Restor Dent Endod.
2012 Nov;37(4):220-227.
A comparison of the shaping ability of reciprocating NiTi instruments in simulated curved canals
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Dankook University College of Dentistry, Cheonan, Korea. raindrop@dku.edu
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The study was to compare the shaping ability of Reciproc (VDW) and WaveOne (Dentsply Maillefer) instruments compared with ProTaper, Profile and hand instrument during the preparation of simulated root canals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
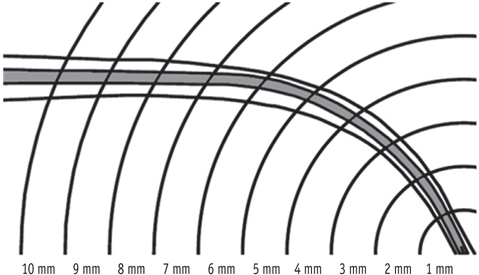
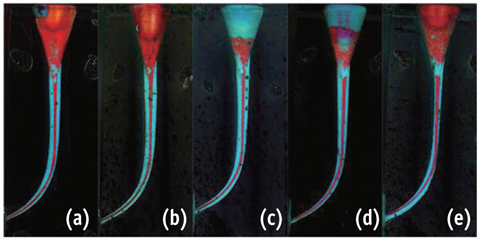
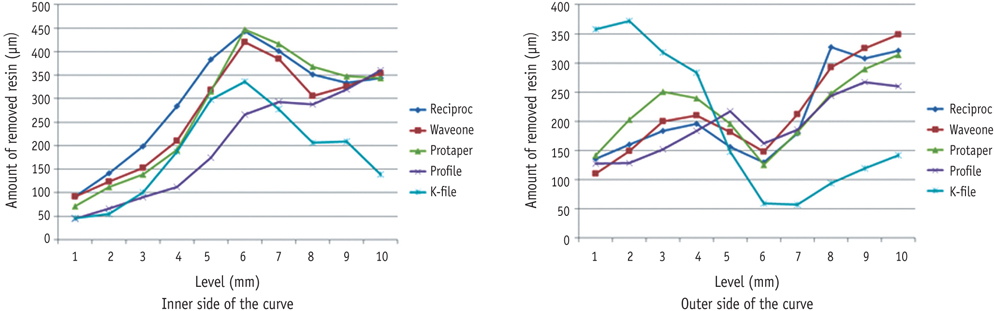
Five groups (n = 5) were established. Reciproc, WaveOne, ProTaper, Profile and K file (K-flexo file) were used to prepare the resin simulated canals. A series of preoperative and postoperative images were taken by a microscope and superimposed in 2 different layers. The amount of resin removed from both the inner and the outer sides of the canal was measured to the level of 10 mm from the apical tip, with a 1 mm increment.
RESULTS
The mean of resin removal from the inner canal wall was not different from the outer canal wall for Reciproc and WaveOne groups at apical third (1 - 3 mm level). There was no difference in the change of working length and maintenance of canal curvature. NiTi instruments are superior to stainless-steel K file in their shaping ability.
CONCLUSIONS
Within the limitation of this present study, Reciproc and WaveOne instruments maintained the original canal curvature in curved canals better than ProTaper and Profile, which tend to transport towards the outer canal wall of the curve in the apical part of the canal.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cohen S, Hargreaves KM. Pathways of the pulp. 2006. 9th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Inc;305.2. Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am. 1974. 18:269–296.3. Garip Y, Gunday M. The use of computed tomography when comparing nickel-titanium and stainless steel files during preparation of simulated curved canals. Int Endod J. 2001. 34:452–457.
Article4. Walia HM, Brantley WA, Gerstein H. An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of Nitinol root canal files. J Endod. 1988. 14:346–351.
Article5. Thompson SA, Dummer PM. Shaping ability of Profile .04 taper series 29 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part1. Int Endod J. 1997. 30:1–7.6. Wu MK, Wesselilnk PR. Efficacy of three techniques in cleaning the apical portion of curved root canals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995. 79:492–496.
Article7. Zmener O, Banegas G. Comparison of three instrumentation technique in the preparation of simulated curved root canals. Int Endod J. 1996. 29:315–319.
Article8. Thompson SA. An overview of nickel-titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int Endod J. 2000. 33:297–310.
