J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Jul;57(7):1050-1055. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.7.1050.
Correlation among Myopic Correction, Axial Length and Aberration after Orthokeratology Lens Treatment in Myopic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. jiel75@hanmail.net
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2317564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.7.1050
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the correlation among the amount of myopic correction, axial length elongation, and higher order aberrations after treatment with orthokeratology lenses in myopic patients.
METHODS
Eighteen patients (36 eyes) treated with orthokeratology lenses for more than 12 months were recruited for this study. Visual acuity, spherical equivalent, axial length, and higher order aberrations were measured at baseline and 1, 6, and 12 months after wearing lenses. Correlations among them were analyzed.
RESULTS
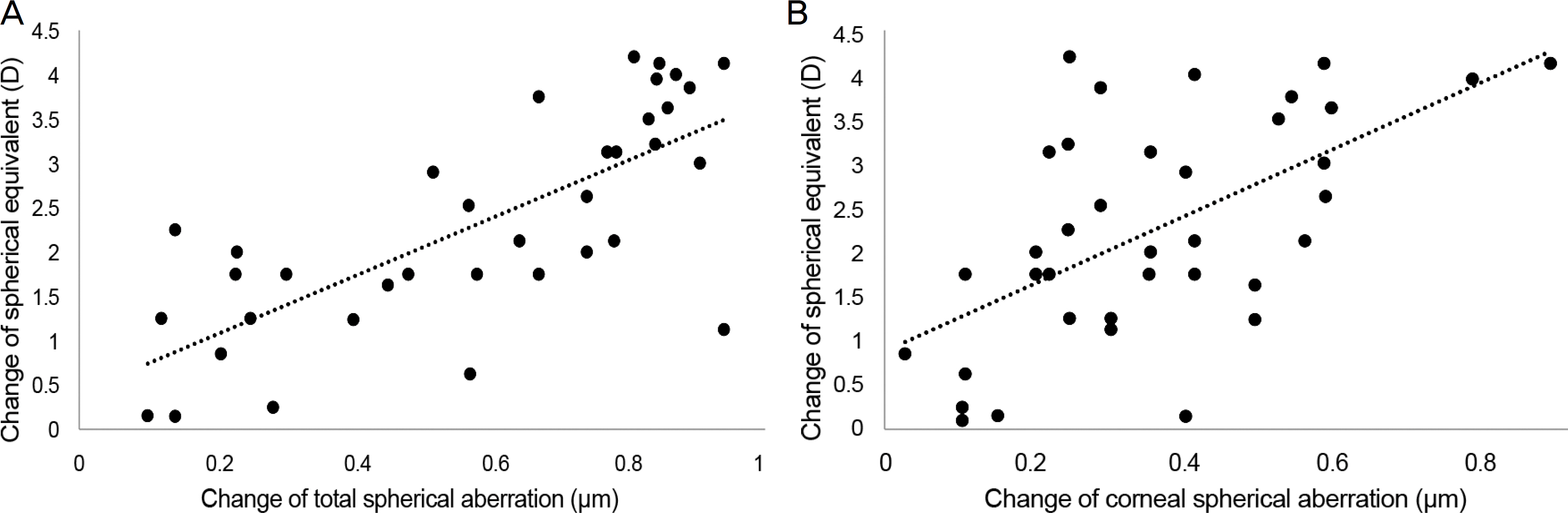
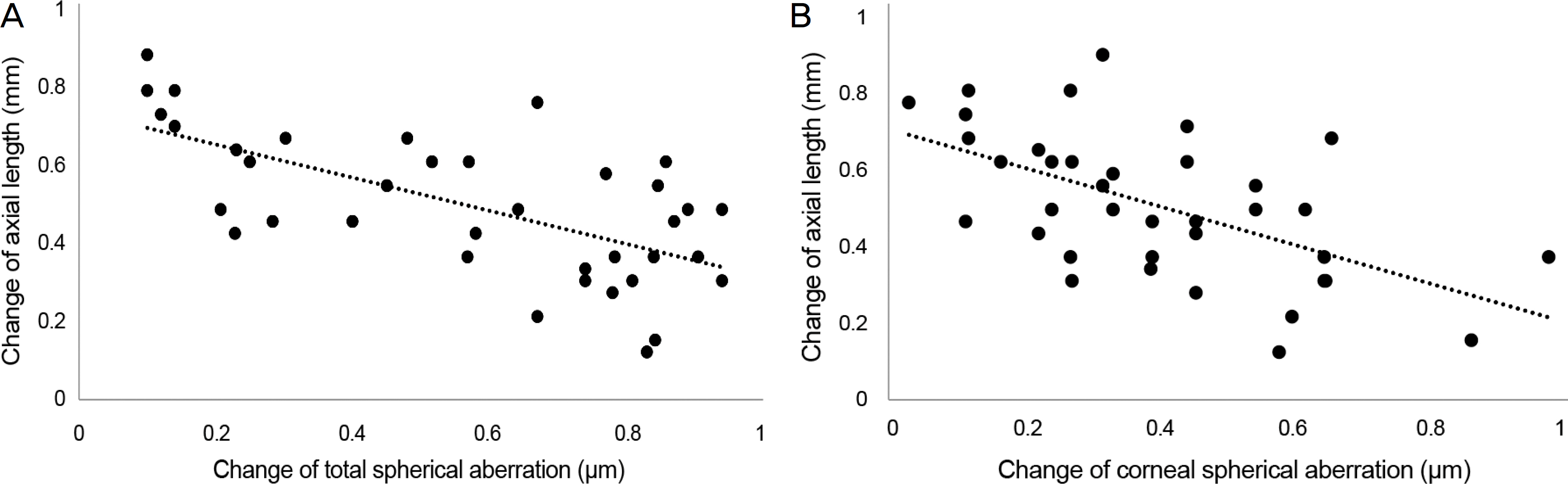
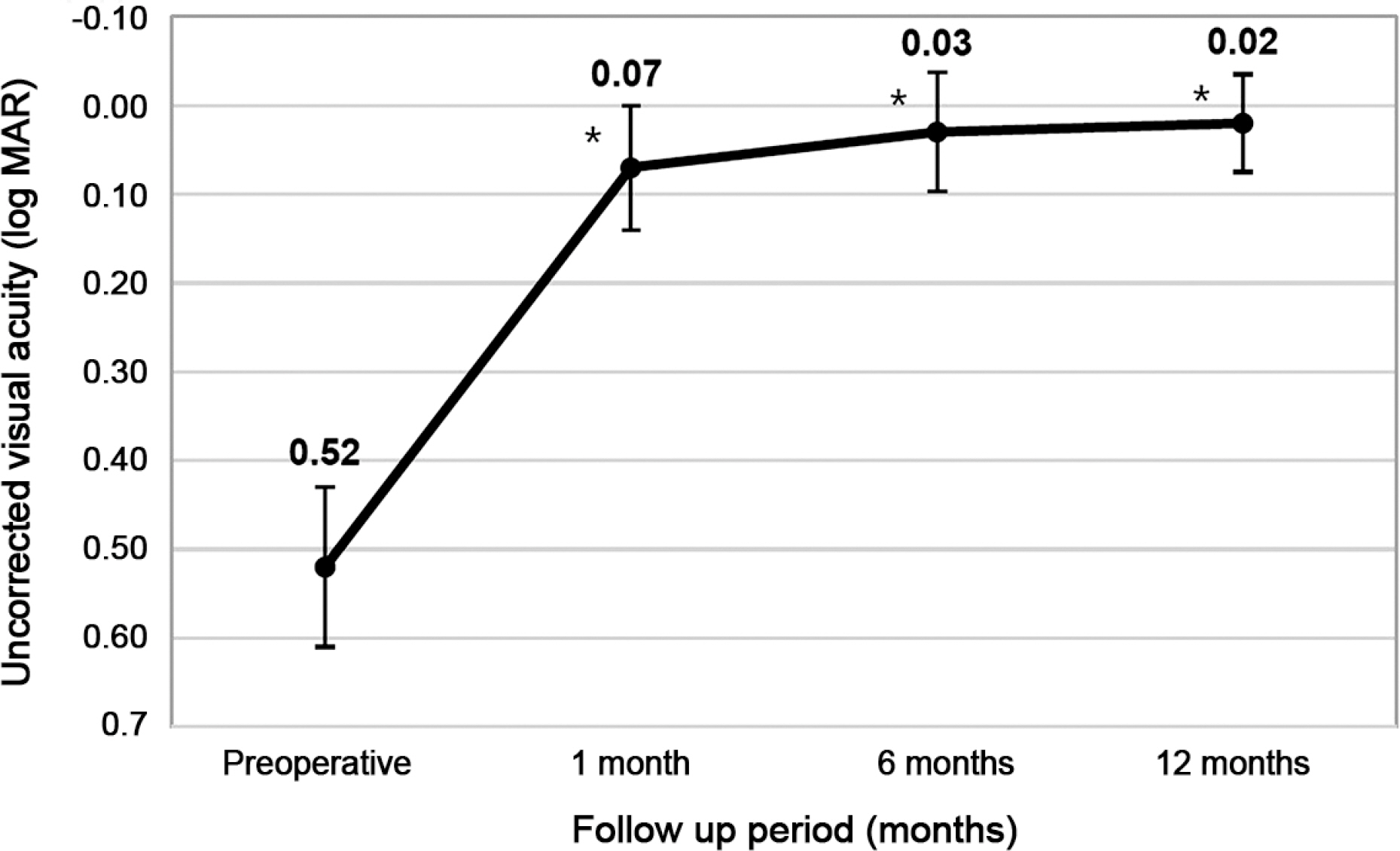
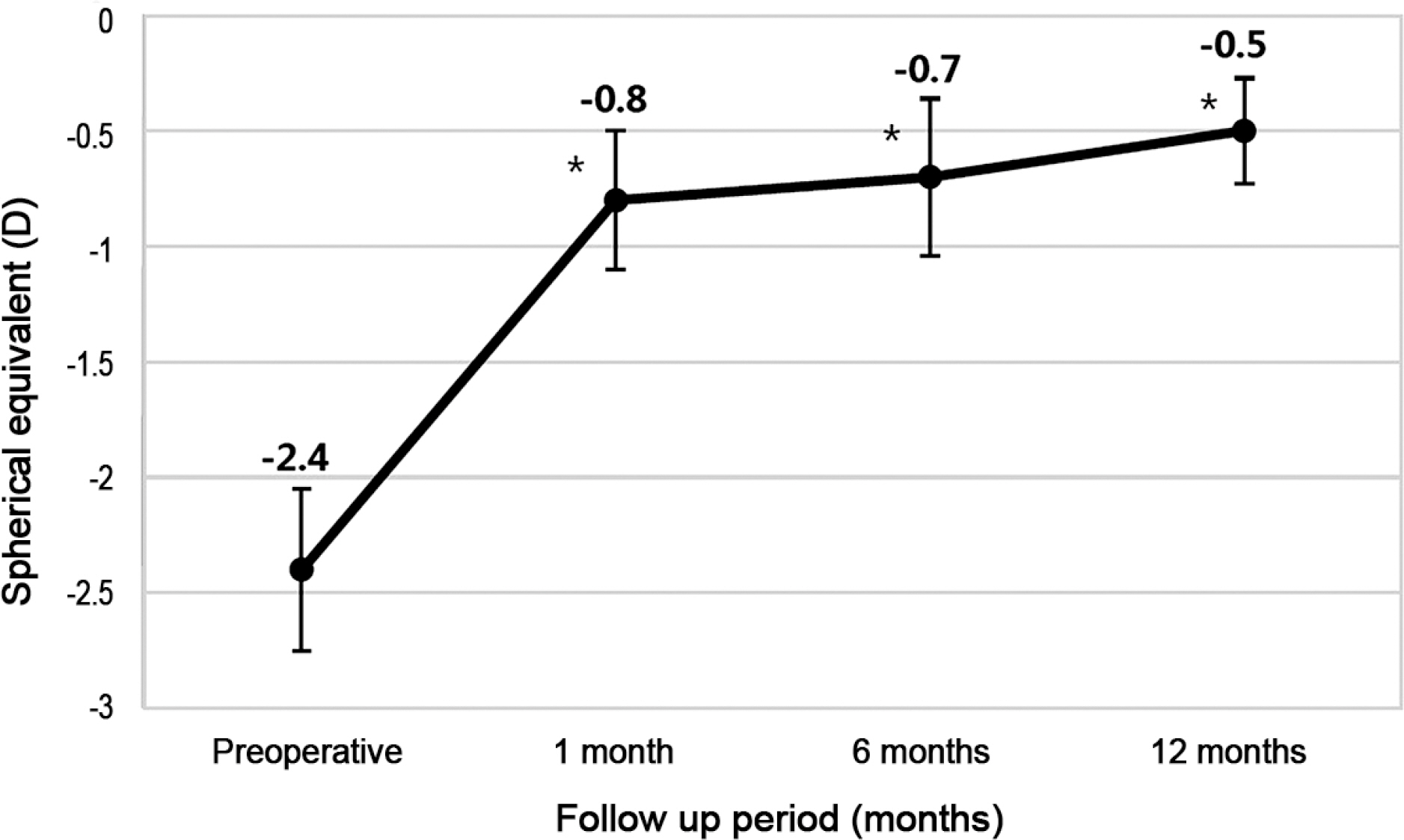
Total higher order, spherical, vertical and horizontal coma aberrations were significantly increased from 0.85 ± 1.47, −0.22 ± 0.40, 0.40 ± 0.47, 0.22 ± 0.31 to 1.11 ± 0.72, 0.10 ± 0.38, 0.79 ± 0.63, 0.66 ± 1.29 after 1 month repectively (p < 0.05), but root mean square (RMS) total and trefoil aberrations were not (p > 0.05), remaining up to 12 months.Total and corneal spherical aberrations were positively correlated to the amount of myopic correction (p = 0.001 and p = 0.028, repectively) and negatively to the amount of axial length elongation (p = 0.036 and p = 0.079, repectively). Uncorrected visual acuity and spherical equivalent were significantly improved from 0.52 ± 0.08 and −2.41 ± 0.36 to 0.07 ± 0.07 and −0.84 ± 0.32 after 1 month respectively. This improvement was maintained up to 12 months (p = 0.002 and p = 0.001, respectively). Axial length was continuously increased from 24.31 ± 0.53 mm to 24.91 ± 0.60 mm after 12 months, but showed no significant changes (p = 0.721).
CONCLUSIONS
Although orthokeratology lenses were effective for the correction of myopia, they increased higher order aberrations depending on the amount of myopic correction. Physicians should consider higher order aberrations. Further studies regarding the relationship between axial length elongation and higher order aberrations to retard myopic progression should be conducted.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cho P, Cheung SW. Retardation of myopia in Orthokeratology (ROMIO) study: a 2-year randomized clinical trial. Invest abdominal Vis Sci. 2012; 53:7077–85.
Article2. Alharbi A, Swarbrick HA. The effects of overnight abdominal lens wear on corneal thickness. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:2518–23.3. Shin DB, Yang KM, Lee SB, et al. Effect of reverse geometry lens on correction of moderate-degree myopia and cornea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1748–56.4. Yun YM, Kim MK, Lee JL. Change of corneal parameters after abdominal reverse geometry lens in moderate degree myopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1478–85.5. Mountford J. An analysis of the changes in corneal shape and abdominal error induced by accelerated orthokeratology. Int Contact Lens Clin. 1997; 24:128–44.6. Cheung SW, Cho P, Fan D. Asymmetrical increase in axial length in the two eyes of a monocular orthokeratology patient. Optom Vis Sci. 2004; 81:653–6.
Article7. Cho P, Cheung SW, Edwards M. The longitudinal orthokeratology research in children (LORIC) in Hong Kong: a pilot study on abdominal changes and myopic control. Curr Eye Res. 2005; 30:71–80.8. Jeon HM, Ahn DS, Lee DJ, et al. The effects of overnight abdominal lens wear on ocular scatter. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1595–9.9. Walline JJ, Jones LA, Sinnott LT. Corneal reshaping and myopia progression. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:1181–5.
Article10. Kakita T, Hiraoka T, Oshika T. Influence of overnight abdominal on axial elongation in childhood myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:2170–4.11. Yoon G, Macrae S, Williams DR, Cox IG. Causes of spherical aberration induced by laser refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:127–35.
Article12. Roberts C. Biomechanics of the cornea and wavefront-guided laser refractive surgery. J Refract Surg. 2002; 18:S589–92.
Article13. Ahn SM, Seok SS, Park CY. Considering spherical aberration in choosing the wavefront map for laser vision correction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:147–56.
Article14. Choi JH, Ryu JW, Lee YC, Kim HS. An analysis of correlation with visual acuity, refractive error and corneal astigmatism after wearing of reverse geometry lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1266–73.15. Hiraoka T, Matsumoto Y, Okamoto F, et al. Corneal higher-order aberrations induced by overnight orthokeratology. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:429–36.
Article16. Berntsen DA, Barr JT, Mitchell GL. The effect of overnight contact lens corneal reshaping on higher-order aberrations and best-cor-rected visual acuity. Optom Vis Sci. 2005; 82:490–7.
Article17. Stillitano IG, Chalita MR, Schor P, et al. Corneal changes and wavefront analysis after orthokeratology fitting test. Am J abdominal. 2007; 144:378–86.
Article18. Hiraoka T, Kakita T, Okamoto F, Oshika T. Influence of ocular wavefront aberrations on axial length elongation in myopic abdominal treated with overnight orthokeratology. Ophthalmology. 2015; 122:93–100.19. Charman WN. Near vision, lags of accommodation and myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1999; 19:126–33.
Article20. Goss DA, Rainey BB. Relationship of accommodative response and nearpoint phoria in a sample of myopic children. Optom Vis Sci. 1999; 76:292–4.
Article21. Gwiazda J, Thorn F, Bauer J, Held R. Myopic children show insufficient accommodative response to blur. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993; 34:690–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Myopic Progression before and after Orthokeratology Lens Treatment
- Influence of Orthokeratology Lens on Axial length Elongation and Myopic Progression in Childhood Myopia
- Patient Evaluation for Orthothokeratology Lens
- Interrelationship of the Refractory Error and the Ocular Axial Length and the Anterior Chamber Depth in the Myopic Eyes
- The Effect of Atropine on Myopic Progression in Children