Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Jun;20(2):132-135. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.132.
Paradoxical Response of Giant Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm after Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea. sungho.hwng@gmail.com
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2327427
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.132
Abstract
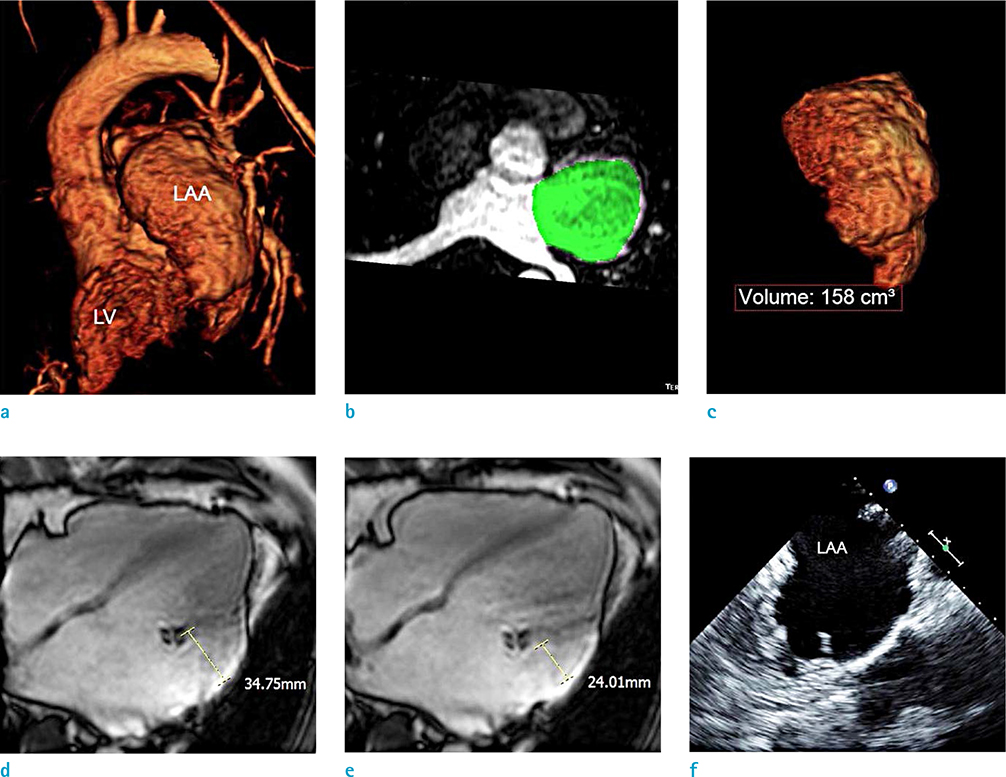
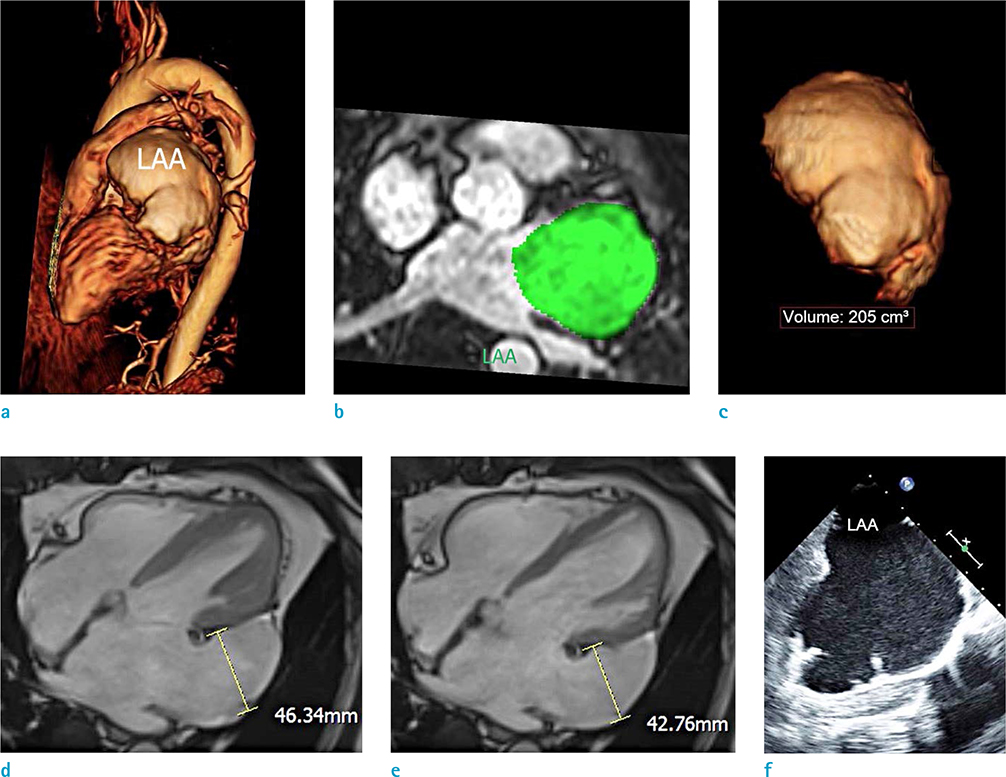
- We report the case of a 43-year-old male with both giant left atrial appendage (LAA) aneurysm and drug-refractory atrial fibrillation (AF). The patient was treated with percutaneous electrical isolation of cardiac arrhythmogenic substrate, and has been free of AF symptom over one year. Although the surgical resection of giant LAA aneurysm is mostly used to prevent systemic thromboembolism, we have performed follow-up of the giant LAA aneurysm using cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) after the successful catheter ablation of refractory AF. At one-year follow-up CMR, the giant LAA aneurysm showed remarkable enlargement as well as decreased contractility. Additionally, one-year follow-up TEE showed spontaneous echo contrast as an indicator of blood stasis in the giant LAA aneurysm. Those findings of giant LAA aneurysm suggest that the risk of thromboembolism may be high despite termination of AF.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Conradi G, Deetjen A, Mollmann S, Hamm CW, Dill T. Symptomatic atrial fibrillation as the first symptom of a giant left atrial appendage aneurysm. Clin Res Cardiol. 2006; 95:614–616.2. Ulucam M, Muderrisoglu H, Sezgin A. Giant left atrial appendage aneurysm: the third ventricle. