Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Jan;72(1):68-71.
Treatment of Massive Hemoptysis Occurred from Destroyed Lung: Prevention of Contralateral Aspiration Using Endobronchial Blocker Followed by Pneumonectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea. kmctskdh@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
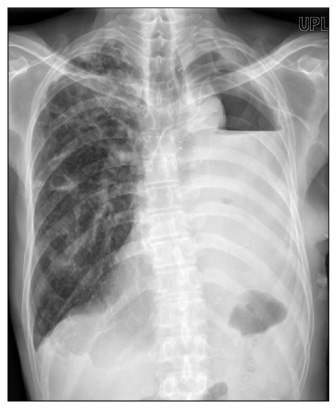
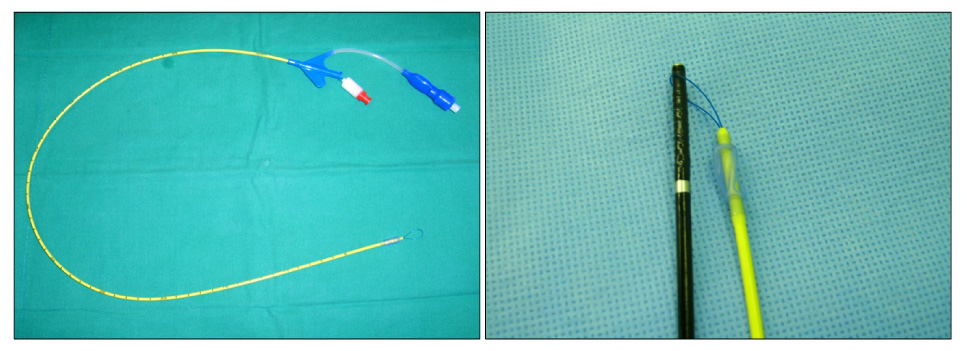
- Untreated massive hemoptysis, especially in patients with tuberculous-destroyed lung, is a serious complication resulting in considerable morbidity and mortality. We report a case of a patient who had active tuberculosis and a destroyed left lung with massive bleeding. He was transferred to our clinic with intubation of a right-sided Robertshaw double lumen tube and right upper lobe collapse likely due to tube malposition that was presented on chest X-ray. Because hemoptysis had persisted after bronchial arterial embolizaton, we replaced the double lumen tube with a conventional endotracheal tube and inserted an endobronchial blocker into the left main bronchus through an endotracheal tube guided by bronchoscopy to prevent aspiration of blood into the right lung. Left pneumonectomy was performed and hemotpysis was ceased. We suggest that the use of an endobronchial blocker followed by surgery may be a safe and effective modality of treatment in patients with persistent bleeding after bronchial arterial embolization.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee BH, Kim YS, Lee KD, Lee JH, Kim SH. Health-related quality of life measurement with St. George's respiratory questionnaire in post-tuberculous destroyed lung. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008. 65:183–190.2. Ryu YJ, Lee JH, Chun EM, Chang JH, Shim SS. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with tuberculous destroyed lung. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011. 15:246–250.3. Jean-Baptiste E. Clinical assessment and management of massive hemoptysis. Crit Care Med. 2000. 28:1642–1647.4. Sakr L, Dutau H. Massive hemoptysis: an update on the role of bronchoscopy in diagnosis and management. Respiration. 2010. 80:38–58.5. Corder R. Hemoptysis. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2003. 21:421–435.6. Hiebert CA. Balloon catheter control of life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest. 1974. 66:308–309.7. Samara KD, Tsetis D, Antoniou KM, Protopapadakis C, Maltezakis G, Siafakas NM. Bronchial artery embolization for management of massive cryptogenic hemoptysis: a case series. J Med Case Reports. 2011. 5:58.8. Shivaram U, Finch P, Nowak P. Plastic endobronchial tubes in the management of life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest. 1987. 92:1108–1110.9. Campos JH, Kernstine KH. A comparison of a left-sided Broncho-Cath with the torque control blocker univent and the wire-guided blocker. Anesth Analg. 2003. 96:283–289.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Aspiration of Blood from the Left Lung to the Right Lung and Hypoxemia during One-lung Ventilation Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube
- One - Lung Anesthesia Using Unient Tube - 2 Cases Report
- Double-lumen Endotracheal Tube in the Management of Massive hemoptysis
- Clinical Evaluation of Risk Factors Affection Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality in the Surgical Treatment of Tuberculous Destroyed Lung
- Clinical Results of Pulmonary Resection for Hemoptysis of Inflammatory Lung Disease