Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Jun;40(3):534-539. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.3.534.
Thoracic Radiculopathy due to Rare Causes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. rehab8520@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2327617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.3.534
Abstract
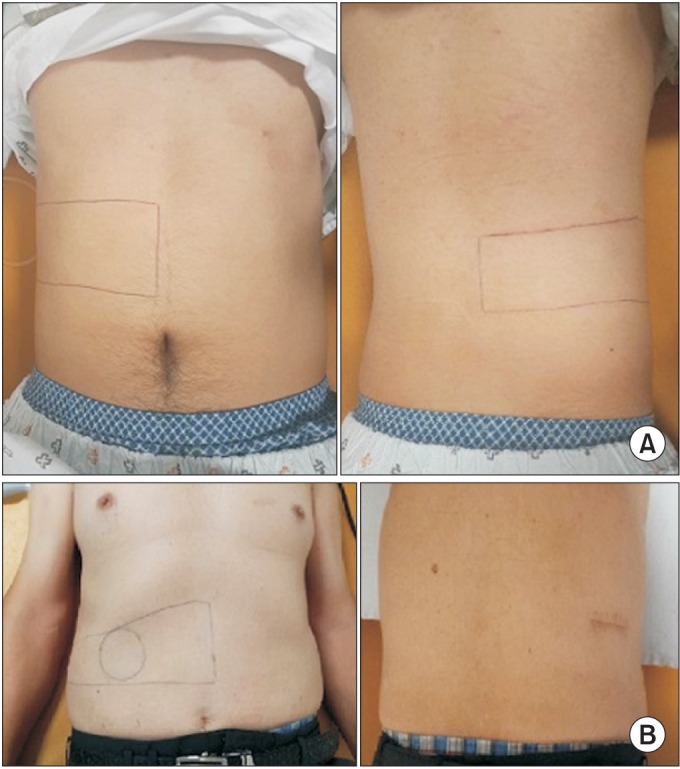
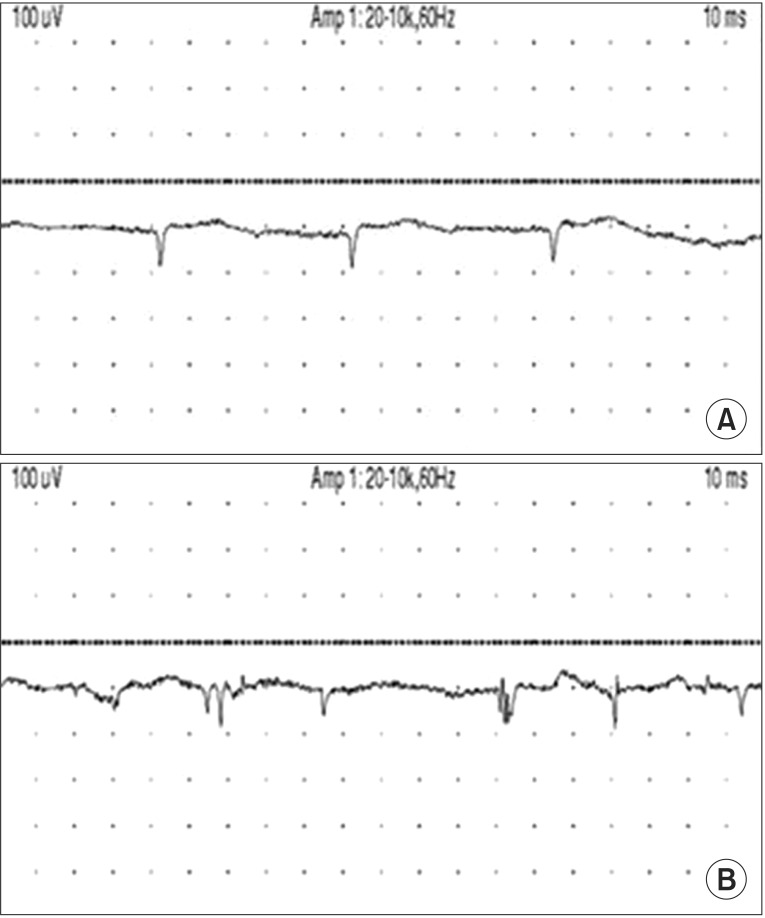
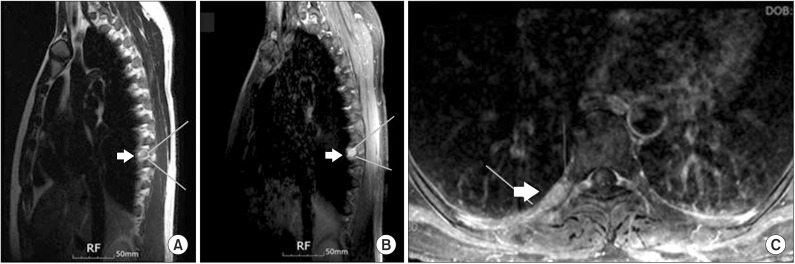
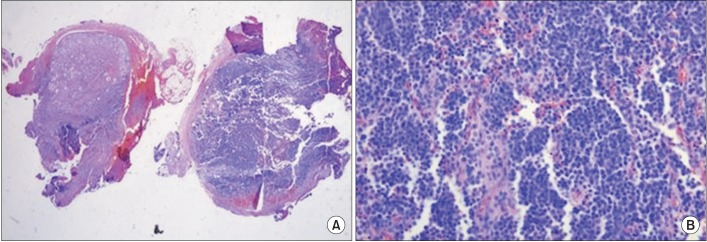
- Thoracic radiculopathy represents an uncommon spinal disorder that is frequently overlooked in the evaluation of thoracic, or abdominal pain syndrome. The clinical representation of this uncommon disorder is often atypical. With many differential diagnoses to consider, it is not surprising that the cause of thoracic radiculopathy is often not discovered for months, or years, after the symptoms arise. We report two rare cases of thoracic radiculopathy; one case was caused by extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma (EES) along the thoracic paraspinal area, and the other by foraminal stenosis, due to a bony spur of the thoracic vertebra. As such, thoracic radiculopathy should be considered in the diagnosis of patients with thoracic and abdominal pain, especially if initial diagnostic studies are inconclusive.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Connor RC, Andary MT, Russo RB, DeLano M. Thoracic radiculopathy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2002; 13:623–644. PMID: 12380552.2. Mammis A, Bonsignore C, Mogilner AY. Thoracic radiculopathy following spinal cord stimulator placement: case series. Neuromodulation. 2013; 16:443–447. PMID: 23682904.
Article3. Mukhopadhyay P, Gairola M, Sharma M, Thulkar S, Julka P, Rath G. Primary spinal epidural extraosseous Ewing's sarcoma: report of five cases and literature review. Australas Radiol. 2001; 45:372–379. PMID: 11531770.
