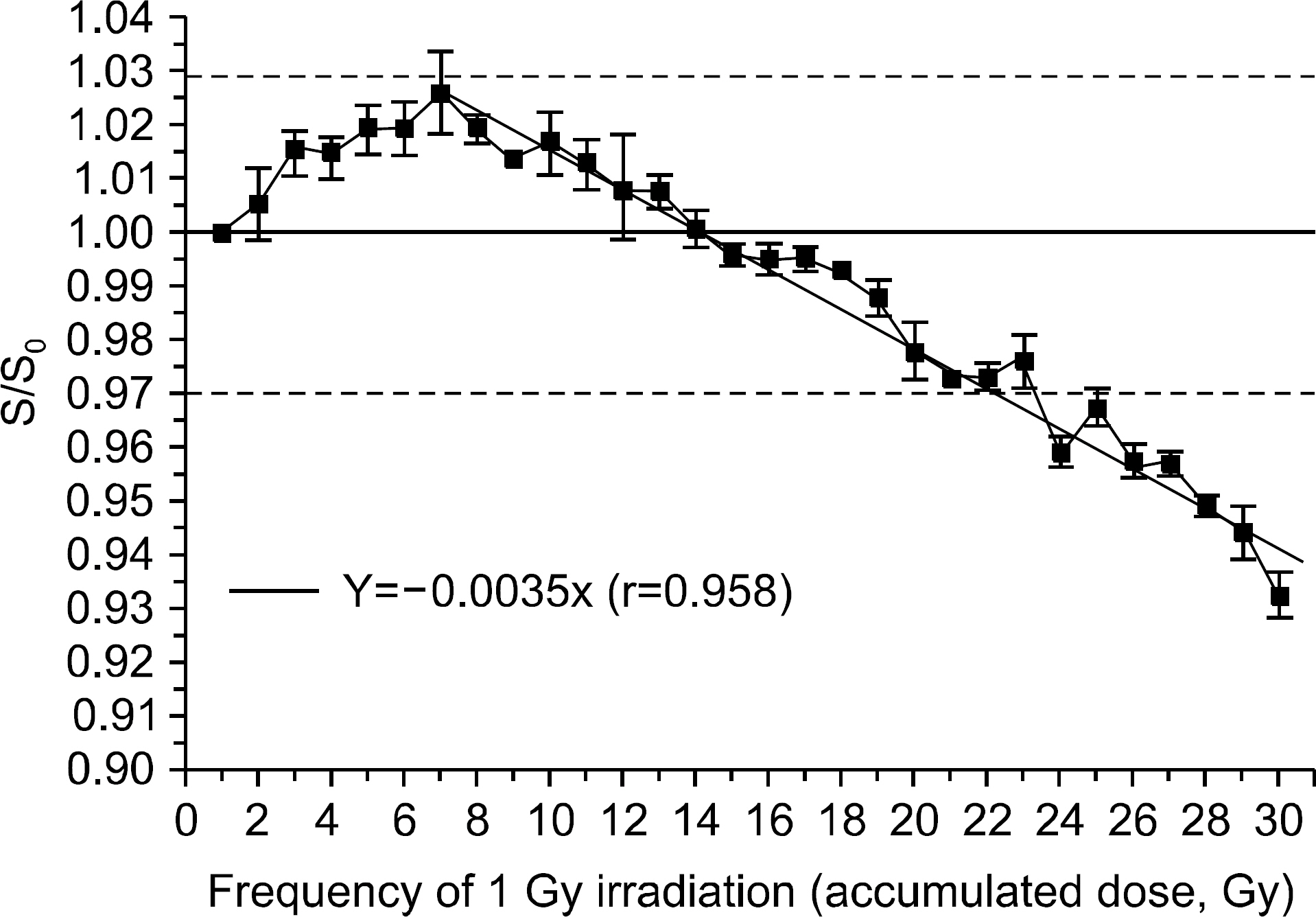
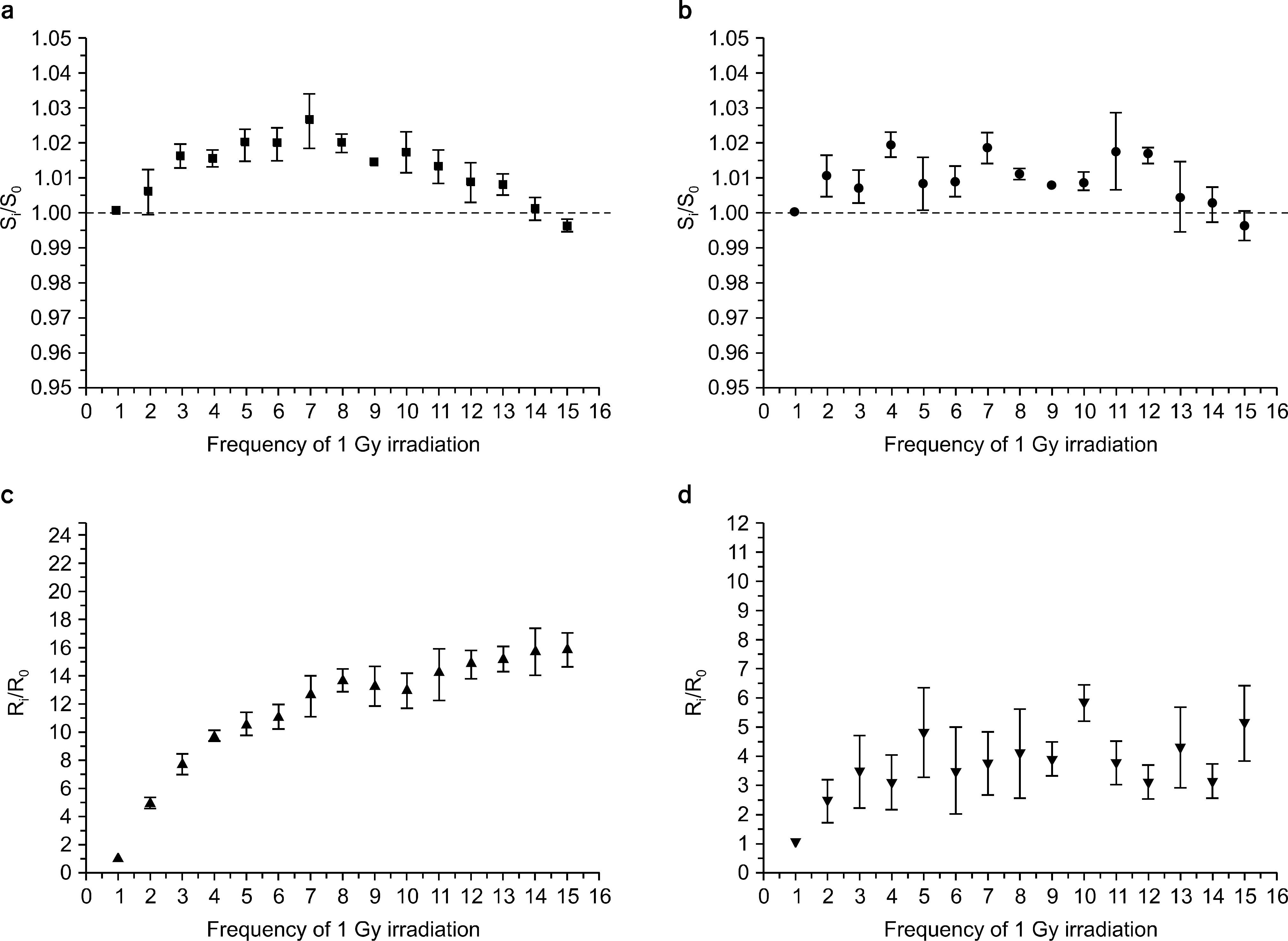
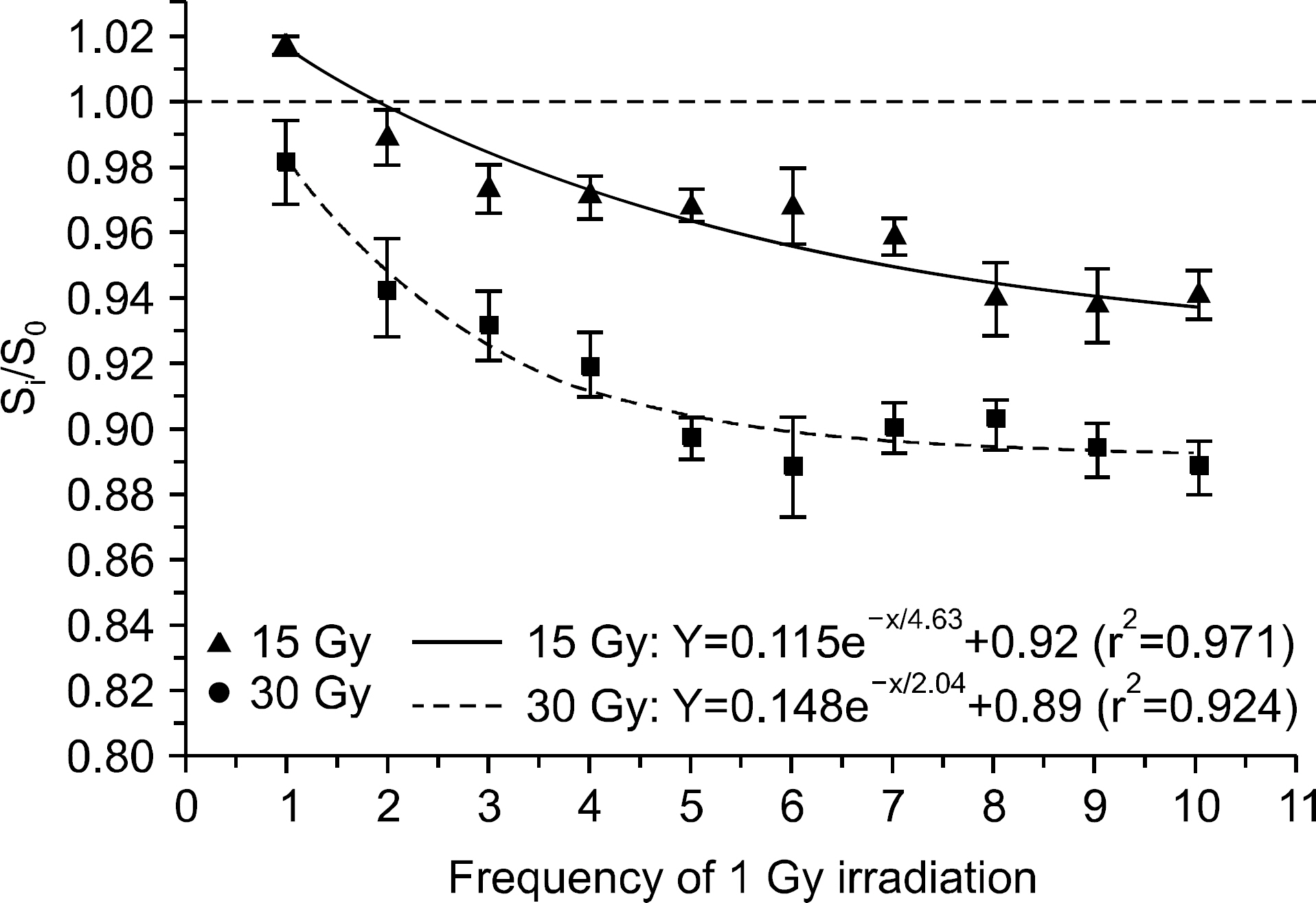
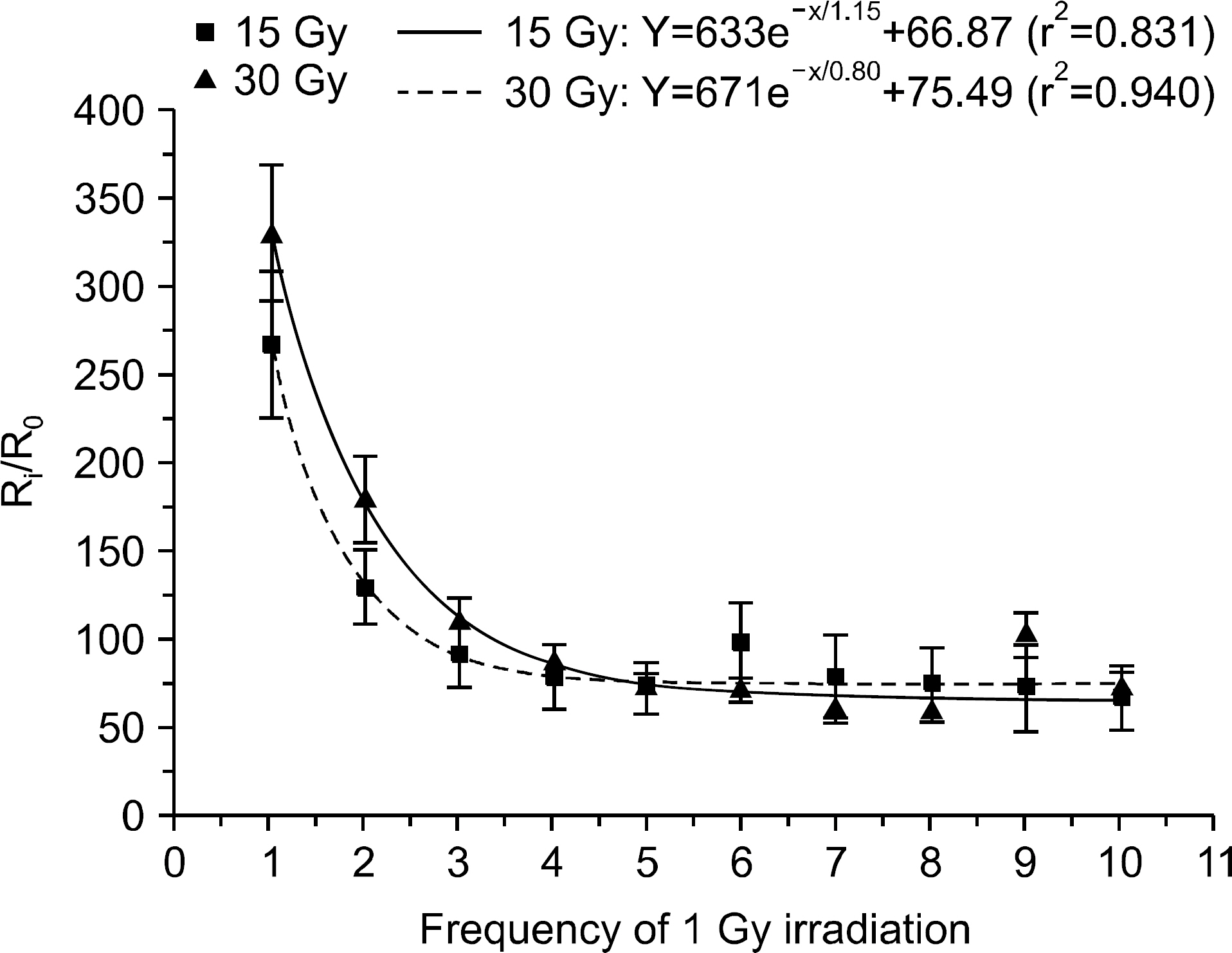
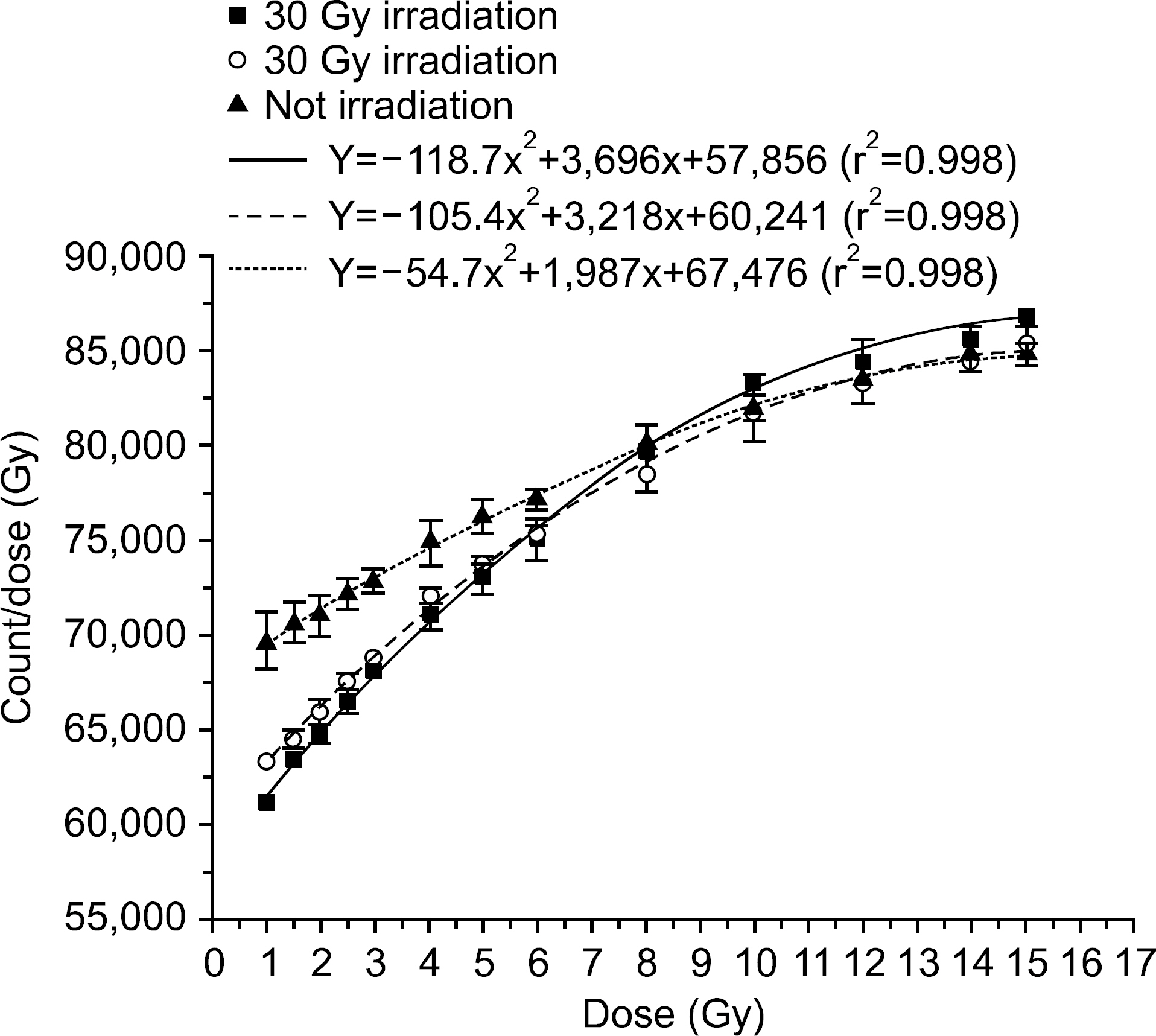
- We investigated the effect of high dose on the sensitivity of optically stimulated luminance dosimeters (OSLDs) on Co-60 gamma rays and used a commercial OLSD (Landauer, Inc., Glenwood, IL). New OSLDs were chosen arbitrarily and were irradiated with 1 Gy repeatedly. We confirmed the change in the radiation sensitivity after repeated irradiation. The OSLD sensitivity increased up to 3% after irradiating for seven times and decreased continuously after the eighth time. It dropped by approximately 0.35 Gy per irradiation. Finally, after irradiating for 30 times, the OSLD sensitivity decreased by approximately 7%. When the OSLDs were irradiated 10 times with 1 Gy after their irradiation using a high dose of 15 Gy and 30 Gy, their sensitivity decreased by 6% and 12%, respectively, compared to that before high-dose irradiation. The change in the OSLD sensitivity with a high dose could be modeled by an exponential equation. We confirmed the radiation sensitivity variation caused by a high dose, and the irradiation history of dosimeters was considered to reuse OSLDs irradiated with a high dose.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jursinic PA. Characterization of optically stimulated luminescent dosimeters, OSLDs for clinical dosimetric measurements. Med. Phys. 34(12):4594–4604. 2007.
Article2. Bao Qunan, Hrycushko Brian, Dugas Joseph P, Hanger Frederick H and Solberg Timothy D. A technique for pediatric total skin electron irradiation. Radiation Oncology. 7:40. 2012.
Article3. Im In-Chul, Yu Yun-Sik, Lee Jae-Seung: Measurement of skin dose for rectal cancer patient in radiotherapy using optically stimulated luminescence detectors(OSLDs). Journal of radiation protection. 36(2):86–92. 2011.4. Lee Jeong-Ok, Lee Jae-Seung, Jeong Dong-Hyeok: Measurement of tumor dose using Optically stimulated luminescence detectors(OSLDs). Journal of radiation protection. 36(3):160–167. 2011.5. Kim Jong-Eon, Im In-Chul, Min Byung-In: Measurement of the skin dose of patient using the optically stimulated luminescent dosimeter at diagnostic radiography. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association. 11(9):437–442. 2011.6. Jursinic PA. Changes in optically stimulated luminescent dosimeter (OSLD) dosimetric characteristics with accumulated dose. Med. Phys. 37(1):132–140. 2010.
Article7. Mrˇcela I, Bokuli´c T, Izewska J, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence in vivo dosimetry for radiotherapy: physical characterization and clinical measurements in 60Co beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 56(18):6065–6082. 2011.8. Omotayo AA, Cygler JE, and Sawakuchi GO. The effect for different bleaching wavelengths on the sensitivity of Al2O3: C optically stimulated luminescence detectors (OSLDs) exposed to 6MV photon beams. Med. Phys. 39(9):5457–5468. 2012.9. Su Chul Han, Sang Hyoun Choi, Seungwoo Park, et al. Evaluation of dosimetric characteristics of rproducibility, lnearity and dose dependence of optically stimulated luminescence dosimeters in Co-60 gamma-rays. Korean Jouranl of Medical Physics. 25(1):31–36. 2014.10. Lye J, Dunn L, Kenny J, et al. Remote auditing of radio therapy facilities using optically stimulated luminescence dosimeters. Med. Phys. 41(3):032102–1. -10 (. 2014.11. Viamonte A, da Rosa LA, Buckley LA, A Cherpak A, Cygler JE. Radiotherapy dosimetry using a commercial OSL system. Med. Phys. 35(4):1261–1266. 2008.
Article12. Yukihara EG and McKeever SW. Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dosimetry in Medicine, Phys. Med. Biol. 53(20):351–379. 2008.13. Kim DW, Chung WK, Shin DO, et al. Dose response of commercially available optically stimulated luminescent detector, A2O3: C for megavoltage photons and electrons. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 149(2):101–108. 2012.14. Endo A, Katoh T, Kobayashi I, Joshi R, Sur J, and Okano T. Characterization of optically luminescence dosimeters to measure organ dose in diagnostic radiology. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 41(3):211–216. 2012.15. Al-Senan RM, Hatab MR. Characteristics of an OSLD in the diagnostics energy range. Med. Phys. 38(7):4396–4405. 2011.16. IAEA Human health report No.8: Development of procedures for In vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy. 2013.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Dosimetric Characteristics of Reproducibility, Linearity and Dose Dependence of Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dosimeters in Co-60 Gamma-rays
- The Accuracy of the Calculated Dose for a Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device
- Evaluation of Phantom Dose in a Rotating Total Skin Electron Irradiation (RTSEI) Using Monte Carlo Method and Optically Stimulated Luminescent Dosimeter (OSLD)
- In vivo dosimetry and acute toxicity in breast cancer patients undergoing intraoperative radiotherapy as boost
- Radiation hazards to vascular surgeon and scrub nurse in mobile fluoroscopy equipped hybrid vascular room