Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Jun;74(6):274-279.
A Case of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis with Endobronchial Nodular Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. yshpul@wku.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
Abstract
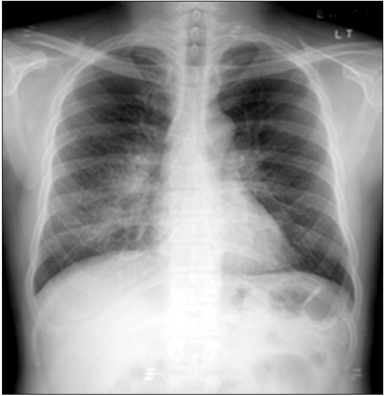
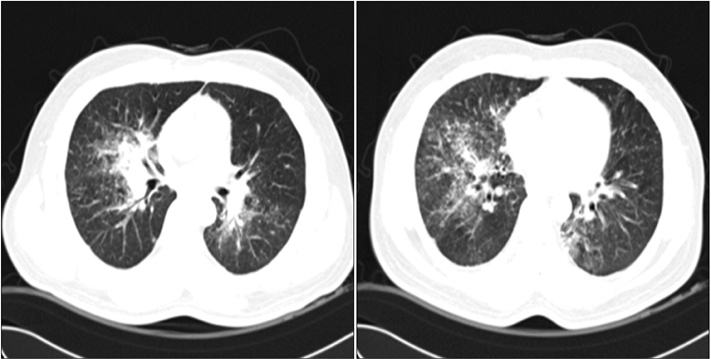
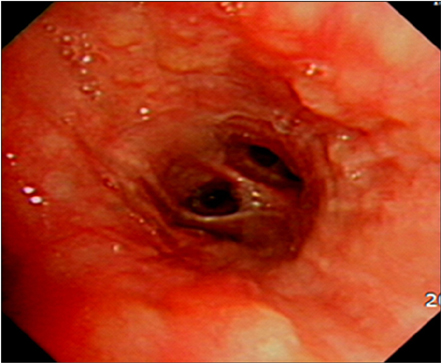
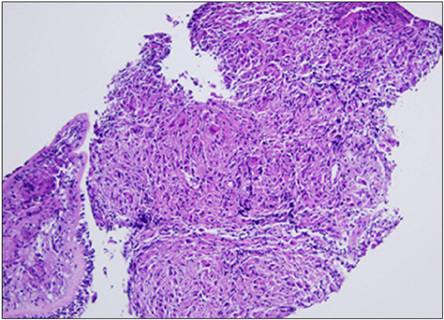
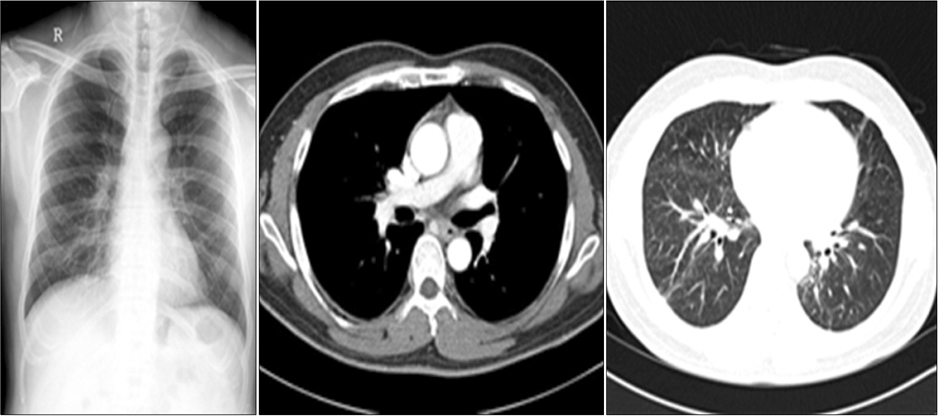
- Sarcoidosis is a multisystemic disorder of unknown cause that is characterized pathologically by noncaseating granulomas. Diagnosis is based on the exclusion of other infectious, interstitial, and neoplastic diseases and on the typical pathology. Although the lungs and mediastinal lymph nodes are almost involved, endobronchial nodular lesions of sarcoidosis with lung involvements are rare. We report a case of sarcoidosis with lung involvements and endobronchial nodules as confirmed by bronchial biopsy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2153–2165.2. Kim DS, Ahn JJ. Sacoidosis in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2000; 49:274–280.3. Newman LS, Rose CS, Maier LA. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1224–1234.4. Choi HH, Hong YA, Choi JK, Kim JS, Kim SJ, Kim SC, et al. A case of sarcoidosis that was initially misdiagnosed as nontuberculous mycobacteria pulmonary disease. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009; 66:309–313.5. Hanno R, Callen JP. Sarcoidosis: a disorder with prominent cutaneous features and their interrelationship with systemic disease. Med Clin North Am. 1980; 64:847–866.6. Sharma OP. Sarcoidosis: a worldwide phenomenon. Sarcoidosis. 1984; 1:11–15.7. Nam JE, Ryu YH, Park JG, Choe KO, Im JG, Lee KS, et al. High resolution CT findings of pseudoalveolar sarcoidosis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2002; 47:191–196.8. Tay HL, Vaughan-Jones R, Qureshi SS. Ethmoidal sarcoidosis. J Laryngol Otol. 1994; 108:682–684.9. Nishimura K, Itoh H, Kitaichi M, Nagai S, Izumi T. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: correlation of CT and histopathologic findings. Radiology. 1993; 189:105–109.10. Lee SJ, Kim JY, Lee JC, Kim GS, Yoo CG, Kim YW, et al. A case of sarcoidosis involving bone marrow, skin, uvea, joints, liver. Korean J Med. 1997; 53:580–585.11. Chung SG, Park CH. Axillary lymph node sarcoidosis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2001; 61:220–223.12. Lee BH, Kim JM, Kim DW, Kim JH, Bang KT, Lee KY, et al. A case of sarcoidosis with cavitation. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005; 59:546–550.