J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Dec;8(4):541-547.
Reconstruction of Lumbar Kyphosis with circumferential Fusion by Posterior-Anterior-Posterior Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea Veterans Hospital, Seoul, Korea. sukha-osdr@hanmail.net
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: Six patients with the lumbar kyphosis who underwent the circumferential fusion by posterior-anterior-posterior method were reviewed retrospectively from January 1998 to June 1999.
OBJECTIVES
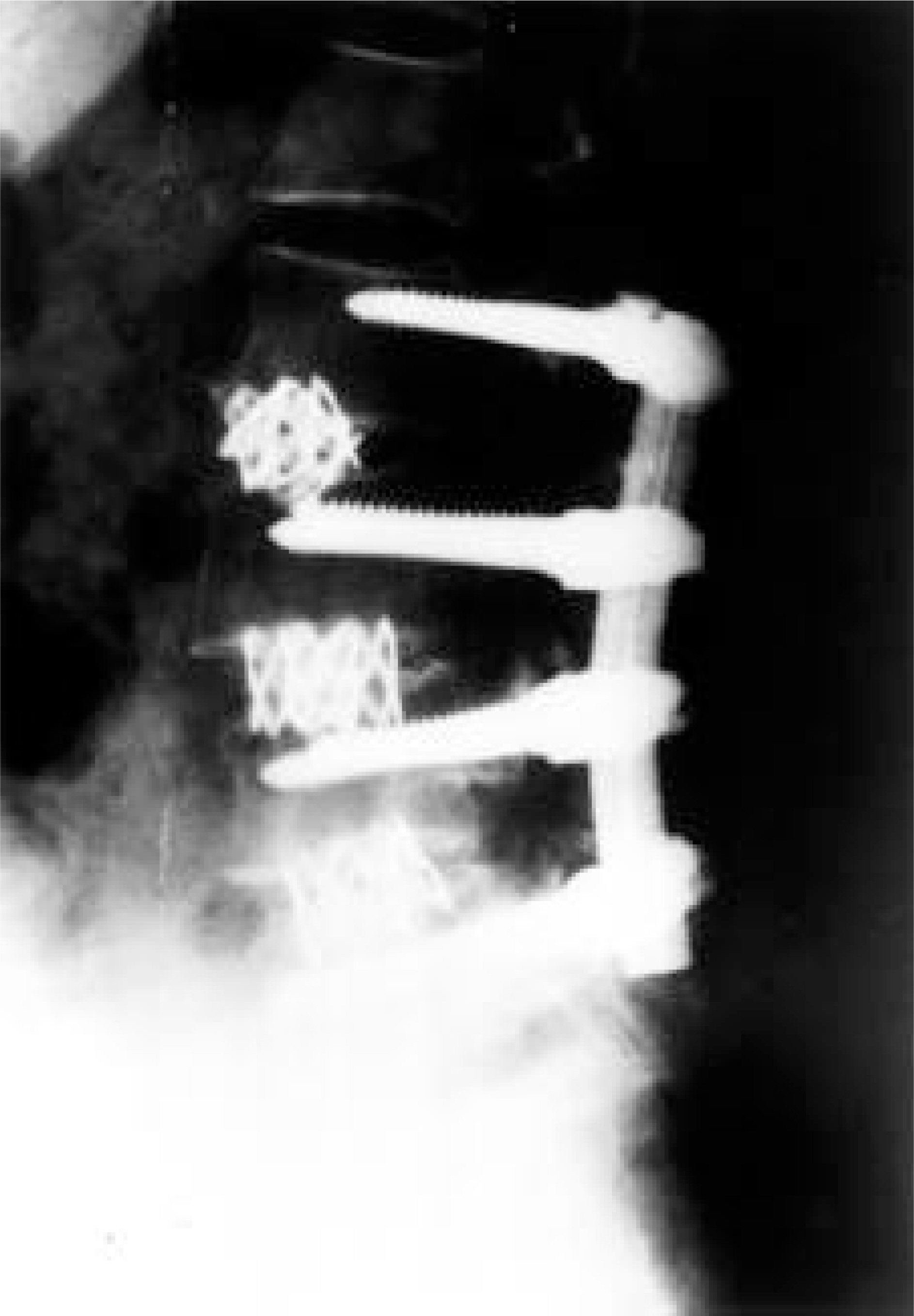
To determine whether patients with lumbar kyphosis can be successfully treated by circumferential fusion by posterior-anterior-posterior method. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: In the lumbar kyphosis, many procedures have been reported to correct the deformity, including multiple osteotomy, transpedicular vertebral resection, posterior interbody fusion, etc. Circumferential fusion by posterior-anterior-posterior method is suggested in this report as a valuable technique for excellent deformity correction and maintenance. MATERIAL AND METHODS: The surgery consists of posterior structural release with decompression followed by anterior structural release with interbody fusion by use of bone graft and posterior fixation. Clinical and radiologic results of the lumbar lordosis, sacral inclination and C7 plumb-line were assessed. RESULT: The mean segments of anterior and posterior fusion were 2.8 and 3.5 respectively. All clinical symptoms of patients had been improved in more than good. The average angle of lumbar lordosis was corrected from kyphosis 2.8degree preoperatively to lordosis 31.2degree postoperatively. At the last follow-up, the average loss of correction was 2.3degree . The average angle of sacral inclination was corrected from 6.7degree to 50.8degree . The distance from supero-posterior corner of S1 to C7 plumb line was reduced from 11.0 cm to 2.75 cm.
CONCLUSION
The circumferential fusion by posterior-anterior-posterior method offer an effective surgical treatment, which produce excellent deformity correction, fusion rate, maintenance of the correction and good clinical outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Berhardt M, Bridwell KH. Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine. 14:717–721. 1989.
Article2). Bradford DS, Tribus CB. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of rigid coronal decompensation. Spine. 22:1590–1599. 1997.
Article3). Farcy JP, Schwab FJ. Management of flatback and related kyphotic decompensation syndromes. Spine. 22:2452–2457. 1997.
Article4). Gelb DE, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH. An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in 100 asymptomatic middle and older aged volunteers. Spine. 20:1351–1358. 1995.
Article5). Gertzbein SD, Betz R, Clemente D, Errico T, Hammerberg K, Robbins S, Shepherd E, Weber A, Kerina M, Albin J, Wolk D, Ensor K. Semirigid instrumentation in the management of lumbar spinal conditions combined with circumferential fusion: A multicenter study. Spine. 21:1918–1925. 1996.6). Jackskon RP, McManus AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex and size: A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine. 19:1611–1618. 1994.7). Kim EH, Cho KN, Kim CH. Surgical treatment of post-traumatic kyphosis. J of Korean Orthop. Assoc. 33:367–374. 1998.8). Kim EH, Woo BC, Cho DY. The change of lumbar lordosis after pedicular screw fixation of degenerative lumbar spine. Journal of Korean Spine Surg. 4:114–121. 1997.9). Kim KT. Kyphosis. Journal of Korean Spine Surg. 6:306–315. 1999.10). Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KWE, Cauchoix J, Mc-Ivor G. Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop. 99:30–50. 1974.11). Kostuik JP, Maurais GR, Richardson WJ, Okajima Y. Combined single stage anterior and posterior osteotomy for correction of iatrogenic lumbar kyphosis. Spine. 13:257–266. 1988.12). Kostuik JP, Matsusaki H. Anterior stabilization, instrumentation, and decompression for post traumatic kyphosis. Spine. 14:379–386. 1989.13). Kim EG. Clinical study of lumbar degenerative kyphosis. Journal of Korean Spine Surg. 4:27–35. 1997.14). Lee CS, Oh WH, Chung SS, Lee SG, Lee JY. Analysis of the sagittal alignment of the normal spines. J of Korean Orthop. Assoc. 34:949–954. 1999.15). Lehmer SM, Keppler L, Biscup RS, Enker P, Miller SD, Steffee D. Posterior transvertebral osteotomy for adult thoracolumbar kyphosis. Spine. 19:2060–2067. 1994.
Article16). Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, Ha KY, Kim SS, Sun DH. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine. 20:1910–1916. 1995.
Article17). Ogilvie JW. Anterior and posterior spinal surgery: sameday, staged anterior first, posterior first, or simultaneous? Instructional Course Lecture. 99-100:1996.18). Shufflebarger HL, Grimm JO, Bui V, Thomson JD. Anterior and posterior spinal fusion, staged versus sameday surgery. Spine. 16:930–933. 1990.
Article19). Simmons EH. Kyphotic deformity of the spine in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop. 128:65–77. 1977.
Article20). Smith-Petersen MN, Larson CB, Aufrane OE. Osteotomy of the spine for correction of flexion deformity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg. 27:1–11. 1945.
Article21). Stagnara P, Du Mauroy JC, Dran G. Reci procal angulation of vertebral bodies in a sagittal plane: Approach to references for the evaluation of kyphosis and lordosis. Spine. 7:335–342. 1982.22). Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Liu Y, Chung ER, Lee CS. Treatment of fixed lumbosacral kyphosis by posterior vertebral column resection. Journal of Korean Spine S urg. 5:307–313. 1998.23). Takemitsu Y, Harada Y, Iwahara T, Miyamoto M, Mitatake Y. Lumbar degenerative kyphosis. clinical, radiological and epidermiological studies. Spine. 13:1317–1326. 1988.24). White III AA, Panjabi MM, Thomas CL. The clinical biomechanics of kyphotic deformity. Clin Orthop. 128:8–17. 1977.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three-column reconstruction through the posterior approach alone for the treatment of a severe lumbar burst fracture: a case report
- Anterior and Posterior Fusion in Spine Tuberculosis
- Circumferential Operations of the Cervical Spine
- Results of Single-Staged Posterior Decompression and Circumferential Fusion Using a Transpedicular Approach to Correct a Kyphotic Deformity due to Thoracolumbar Spinal Tuberculosis
- The Extended Posterior Circumferential Decompression Technique in the Management of Tubercular Spondylitis with and without Paraplegia