J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2006 Dec;13(4):323-326.
Acute Myelopathy due to Ruptured HNP in Cervical OPLL Patient: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Seoul, Korea. hd1404@hanafos.com
Abstract
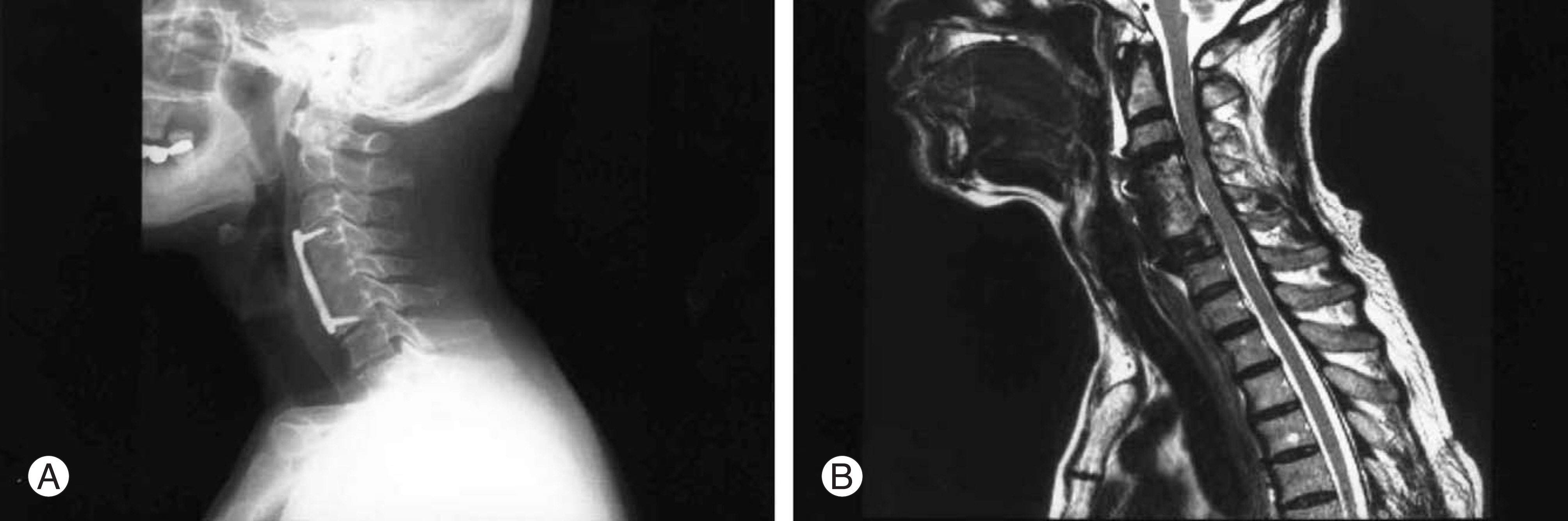
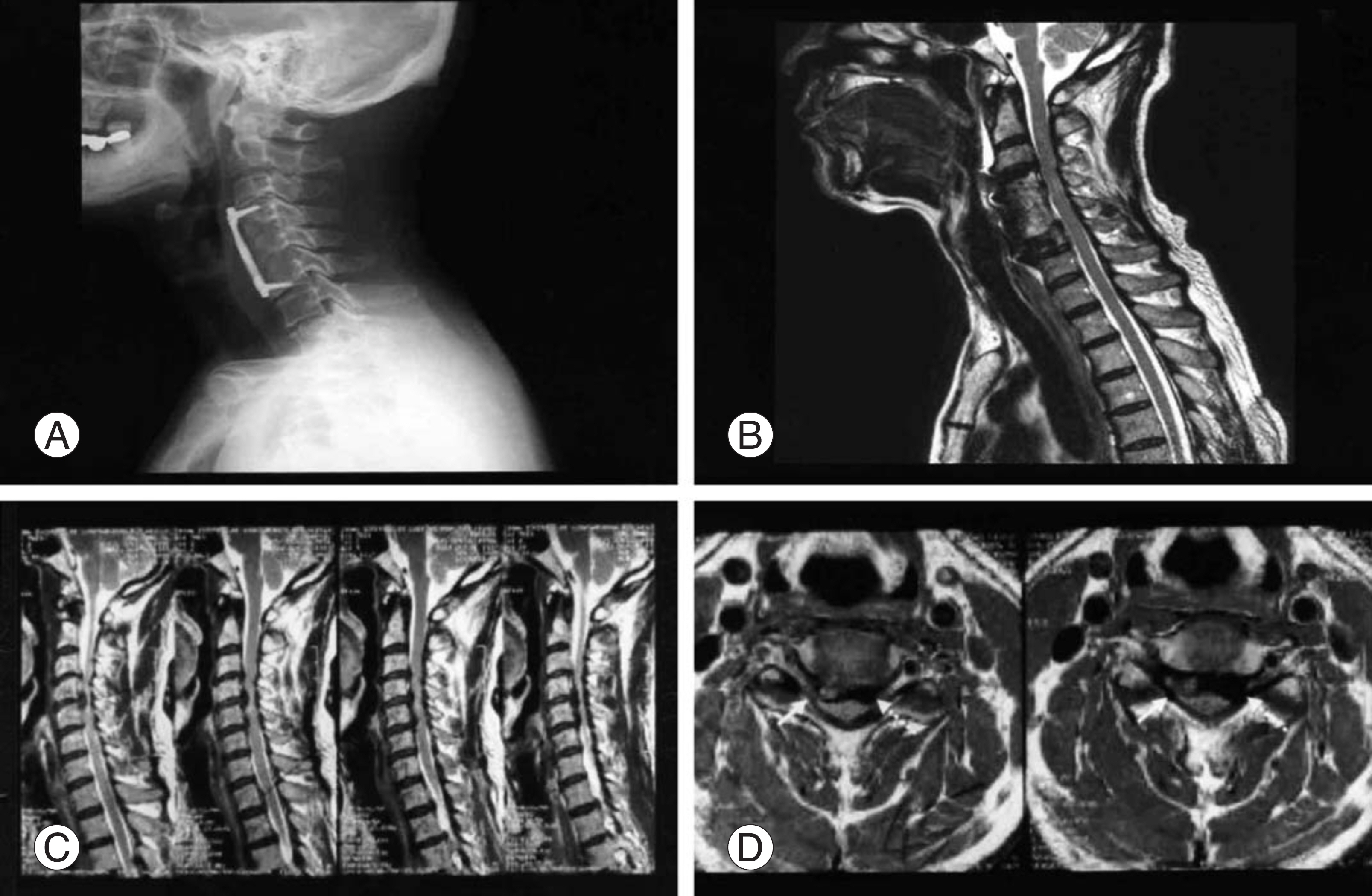
- Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) is an uncommon disorder that may be associated with slowly progressing neurological symptoms. We encountered a case of acute cervical myelopathy due to a ruptured disc in an asymptomatic patient with OPLL, who was surgically managed by the anterior approach and fusion. We report the case with a review of the relevant literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1). Matsunaga S, Kukita M, Hayashi K, Shinkura R, Koriyama C, Sakou T, Komiya S. Pathogenesis of myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:168–172.
Article2). Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Taketomi E, Yamaguchi M, Okano T. The natural course of myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine. Clin Orthop. 1994; 305:168–177.
Article3). Tsuyama N. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Clin Orthop. 1984; 184:71–84.
Article4). Tsuyama N, Imai T, Hotta Y. Histopathological findings of the ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine and their significance. J Jpn Orthop Assoc. 1981; 55:387–397.5). Hanakita J, Suwa H, Namura S, Mizuno M, Ootsuka T, Asahi M. The significance of the cervical soft disc herniation in the ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine. 1994; 19:412–418.
Article6). Belanger TA, Roh JS, Hanks SE, Kand JD, Emery SE, Bolman HH. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Results of anterior cervical decompression and arthrodesis in sixty-one north American patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005; 87A:610–615.7). Harsh GR 4th, Sypert GW, Weinstein PR, Ross DA, Wilson CB. Cervical spine stenosis secondary to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg. 1987; 67:349–357.
Article8). Kojima T, Waga S, Kubo Y, Kanamaru K, Shimosaka S, Shimizu T. Anterior cervical vertebrectomy and interbody fusion for multilevel spondylosis and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Neurosurg. 1989; 24:864–872.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Cervical Myelopathy Due to Ruptured Disc During Leisure Sports Activity in Adjacent Segment
- Anterior Decompression and Fusion for the Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Narrative Review
- A Case Quadriplegia due to Minor Head Trauma Associated with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine
- Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction Found After Cervical Laminoplasty for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
- Spinal Cord Injury Incurred by Neck Massage