World J Mens Health.
2015 Apr;33(1):36-38. 10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.1.36.
Spontaneous Corpus Cavernosum Abscess in a Healthy Man Using Long-Term Androgenic Anabolic Steroids
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Baskent University Zubeyde Hanim Practice and Research Center, Izmir, Turkey. emretuzel@gmail.com
- KMID: 2320738
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.1.36
Abstract
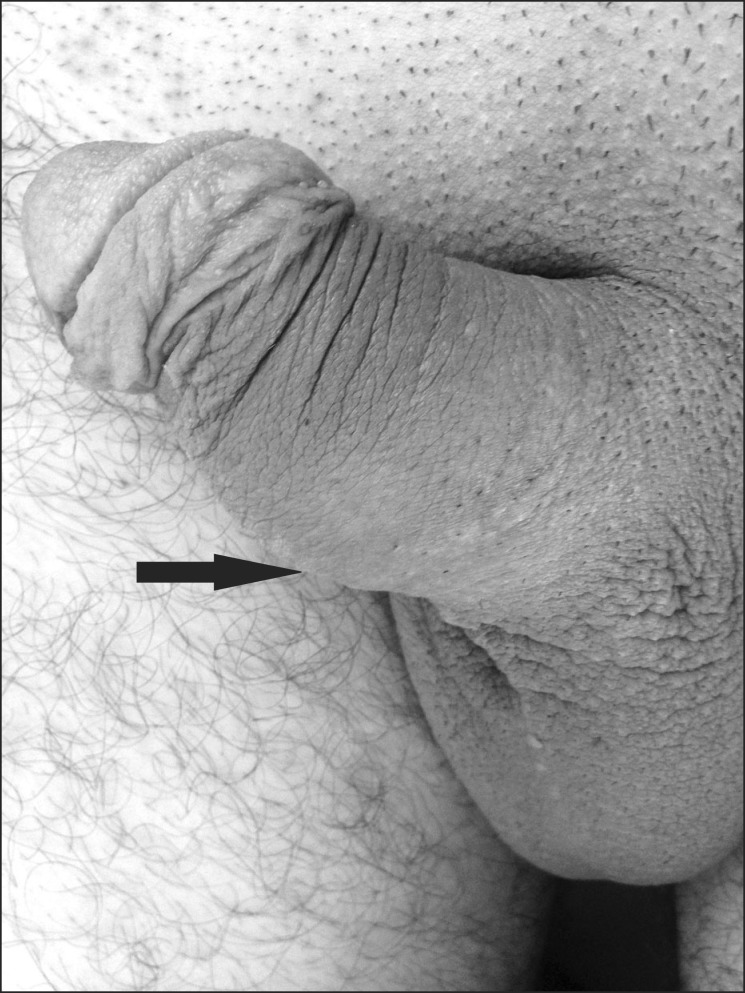
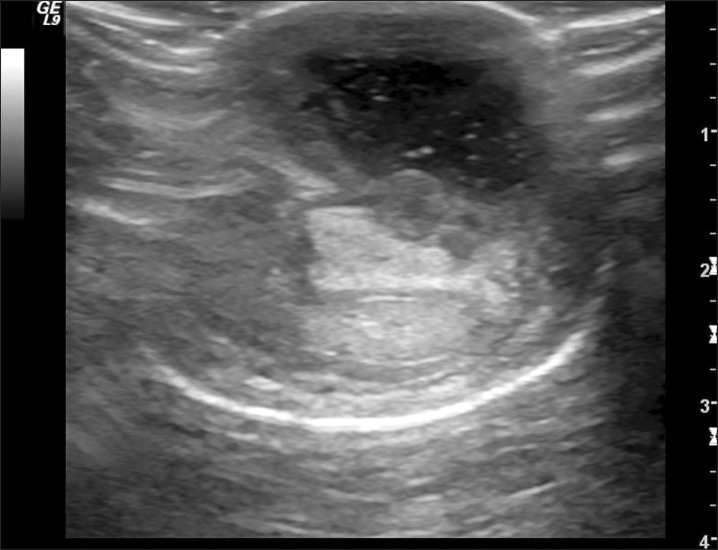
- Abscess formation of the corpus cavernosum is very rare. Here, we report a case of long-term anabolic androgenic steroid (AAS) abuse that is suspected to have facilitated the development of a corpus cavernosum abscess in a healthy bodybuilder. Cultures obtained from the abscess contained Staphylococcus epidermidis, a microorganism that almost exclusively affects immunocompromised patients. Therefore, prompt drainage of pus from cavernosal bodies should be the primary aim of the treatment. This case illustrates the potential danger of AAS suppressing the immune system and causing a serious infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ehara H, Kojima K, Hagiwara N, Phuoc NB, Deguchi T. Abscess of the corpus cavernosum. Int J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:553–554. PMID: 17398131.
Article2. Song W, Ko KJ, Shin SJ, Ryu DS. Penile abscess secondary to neglected penile fracture after intracavernosal vasoactive drug injection. World J Mens Health. 2012; 30:189–191. PMID: 23596611.
Article3. Köksal T, Kadioğlu A, Tefekli A, Usta M, Beşişik A, Erol B. Spontaneous bacterial abscess of bilateral cavernosal bodies. BJU Int. 1999; 84:1107–1108. PMID: 10571649.
Article4. Dugdale CM, Tompkins AJ, Reece RM, Gardner AF. Cavernosal abscess due to Streptococcus anginosus: a case report and comprehensive review of the literature. Curr Urol. 2013; 7:51–56. PMID: 24917758.5. Pope HG Jr, Wood RI, Rogol A, Nyberg F, Bowers L, Bhasin S. Adverse health consequences of performance-enhancing drugs: an Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr Rev. 2014; 35:341–375. PMID: 24423981.
Article6. Otto M. Staphylococcus epidermidis: the accidental pathogen. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009; 7:555–567. PMID: 19609257.7. Marshall-Gradisnik S, Green R, Brenu EW, Weatherby RP. Anabolic androgenic steroids effects on the immune system. Cent Eur J Biol. 2009; 4:19–33.8. Calabrese LH, Kleiner SM, Barna BP, Skibinski CI, Kirkendall DT, Lahita RG, et al. The effects of anabolic steroids and strength training on the human immune response. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1989; 21:386–392. PMID: 2674590.
Article9. van Breda E, Keizer HA, Kuipers H, Wolffenbuttel BH. Androgenic anabolic steroid use and severe hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction: a case study. Int J Sports Med. 2003; 24:195–196. PMID: 12740738.
Article10. Park SM, Hwang CH, Heo C, Woo JH, Lee TH, Hong SJ, et al. Abscess of the penile corpus cavernosum. Korean J Urol. 2005; 46:1224–1227.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acne Conglobata Induced by Anabolic Androgenic Steroids
- Severe Persistent Jaundice after the Abuse of an Anabolic Androgenic Steroid Analogue
- Pharmacologic Effect of Phentolamine on Norepinephrine Induced Contraction of Corpus Cavernosum
- A Fibrotic Nodule in the Corpus Cavernosum
- Hepatocellular carcinoma in body builders; an emerging rare but serious complication of androgenic anabolic steroid use