Article4. Yasuda T, Suzuki K, Kanamori M, Hori T, Huang D, Bridge JA, et al. Extraskeletal Ewing's sarcoma of the thoracic epidural space: case report and review of the literature. Oncol Rep. 2011; 26:711–715. PMID: 21617880.
Article5. Su JL, Tan WC, Chao CC, Tsai CM, Wu CH. An initial presentation of flank pain caused by thoracic disc herniation. J Emerg Crit Care Med. 2010; 21:221–226.6. Ozturk C, Tezer M, Sirvanci M, Sarier M, Aydogan M, Hamzaoglu A. Far lateral thoracic disc herniation presenting with flank pain. Spine J. 2006; 6:201–203. PMID: 16517394.
Article7. Iwamoto Y. Diagnosis and treatment of Ewing's sarcoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007; 37:79–89. PMID: 17272319.
Article8. Guyot-Drouot MH, Cotten A, Flipo RM, Lecomte Houcke M, Delcambre B. Contribution of magnetic resonance imaging to the diagnosis of extraskeletal Ewing's sarcoma. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1999; 66:516–519. PMID: 10567983.9. Rustagi T, Badve S, Parekh AN. Sciatica from a foraminal lumbar root schwannoma: case report and review of literature. Case Rep Orthop. 2012; 2012:142143. PMID: 23259107.
Article10. Dumitru D, Zwarts MJ. Lumbosacral plexopathies and proximal mononeuropathies. In : Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts MJ, editors. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;2002. p. 750–751.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diabetic Thoracic Radicalopathy Manifested as Acute Upper Abdominal Pain
- Conservative Treatment of Thoracic Radiculopathy due to Ossification of the Yellow Ligament in a Young Patient: A case report
- Thrombolith of the Extradural Vertebral Venous Plexus as a Cause of Lumbar Radiculopathy: A case Report
- Diabetic Cervical Radiculopathy with Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder
- Idiopathic Thoracic Epidural Lipomatosis with Chest Pain