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2005; 21:225–230.3. Mathur A, Zehr KJ, Sinak LJ, Rea RF. Left atrial appendage aneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005; 79:1392–1393.4. Bhargava M, Di Biase L, Mohanty P, et al. Impact of type of atrial fibrillation and repeat catheter ablation on long-term freedom from atrial fibrillation: results from a multicenter study. Heart Rhythm. 2009; 6:1403–1412.5. Hof IE, Wildbergh TX, van Driel VJ, et al. Atrial fibrillation with a giant left atrial appendage can be successfully treated with pulmonary vein antrum isolation. Neth Heart J. 2012; 20:179–181.6. Bhagirath P, van der Graaf AW, Karim R, et al. Multimodality imaging for patient evaluation and guidance of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation - current status and future perspective. Int J Cardiol. 2014; 175:400–408.7. Hwang SH, Oh YW, Lee DI, Shim J, Park SW, Kim YH. Evaluation of quantification methods for left arial late gadolinium enhancement based on different references in patients with atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015; 31:Suppl 1. 91–101.8. Chang SH, Tsao HM, Wu MH, et al. Morphological changes of the left atrial appendage after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007; 18:47–52.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Underdevelopment of Left Atrial Appendage
- The Treatment of Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm by a Minimally Invasive Approach
- A Case of Successful Ablation of Right-Sided Accessory Pathway during Atrial Fibrillation
- The Influence of Electrical Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation on Left Atrial Appendage Function: A Transesophageal Echocardiography Study
- Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Related to a Congenital Pericardial Defect and Left Atrial Appendage Herniation