Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 Dec;67(6):545-550.
The Usefulness of Endobronchial Ultrasonogram for Peripheral Lung Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. oaks70@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
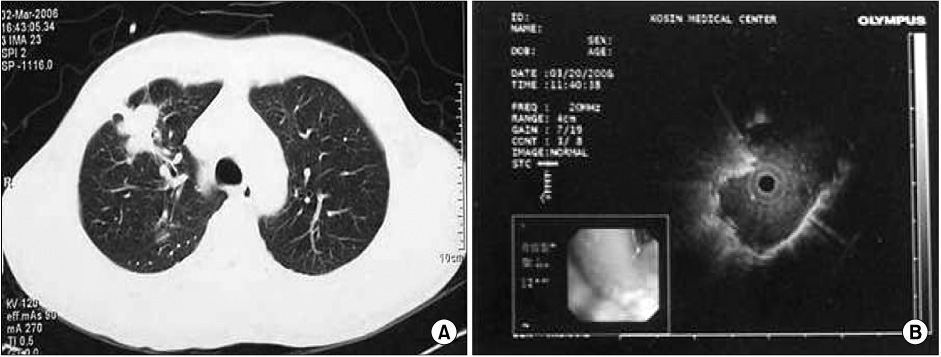
Endobronchial ultrasonogram (EBUS) has increased the diagnostic yield of a bronchoscopic biopsy of peripheral pulmonary lesions (PPL). This study evaluated the diagnostic yield of EBUS-guided transbronchial biopsy (TBB) and the visibility of EBUS PPL. METHODS: Between August 2007 and November 2008, 50 patients (32 men and 18 women, median age, 61.1+/-10 yrs; range, 16 to 80 yrs) whose PPL lesions could not be detected with flexible bronchoscopy were enrolled in this study. Among the 50 patients, 40 cases were malignant lesions (adenocarcinoma 25, squamous cell carcinoma 10, small cell carcinoma 5) and 10 cases were benign lesions (tuberculoma 7, fungal ball 1, other inflammation 2). RESULTS: The mean diameter of the target lesion was 35.4+/-4.3 mm. Of the 50 patients examined, the overall diagnostic yield by EBUS-TBLB was 46.0% (23/50). The visualization yield of EBUS was 66.0% (33/50). A definitive diagnosis of PPL localized by EBUS was established using EBUS-TBLB in 69.6% (23/33) of cases. The diagnostic yields from washing cytology and brushing cytology from a bronchus identified by EBUS were 27.0% and 45.4% respectively. The diagnostic yields reached 78.7% when the three tests (washing cytology, brushing cytology and EBUS-TBLB) were combined. The visualization yield of EBUS in lesions <20 mm was significantly lower than that in lesions > or =20 mm (p=0.04). The presence of a bronchus leading to a lesion (open bronchus sign) on the chest CT scan was associated with a high visualization yield on EBUS (p=0.001). There were no significant complications associated with EBUS-TBLB. CONCLUSION: EBUS-TBLB is a safe and effective method for diagnosing PPL. The lesion size and open bronchus signs are significant factors for predicting the visualization of EBUS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Laspas F, Roussakis A, Efthimiadou R, Papaioannou D, Papadopoulos S, Andreou J. Percutaneous CT-guided fine-needle aspiration of pulmonary lesions: results and complications in 409 patients. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2008. 52:458–462.2. Yasufuku K, Nakajima T, Fujiwara T, Chiyo M, Iyoda A, Yoshida S, et al. Role of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the management of lung cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008. 56:268–276.3. Ømark Petersen H, Eckardt J, Hakami A, Olsen KE, Jørgensen OD. The value of mediastinal staging with endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in patients with lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009. 36:465–468.4. Gomez M, Silvestri GA. Endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009. 6:180–186.5. Kurimoto N, Miyazawa T, Okimasa S, Maeda A, Oiwa H, Miyazu Y, et al. Endobronchial ultrasonography using a guide sheath increases the ability to diagnose peripheral pulmonary lesions endoscopically. Chest. 2004. 126:959–965.6. Asano F, Matsuno Y, Tsuzuku A, Anzai M, Shinagawa N, Yamazaki K, et al. Diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions using a bronchoscope insertion guidance system combined with endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath. Lung Cancer. 2008. 60:366–373.7. Asahina H, Yamazaki K, Onodera Y, Kikuchi E, Shinagawa N, Asano F, et al. Transbronchial biopsy using endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath and virtual bronchoscopic navigation. Chest. 2005. 128:1761–1765.8. Shinagawa N, Yamazaki K, Onodera Y, Asano F, Ishida T, Moriya H, et al. Virtual bronchoscopic navigation system shortens the examination time: feasibility study of virtual bronchoscopic navigation system. Lung Cancer. 2007. 56:201–206.9. Hurter T, Hanrath P. Endobronchial sonography in the diagnosis of pulmonary and mediastinal tumors. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1990. 115:1899–1905.10. Herth FJ, Ernst A, Becker HD. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial lung biopsy in solitary pulmonary nodules and peripheral lesions. Eur Respir J. 2002. 20:972–974.11. Kikuchi E, Yamazaki K, Sukoh N, Kikuchi J, Asahina H, Imura M, et al. Endobronchial ultrasonography with guide-sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions. Eur Respir J. 2004. 24:533–537.12. Paone G, Nicastri E, Lucantoni G, Dello Iacono R, Battistoni P, D'Angeli AL, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-driven biopsy in the diagnosis of peripheral lung lesions. Chest. 2005. 128:3551–3557.13. Yamada N, Yamazaki K, Kurimoto N, Asahina H, Kikuchi E, Shinagawa N, et al. Factors related to diagnostic yield of transbronchial biopsy using endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath in small peripheral pulmonary lesions. Chest. 2007. 132:603–608.14. Yoshikawa M, Sukoh N, Yamazaki K, Kanazawa K, Fukumoto S, Harada M, et al. Diagnostic value of endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions without X-ray fluoroscopy. Chest. 2007. 131:1788–1793.15. Shinagawa N, Yamazaki K, Onodera Y, Asahina H, Kikuchi E, Asano F, et al. Factors related to diagnostic sensitivity using an ultrathin bronchoscope under CT guidance. Chest. 2007. 131:549–553.16. Fielding DI, Robinson PJ, Kurimoto N. Biopsy site selection for endobronchial ultrasound guide-sheath transbronchial biopsy of peripheral lung lesions. Intern Med J. 2008. 38:77–84.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endobronchial IVletastasis of Parosteal Osteosarcoma: A Case Report
- A Case of Endobronchial Fibroepithelial Polyp
- Photodynamic Therapy for Endobronchial Obstruction due to Recurrent Lung Cancer : 2 Cases Report
- Endobronchial actinomycosis simulating endobronchial tuberculosis: a case report
- A Case of Endobronchial Lipoma causing left lung collapse