J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs.
2014 Dec;23(4):199-207. 10.12934/jkpmhn.2014.23.4.199.
Development of Expert Competency Model for Preventing Adolescent Addictive Behavior and Educational Needs of Psychiatric Mental Health Nurses
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea. jungsy@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2322748
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2014.23.4.199
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted to develop an expert competency model for preventing adolescent addictive behavior and to analyze educational needs of psychiatric mental health nurses in Korea.
METHODS
The process involved competency modeling using to the expert's delphi construction and analyzing validity using to the development of the expert competency scale. Participants were 441 experts and 137 psychiatric mental health nurses in 2 cities.
RESULTS
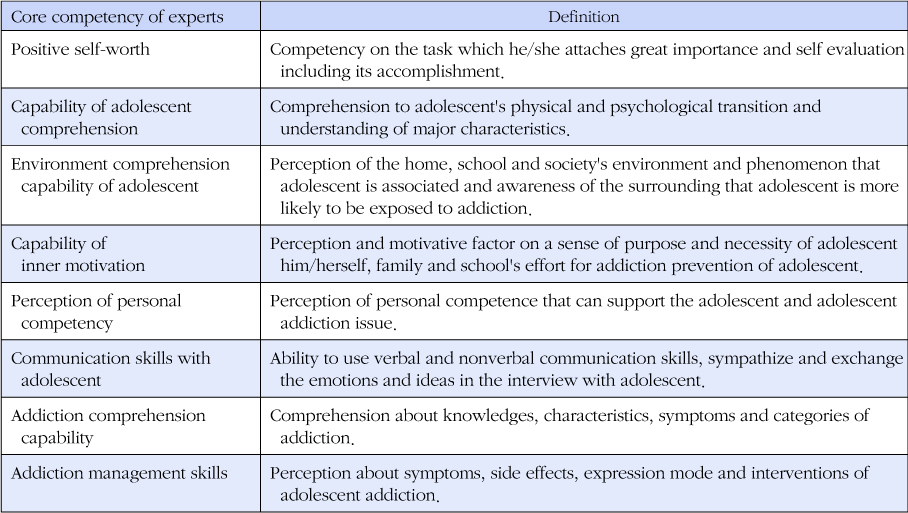
The expert competency model for preventing adolescent addictive behavior included positive self-worth, capability of adolescents comprehension, environment comprehension capability of adolescent, capability of inner motivation, perception of personal competency, communication skills with adolescent, addiction comprehension capability, and addiction management skills. The developed expert competency scale demonstrates good reliability and validity. Psychiatric mental health nurses' highest educational needs from expert competency scale were addiction management skills and communication skills with adolescents.
CONCLUSION
The study findings indicate that the expert competency model for preventing adolescent addictive behavior has good validity and reliability when applied to adolescents. It provides the first step toward developing an education program or guidelines for experts including psychiatric mental health nurses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clark H, Ringwalt CL, Shamblen SR, Hanley SM. Project SUCESS' effect on substance use-related attitudes and behaviors: a randomized controlled trial in alternative high schools. J Drug Educ. 2011; 41(1):17–44. http://dx.doi.org/10.2190/DE.41.1.b.
Article2. Ellickson PL, Tucker JS, Klein DJ, Saner H. Antecedents and outcomes of marijuana use initiation during adolescence. Prev Med. 2004; 39(5):976–984. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.04.013.
Article3. Hyder AA, Juul NH. Games, gambling, and children: applying the precautionary principle for child health. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs. 2008; 21(4):202–204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6171.2008.00155.x.
Article4. Eaton DK, Kann L, Kinchen S, Shanklin S, Ross J, Hawkins J, et al. Youth risk behavior surveillance-United States, 2007. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2008; 57(4):1–131.5. Hardoon KK, Gupta R, Derevensky JL. Psychosocial variables associated with adolescent gambling. Psychol Addict Behav. 2004; 18(2):170–179. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.18.2.170.
Article6. Park HS, Jung SY. Construction of the addiction prevention core competency model for preventing addictive behavior in adolescents. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013; 43(6):714–725. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.714.
Article7. Park HS, Jung SY. A study on the role and efficient integration of school, family, and community for adolescent's addiction prevention. J Ment Sci. 2013; 1:44–58.8. Calhoun JG, Dollett L, Sinioris ME, Wainio JA, Butler PW, Griffith JR, et al. Development of an interprofessional competency model for healthcare leadership. J Healthcare Manag. 2008; 53(6):375–390.
Article9. Campion MA, Fink AA, Ruggeberg BJ, Carr L, Pillips GM, Odman RB. Doing competencies well: best practices in competency modeling. Pers Psychol. 2011; 64:225–262. http://dxdoi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2010.01207.x.
Article10. Spencer LM, Spencer SM. Competence at work. Seoul: PSI Consulting;2005. p. 452.11. Shippmann JS, Ash RA, Batjtista M, Carr L, Eyde L, Hesketh B, et al. The practice of competency modeling. Pers Psychol. 2000; 53:703–740.
Article12. Brannick MT, Levine EL, Morgeson FP. Job and work analysis: methods, research, and application in human resource management. 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: Sage;2012. p. 360.13. Lee YF, Altschuld JW, Hung HL. Practices and challenges in educational program evaluation in the Asia-Pacific region: results of a delphi study. Eval Program Plann. 2008; 31:368–375. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2008.08.003.
Article14. Kim YI. Educational needs analysis of job competencies for elementary invention teachers. J Korean Pract Arts Educ. 2014; 27(1):201–218.15. Park KM, Lee KN. Case research on educational needs of engineering students about program outcomes (PO). J Eng Educ Res. 2011; 14(3):38–44.16. Lee MS, Kwon KI. Need assessment on educational contents of group work supervision according to careers of group workers. Korean J Couns. 2009; 10(2):911–931.17. Bozorgmehr K, Schubert K, Menzel-Severing J, Tinnemann P. Global health education: a cross-sectional study among German medical students to identify needs, deficits and potential benefits (Part 1 of 2: mobility patterns & educational needs and demands). BMC Med Educ. 2010; 10(66):1–20. http://dxdoi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-10-66.18. Lynn MR. Determination and quantification of content validity. Nurs Res. 1986; 35:382–385.
Article19. Lee HS, Kim Y. Korean SPSS 10.0 guide for the beginner. Seoul: Bubmoonsa;2002. p. 420.20. Maultsby CD. In service needs of agricultural science teachers in area I, II, and IV. [master's thesis]. Texas: Tech University;1997. 245.21. Field A. Discovering statistics using SPSS for Windows. London: Sage;2000. p. 512.22. Kadioğlu H, Sisman FN, Ergun A. Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of children's somatization inventory. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2012; 6:9–12. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2012.02.004.
Article23. Habor J, Lobiondo-Wood G, editors. Reliability and validity. Nursing research. 6th ed. Missouri: Mosby Elsevier;2006. p. 399.24. Ryu CS. SPSS 14.0 for windows. 5th ed. Seoul: Elite;2006. p. 529.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Construction of the Addiction Prevention Core Competency Model for Preventing Addictive Behavior in Adolescents
- Development of the Competency Model for Prevention of Adolescent Risk Behavior
- Care Burden for Mental Illness Patients, Attitude toward Mental Illness and Psychiatric Nursing Competency in Non-psychiatric Nurses
- Effects of a Competency-Based Education Program for Inpatient Psychiatric Nurses: A Pre-Post Intervention Study
- Validation of Addictive Personality Scale for Screening Adolescents