Korean J Phys Anthropol.
2016 Jun;29(2):47-51. 10.11637/kjpa.2016.29.2.47.
The Tip Level of the Conus Medullaris by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Cadaver Studies in Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea. irhyu@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2328100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.2016.29.2.47
Abstract
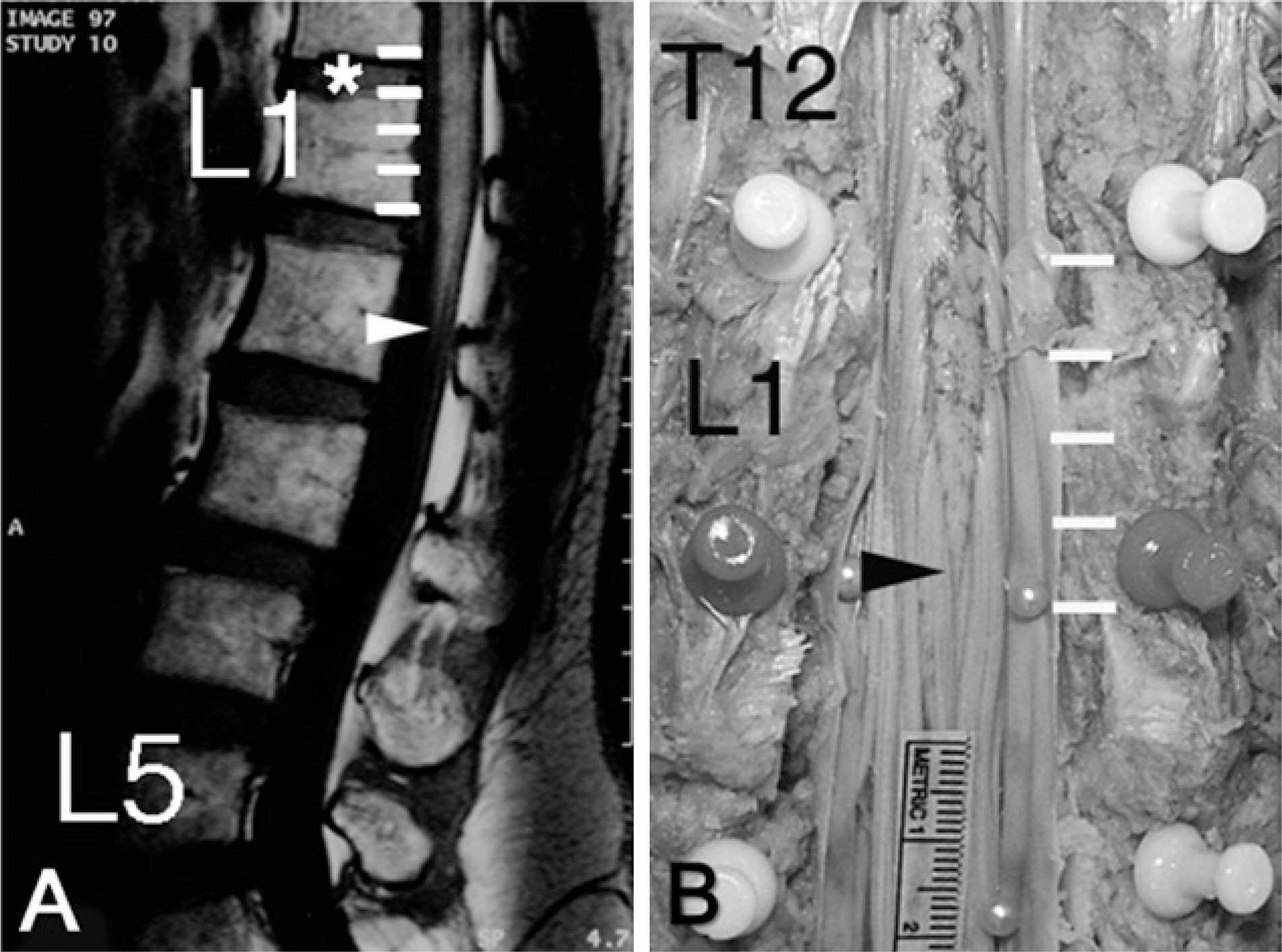
- The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system, and its caudal end is named as the conus medullaris. Many researchers have reported the tip level of the conus medullaris by magnetic resonance imaging studies; others by cadaver dissection. The tip level of magnetic resonance imaging studies seemed to be higher than that of cadaver studies. We evaluated the tip level the conus medullaris with magnetic resonance imaging and cadaver dissection in Korean adult population. MR data were scanned with T1-weighted, mid-sagittal magnetic resonance imaging of 248 living persons (mean age, 42.3±16.0 years; range, 12-85 years) and cadaver data were collected by dissections of 118 cadavers (mean age, 56.0±14.9 years; range, 16-94 years). The mean level of conus tip was found to be at the middle third of 1st lumbar vertebra (range, lower third T12 - lower third L2) from magnetic resonance imaging study and the upper third of 2nd lumbar vertebra (range, lower third T12 - lower third L3) from cadaver dissection study. The tip level of conus medullaris from magnetic resonance imaging study was higher than that from cadaver dissection study (p<0.05).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Morphometric Analysis of Distances between Sacral Hiatus and Conus Medullaris Using Magnetic Resonance Image in Korean Adult
Tai Soo Park, Byeong-Wook Hwang, Sang-Joon Park, Sun-Yong Baek, Sik Yoon
Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2016;29(4):145-154. doi: 10.11637/kjpa.2016.29.4.145.
Reference
-
References
1. Wilson DA, Prince JR. MR imaging determination of the location of the normal conus medullaris throughout childhood. AJR. 1989; 152:1029–32.
Article2. Saifuddin A, Burnett SJ, White J. The variation of position of the conus medullaris in an adult population. A magnetic resonance imaging study. Spine. 1998; 23:1452–6.3. Demiryurek D, Aydingoz U, Aksit MD, Yener N, Geyik PO. MR imaging determination of the normal level of conus medullaris. Clin Imaging. 2002; 26:375–7.4. Kim JT, Bahk JH, Sung J. Influence of age and sex on the position of the conus medullaris and Tuffier's line in adults. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:1359–63.
Article5. McCotter RE. Regarding the length and extent of the human medulla spinalis. Anat Rec. 1916; 26:559–64.
Article6. Needles JH. The caudal level of termination of the spinal cord in American whites and American Negroes. Anat Rec. 1935; 63:417–24.
Article7. Reimann AF, Anson BJ. Vertebral level of termination of the spinal cord with report of a case of sacral cord. Anat Rec. 1944; 83:127–38.
Article8. Williams PL, Warwick R. (eds) Spinal medulla or cord. In: Gray's Anatomy. 36th ed.New York: Churchill Livingstone;1980. pp.p. 864–896.9. Carpenter MB, Sutin J. (eds) Spinal cord: gross anatomy and internal structure. In: Human neuroanatomy. 8th ed.Baltimore: Lippincott William & Wilkins;1983. pp.p. 232–264.10. Boonpirak N, Apinhasmit W. Length and caudal level termination of the spinal cord in Thai adults. Acta Anat (Basel). 1994; 149:74–8.11. Hara K. Changes by age group in the caudal level of termination of the spinal cord in Japanese adults. Acta Anat Nippon. 1987; 62:329–33.12. Barson AJ. The vertebral level of termination of the spinal cord during normal and abnormal development. J Anat. 1970; 106:489–97.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Observations of the Conus Medullaris in a Korean Population
- Normal Variations of the Spinal Cord Termination
- Intramedullary Spinal Cystic Teratoma of the Conus Mudullaris with Caudal Exophytic Growth: Case Report
- The Variation of Position of the Conus Medullaris in Korean Adults - A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study -
- An Intramedullary Neurenteric Cyst in the Conus Medullaris with Recurrent Meningitis