Restor Dent Endod.
2014 Nov;39(4):319-323. 10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.319.
Clinical management of a fused upper premolar with supernumerary tooth: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Program in Conservative Dentistry, Department of Dentistry, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Conservative Dentistry, Kyung Hee University Dental Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Conservative Dentistry, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry and Oral Biology Research Institute, Kyung Hee University Dental Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea. shpark94@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2316914
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.319
Abstract
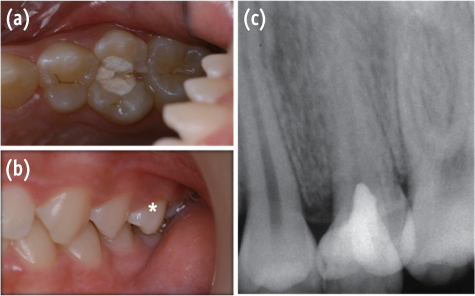
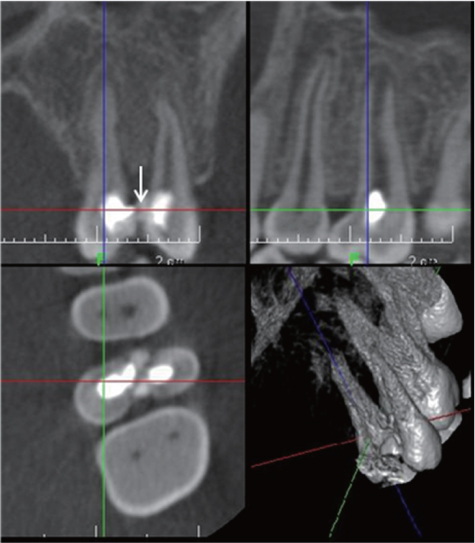
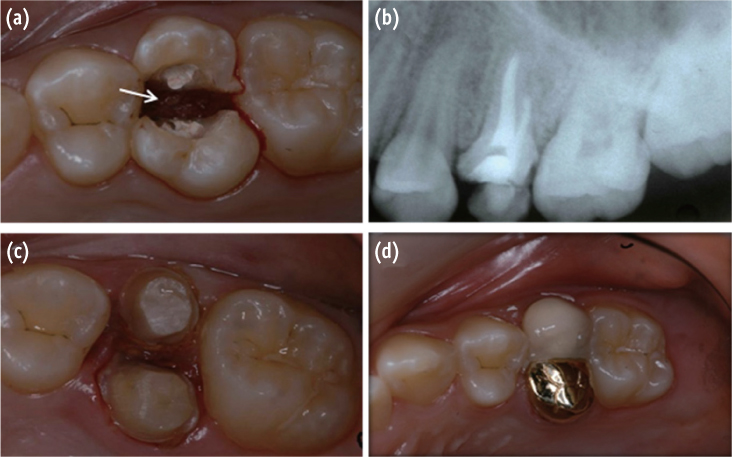
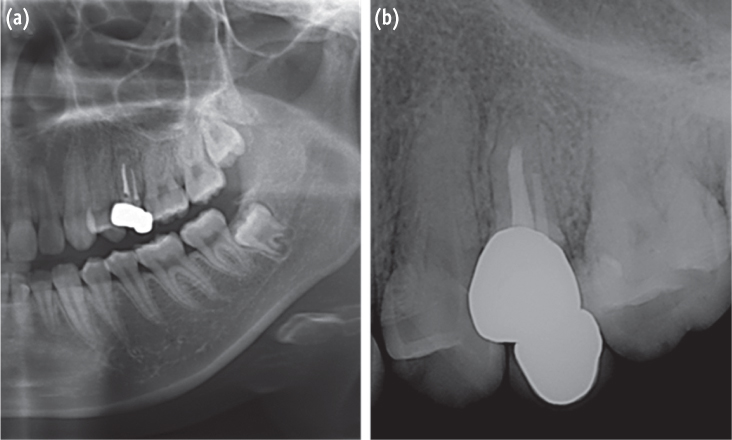
- In dentistry, the term 'fusion' is used to describe a developmental disorder of dental hard tissues. In the permanent dentition, fusion of a normal tooth and a supernumerary tooth usually involves the incisors or canines. However, a few cases of fusion involving premolars have also been reported to date. We present a rare case in which fusion of the maxillary left second premolar and a supernumerary tooth in a 13-year-old girl was diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT, Alphard-3030, Asahi Roentgen Ind. Co., Ltd.). The tooth was bicuspidized after routine nonsurgical root canal treatment, and the separated teeth underwent appropriate restoration procedures. The second premolar and supernumerary tooth remained asymptomatic without any signs of inflammation after a follow-up period of 9 years. Identification of anatomical anomalies is important for treatment in cases involving fusion with supernumerary tooth, and therefore the microscopic examinations and CBCT are essential for the diagnosis. Fused teeth can be effectively managed by the comprehensive treatment which includes both endodontic and periodontal procedures.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report
Miguel Agostinho Beco Pinto Cardoso, Rita Brandão Noites, Miguel André Duarte Martins, Manuel Pedro da Fonseca Paulo
Restor Dent Endod. 2016;41(2):148-153. doi: 10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.148.Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Ameya Parlikar
Restor Dent Endod. 2018;43(4):. doi: 10.5395/rde.2018.43.e44.
Reference
-
1. Knezević A, Travan S, Tarle Z, Sutalo J, Janković B, Ciglar I. Double tooth. Coll Antropol. 2002; 26:667–672.2. Hernandez-Guisado JM, Torres-Lagares D, Infante-Cossio P, Gutierrez-Perez JL. Dental gemination: report of case. Med Oral. 2002; 7:231–236.3. Tsesis I, Steinbock N, Rosenberg E, Kaufman AY. Endodontic treatment of developmental anomalies in posterior teeth: treatment of geminated/fused teeth-report of two cases. Int Endod J. 2003; 36:372–379.
Article4. Maréchaux SC. The treatment of fusion of a maxillary central incisor and a supernumerary: report of a case. ASDC J Dent Child. 1984; 51:196–199.5. de Siqueira VC, Braga TL, Martins MA, Raitz R, Martins MD. Dental fusion and dens evaginatus in the permanent dentition: literature review and clinical case report with conservative treatment. J Dent Child (Chic). 2004; 71:69–72.6. Karacay S, Guven G, Koymen R. Management of a fused central incisor in association with a macrodont lateral incisor: a case report. Pediatr Dent. 2006; 28:336–340.7. Cetinbas T, Halil S, Akcam MO, Sari S, Cetiner S. Hemisection of a fused tooth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 104:e120–e124.
Article8. Tachibana H, Matsumoto K. Applicability of X-ray computerized tomography in endodontics. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990; 6:16–20.
Article9. Matherne RP, Angelopoulos C, Kulild JC, Tira D. Use of cone-beam computed tomography to identify root canal systems in vitro. J Endod. 2008; 34:87–89.
Article10. Song CK, Chang HS, Min KS. Endodontic management of supernumerary tooth fused with maxillary first molar by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2010; 36:1901–1904.
Article11. Simratvir M, Prabhakar M. Clinical management of a unique case of fusion between supernumerary canine and maxillary first premolar. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2011; 39:885–889.12. Hülsmann M, Bahr R, Grohmann U. Hemisection and vital treatment of a fused tooth-literature review and case report. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1997; 13:253–258.13. Liu DG, Zhang WL, Zhang ZY, Wu YT, Ma XC. Three-dimensional evaluations of supernumerary teeth using cone-beam computed tomography for 487 case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 103:403–411.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
- BBilateral Intranasal Supernumerary Teeth
- Mandibular lateral incisor with four root canals: A unique case of double tooth diagnosed using multidetector computed tomography
- A Case of Supernumerary Tooth in Tonsil
- Impacted supernumerary tooth in coronoid process: a case report