Article9. Cheung GS, Liu CS. A retrospective study of endodontic treatment outcome between nickel-titanium rotary and stainless steel hand filing techniques. J Endod. 2009. 35:938–943.
Article10. Kazemi RB, Stenman E, Spangberg LS. A comparison of stainless steel and nickel titanium H-type instruments of identical design: torsional and bending tests. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000. 90:500–506.
Article11. Roane JB, Sabala CL, Duncanson MG Jr. The "balanced force" concept for instrumentation of curved canals. J Endod. 1985. 11:203–211.
Article12. Southard DW, Oswald RJ, Natkin E. Instrumentation of curved molar root canals with the Roane technique. J Endod. 1987. 13:479–489.
Article13. Yared G. Canal preparation using only one Ni-Ti rotary instrument: preliminary observations. Int Endod J. 2007. 41:339–344.
Article14. Peters OA. Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: a review. J Endod. 2004. 30:559–567.
Article15. Schneider SW. A comparison of canal preparation in straight and curved root canals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1971. 32:271–275.16. Schäfer E, Tepel J, Hoppe W. Properties of endodontic hand instruments used in rotary motion. Part2. Instrumentation of curved canals. J Endod. 1995. 21:493–497.
Article17. Schäfer E, Vlassis M. Comparative investigation of two rotary nickel-titanium instruments: ProTaper versus RaCe. Part 1. Shaping ability in simulated curved canals. Int Endod J. 2004. 37:229–238.
Article18. Kum KY, Spängberg L, Cha BY, Jung IY, Lee SJ, Lee CY. Shaping ability of three Profile rotary instrumentation techniques in simulated resin root canals. J Endod. 2000. 26:719–723.
Article19. Ahmad M. The Validity of using simulated root canals models for ultrasonic instrumentation. J Endod. 1989. 15:544–547.
Article20. Alodeh MH, Dummer PM. A comparison of the ability of K-files and Hedstrom files to shape simulated root canals in resin blocks. Int Endod J. 1989. 22:226–235.
Article21. Calberson FL, Deroose CA, Hommez GM, De Moor RJ. Shaping ability of ProTaper nickel-titanium files in simulated resin root canals. Int Endod J. 2004. 37:613–623.
Article22. Paqué F, Musch U, Hülsmann M. Comparison of root canal preparation using RaCe and ProTaper rotary Ni-Ti instruments. Int Endod J. 2005. 38:8–16.
Article23. Ku JH, Chang HS, Chang SW, Cho HH, Bae JM, Min KS. The instrument-centering ability of four Nickel-Titanium instruments in simulated curved root canals. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006. 31:113–118.
Article24. Schäfer E, Dammaschke T. Development and sequelae of canal transportation. Endod Top. 2006. 15:75–90.
Article25. Pruett JP, Clement DJ, Carnes DL Jr. Cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J Endod. 1997. 23:77–85.
Article26. Weine FS. Endodontic therapy. 1982. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby Inc;256–340.27. Cunningham CJ, Senia ES. A three-dimensional study of canal curvatures in the mesial roots of mandibular molars. J Endod. 1992. 18:294–300.
Article28. ElDeeb ME, Boraas JC. The effect of different files on the preparation shape of severely curved canals. Int Endod J. 1985. 18:1–7.
Article29. You SY, Bae KS, Baek SH, Kum KY, Shon WJ, Lee W. Lifespan of one nickel-titanium rotary file with reciprocating motion in curved root canals. J Endod. 2010. 36:1991–1994.
Article30. You SY, Kim HC, Bae KS, Baek SH, Kum KY, Lee W. Shaping ability of reciprocating motion in curved root canals: a comparative study with micro-computed tomography. J Endod. 2011. 37:1296–1300.
Article31. Shen Y, Cheung GS, Bian Z, Peng B. Comparison of defects in ProFile and ProTaper systems after clinical use. J Endod. 2006. 32:61–65.
Article32. Johnson E, Lloyd A, Kuttler S, Namerow K. Comparison between a novel nickel-titanium alloy and 508 nitinol on the cyclic fatigue life of Profile 25/.04 rotary instruments. J Endod. 2008. 34:1406–1409.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the shaping ability of novel thermally treated reciprocating instruments
- A comparison of the shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium files in simulated root canals
- The instrument-centering ability of four Nickel-Titanium instruments in simulated curved root canals
- Effectiveness and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics for retreatment of curved root canals: a systematic review of in vitro studies
- Relative efficacy of three Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates