Korean J Urol.
2013 Jul;54(7):437-441.
Efficacy of Using Three-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis of Capsule Invasion for Decision-Making About Neurovascular Bundle Preservation in Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Related, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan. kazushi@med.kobe-u.ac.jp
- 2Division of Radiology, Department of Internal Related, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
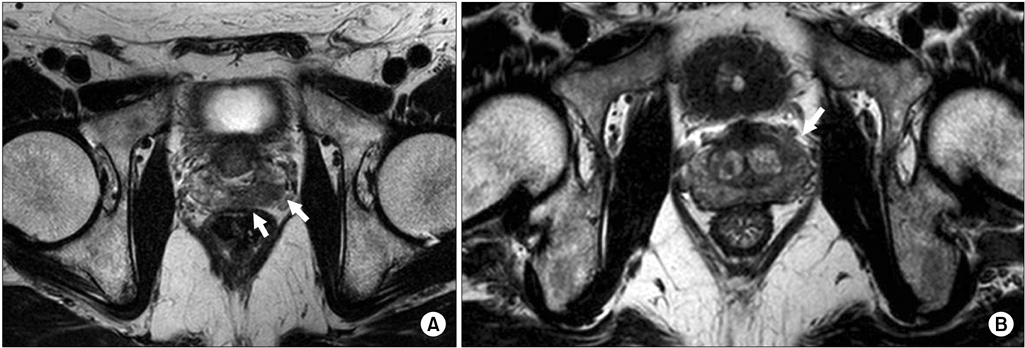
To evaluate the efficacy of using 3-tesla (T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) diagnosis of extracapsular extension (ECE) for decision-making about neurovascular bundle (NVB) preservation in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) for prostate cancer (PC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We prospectively collected data on PC patients (n=67) who underwent preoperative 3-T MRI before RARP. The choice between nerve sparing or resection was based on 3-T MRI findings of ECE. We compared the MRI findings with the pathological data on surgical margins. Our clinical staging in this study was defined only by MRI.
RESULTS
When the data were divided by prostate lobe (right lobe or left lobe, n=134), 3-T MRI showed 28 positive cases of ECE in 134 prostate lobes, allowing NVB preservation in 42 cases (31.3%). Nerve-sparing surgery was achieved in 38.7% of cases in which clinical T2 staging by MRI was reported. The pathological data revealed that 10 of 134 prostate lobes had positive ECE. The overall sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for predicting stage T3 (positive ECE) by side were 60.0% (12 of 20 sides), 86.0% (98 of 114 sides), 42.9% (12 of 28 sides), and 92.5% (98 of 106 sides), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Three-T MRI prior to RARP enables the use of ECE diagnosis to guide decision-making about NVB preservation, with comparatively high specificity and negative predictive value. Further prospective studies are underway to reach more definitive conclusions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hugosson J, Stranne J, Carlsson SV. Radical retropubic prostatectomy: a review of outcomes and side-effects. Acta Oncol. 2011. 50:Suppl 1. 92–97.2. Frota R, Turna B, Barros R, Gill IS. Comparison of radical prostatectomy techniques: open, laparoscopic and robotic assisted. Int Braz J Urol. 2008. 34:259–268.3. McClure TD, Margolis DJ, Reiter RE, Sayre JW, Thomas MA, Nagarajan R, et al. Use of MR imaging to determine preservation of the neurovascular bundles at robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. Radiology. 2012. 262:874–883.4. Brown JA, Rodin DM, Harisinghani M, Dahl DM. Impact of preoperative endorectal MRI stage classification on neurovascular bundle sparing aggressiveness and the radical prostatectomy positive margin rate. Urol Oncol. 2009. 27:174–179.5. Hricak H, Wang L, Wei DC, Coakley FV, Akin O, Reuter VE, et al. The role of preoperative endorectal magnetic resonance imaging in the decision regarding whether to preserve or resect neurovascular bundles during radical retropubic prostatectomy. Cancer. 2004. 100:2655–2663.6. Labanaris AP, Zugor V, Takriti S, Smiszek R, Engelhard K, Nutzel R, et al. The role of conventional and functional endorectal magnetic resonance imaging in the decision of whether to preserve or resect the neurovascular bundles during radical retropubic prostatectomy. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2009. 43:25–31.7. Hsu CY, Joniau S, Oyen R, Roskams T, Van Poppel H. Detection of clinical unilateral T3a prostate cancer - by digital rectal examination or transrectal ultrasonography? BJU Int. 2006. 98:982–985.8. Cornud F, Flam T, Chauveinc L, Hamida K, Chretien Y, Vieillefond A, et al. Extraprostatic spread of clinically localized prostate cancer: factors predictive of pT3 tumor and of positive endorectal MR imaging examination results. Radiology. 2002. 224:203–210.9. Girouin N, Mege-Lechevallier F, Tonina Senes A, Bissery A, Rabilloud M, Marechal JM, et al. Prostate dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with simple visual diagnostic criteria: is it reasonable? Eur Radiol. 2007. 17:1498–1509.10. Villers A, Puech P, Mouton D, Leroy X, Ballereau C, Lemaitre L. Dynamic contrast enhanced, pelvic phased array magnetic resonance imaging of localized prostate cancer for predicting tumor volume: correlation with radical prostatectomy findings. J Urol. 2006. 176(6 Pt 1):2432–2437.11. Jager GJ, Ruijter ET, van de Kaa CA, de la Rosette JJ, Oosterhof GO, Thornbury JR, et al. Local staging of prostate cancer with endorectal MR imaging: correlation with histopathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996. 166:845–852.12. Xu Z, Bensen JT, Smith GJ, Mohler JL, Taylor JA. GWAS SNP Replication among African American and European American men in the North Carolina-Louisiana prostate cancer project (PCaP). Prostate. 2011. 71:881–891.13. Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, Choyke P, Verma S, Villeirs G, et al. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol. 2012. 22:746–757.14. Orvieto MA, Patel VR. Evolution of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Scand J Surg. 2009. 98:76–88.15. Bhatnagar V, Kaplan RM. Treatment options for prostate cancer: evaluating the evidence. Am Fam Physician. 2005. 71:1915–1922.16. Kundu SD, Roehl KA, Eggener SE, Antenor JA, Han M, Catalona WJ. Potency, continence and complications in 3,477 consecutive radical retropubic prostatectomies. J Urol. 2004. 172(6 Pt 1):2227–2231.17. Costello AJ, Brooks M, Cole OJ. Anatomical studies of the neurovascular bundle and cavernosal nerves. BJU Int. 2004. 94:1071–1076.18. Ficarra V, Novara G, Artibani W, Cestari A, Galfano A, Graefen M, et al. Retropubic, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and cumulative analysis of comparative studies. Eur Urol. 2009. 55:1037–1063.19. Lowrance WT, Tarin TV, Shariat SF. Evidence-based comparison of robotic and open radical prostatectomy. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. 10:2228–2237.20. Bloch BN, Rofsky NM, Baroni RH, Marquis RP, Pedrosa I, Lenkinski RE. 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate with combined pelvic phased-array and endorectal coils; Initial experience(1). Acad Radiol. 2004. 11:863–867.21. Kim CK, Park BK, Han JJ, Kang TW, Lee HM. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate at 3 T for differentiation of malignant and benign tissue in transition and peripheral zones: preliminary results. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007. 31:449–454.22. Augustin H, Fritz GA, Ehammer T, Auprich M, Pummer K. Accuracy of 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging for the staging of prostate cancer in comparison to the Partin tables. Acta Radiol. 2009. 50:562–569.23. Hegde JV, Chen MH, Mulkern RV, Fennessy FM, D'Amico AV, Tempany CM. Preoperative 3-Tesla multiparametric endorectal magnetic resonance imaging findings and the odds of upgrading and upstaging at radical prostatectomy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. 85:e101–e107.24. Chandra RV, Heinze S, Dowling R, Shadbolt C, Costello A, Pedersen J. Endorectal magnetic resonance imaging staging of prostate cancer. ANZ J Surg. 2007. 77:860–865.25. Tan CH, Wei W, Johnson V, Kundra V. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the detection of prostate cancer: meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012. 199:822–829.26. Mazaheri Y, Shukla-Dave A, Hricak H, Fine SW, Zhang J, Inurrigarro G, et al. Prostate cancer: identification with combined diffusion-weighted MR imaging and 3D 1H MR spectroscopic imaging--correlation with pathologic findings. Radiology. 2008. 246:480–488.27. Turkbey B, Mani H, Shah V, Rastinehad AR, Bernardo M, Pohida T, et al. Multiparametric 3T prostate magnetic resonance imaging to detect cancer: histopathological correlation using prostatectomy specimens processed in customized magnetic resonance imaging based molds. J Urol. 2011. 186:1818–1824.28. Roethke MC, Lichy MP, Kniess M, Werner MK, Claussen CD, Stenzl A, et al. Accuracy of preoperative endorectal MRI in predicting extracapsular extension and influence on neurovascular bundle sparing in radical prostatectomy. World J Urol. 2012. 01. 17. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00345-012-0826-0.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Pelvic Phased-Array versus Endorectal Coil Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3 Tesla for Local Staging of Prostate Cancer
- MR Imaging of the Prostate and Seminal Tract Using an Endorectal Surface Coil
- Two Different Surgical Approaches for Prostatic Stromal Sarcoma: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy and Open Radical Cysto-Prostatectomy With Ileal Conduit
- Changes in Patterns of Radical Prostatectomy due to Diffusion of Robotic Surgical System: A Nationwide Study Using Health Insurance Claims Data
- Effect of Posterior Urethral Reconstruction (PUR) in Early Recovery of Urinary Continence after Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy