Korean J Urol.
2013 Oct;54(10):677-681.
Twelve-Month Follow-up Results of Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate With a 980-nm Diode Laser for Treatment of Benign Hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea. ggochis@hanmail.net
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted with the use of 12 months of follow-up data to evaluate the efficacy of photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) with the 980-nm diode laser for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The clinical data of 84 men with symptomatic BPH who underwent PVP with the 980-nm K2 diode laser between March 2010 and October 2011 were retrospectively analyzed. Postoperative parameters, including International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), quality of life (QoL) score, maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax), and postvoid residual volume (PVR), were assessed and compared with preoperative baseline values.
RESULTS
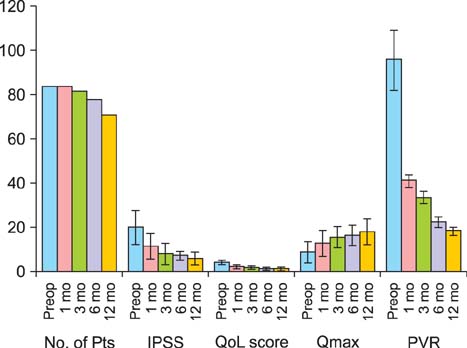
Mean patient age was 72.4+/-6.5 years, and mean preoperative prostate volume was 47.2+/-16.3 g. Mean operative time was 23.3+/-19.1 minutes, and total amount of energy was 128+/-85 kJ. Mean catheterization time was 23.7+/-5.9 hours. At 1 month, significant improvements were noted in IPSS (11.5+/-6.8), QoL score (2.2+/-1.3), Qmax (12.9+/-6.5 mL/s), and PVR (41.2+/-31.3 mL). Three months after surgery, all postoperative follow-up parameters showed significant improvements, and the 6- and 12-month data showed sustained improvement of postoperative follow-up parameters. Bladder neck strictures were observed in 10.7% of the patients and urge incontinence in 16.6%.
CONCLUSIONS
PVP using a K2 diode laser is an effective procedure for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to BPH. PVP leads to an immediate and sustained improvement of subjective and objective voiding parameters. Surgeons should be vigilant for postoperative bladder neck stricture and urge incontinence.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yu X, Elliott SP, Wilt TJ, McBean AM. Practice patterns in benign prostatic hyperplasia surgical therapy: the dramatic increase in minimally invasive technologies. J Urol. 2008; 180:241–245.2. Madersbacher S, Marberger M. Is transurethral resection of the prostate still justified? BJU Int. 1999; 83:227–237.3. Madersbacher S, Alivizatos G, Nordling J, Sanz CR, Emberton M, de la Rosette JJ. EAU 2004 guidelines on assessment, therapy and follow-up of men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction (BPH guidelines). Eur Urol. 2004; 46:547–554.4. Kuntz RM. Laser treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol. 2007; 25:241–247.5. Seitz M, Sroka R, Gratzke C, Schlenker B, Steinbrecher V, Khoder W, et al. The diode laser: a novel side-firing approach for laser vaporisation of the human prostate: immediate efficacy and 1-year follow-up. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:1717–1722.6. Te AE, Malloy TR, Stein BS, Ulchaker JC, Nseyo UO, Hai MA, et al. Photoselective vaporization of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: 12-month results from the first United States multicenter prospective trial. J Urol. 2004; 172(4 Pt 1):1404–1408.7. Bachmann A, Schurch L, Ruszat R, Wyler SF, Seifert HH, Muller A, et al. Photoselective vaporization (PVP) versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): a prospective bi-centre study of perioperative morbidity and early functional outcome. Eur Urol. 2005; 48:965–971.8. Spaliviero M, Araki M, Page JB, Wong C. Catheter-free 120W lithium triborate (LBO) laser photoselective vaporization prostatectomy (PVP) for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Lasers Surg Med. 2008; 40:529–534.9. Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984; 132:474–479.10. Levy A, Samraj GP. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: when to 'watch and wait,' when and how to treat. Cleve Clin J Med. 2007; 74:Suppl 3. S15–S20.11. Sarica K, Alkan E, Luleci H, Tasci AI. Photoselective vaporization of the enlarged prostate with KTP laser: long-term results in 240 patients. J Endourol. 2005; 19:1199–1202.12. Volkan T, Ihsan TA, Yilmaz O, Emin O, Selcuk S, Koray K, et al. Short term outcomes of high power (80 W) potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser vaporization of the prostate. Eur Urol. 2005; 48:608–613.13. Sulser T, Reich O, Wyler S, Ruszat R, Casella R, Hofstetter A, et al. Photoselective KTP laser vaporization of the prostate: first experiences with 65 procedures. J Endourol. 2004; 18:976–981.14. Malek RS. GreenLight HPS Laser Therapy for BPH: Clinical Outcomes and Surgical Recommendations from the International GreenLight User (IGLU) Group. EUR Urol Suppl. 2008; 7:361–362.15. Woo H, Reich O, Bachmann A, Choi B, Collins E, de la Rosette J, et al. Outcome of GreenLight HPS 120-W laser therapy in specific patient populations: those in retention, on anticoagulants, and with large prostates (≥80 ml). Eur Urol Suppl. 2008; 7:378–383.16. Choi B, Tabatabaei S, Bachmann A, Collins E, de la Rosette J, Gomez Sancha F, et al. GreenLight HPS 120-W laser for benign prostatic hyperplasia: comparative complications and technical recommendations. EUR Urol Suppl. 2008; 7:384–392.17. Cecchetti W, Guazzieri S, Tasca A, Dal Bianco M, Zattoni F, Pagano F. 980 nm diode laser and fiber optic resectoscope in endourological surgery. In : In : Laffitte F, Hibst R, Reidenbach HD, Geschwind HJ, Maira G, Pini R, editors. Laser applications in medicine and dentistry. Proceedings of SPIE; 1996 Sep 7; Vienna Austria. 1996. 2922:p. 291–294.18. Kang SH, Choi YS, Kim SJ, Cho HJ, Hong SH, Lee JY, et al. Long-term follow-up results of photoselective vaporization of the prostate with the 120 W greenlight HPS laser for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52:260–264.19. Elzayat EA, Habib EI, Elhilali MM. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a size-independent new "gold standard". Urology. 2005; 66:5 Suppl. 108–113.20. Gilling PJ, Aho TF, Frampton CM, King CJ, Fraundorfer MR. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: results at 6 years. Eur Urol. 2008; 53:744–749.21. Seitz M, Ackermann A, Gratzke C, Schlenker B, Ruszat R, Bachmann A, et al. Diode laser. Ex vivo studies on vaporization and coagulation characteristics. Urologe A. 2007; 46:1242–1247.22. Ruszat R, Wyler S, Rieken M, Seitz M, Reich O, Sroka R, et al. Prospective single-centre comparison of 120 watt photo selective vaporization of the prostate and 200 watt high-intensive diode laser ablation of the prostate. EUR Urol Suppl. 2008; 7:203.23. Wendt-Nordahl G, Huckele S, Honeck P, Alken P, Knoll T, Michel MS, et al. 980-nm Diode laser: a novel laser technology for vaporization of the prostate. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:1723–1728.24. Erol A, Cam K, Tekin A, Memik O, Coban S, Ozer Y. High power diode laser vaporization of the prostate: preliminary results for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2009; 182:1078–1082.25. Ruszat R, Seitz M, Wyler SF, Muller G, Rieken M, Bonkat G, et al. Prospective single-centre comparison of 120-W diode-pumped solid-state high-intensity system laser vaporization of the prostate and 200-W high-intensive diode-laser ablation of the prostate for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2009; 104:820–825.26. Seitz M, Ruszat R, Bayer T, Tilki D, Bachmann A, Stief C, et al. Ex vivo and in vivo investigations of the novel 1,470 nm diode laser for potential treatment of benign prostatic enlargement. Lasers Med Sci. 2009; 24:419–424.27. Seitz M, Bayer T, Ruszat R, Tilki D, Bachmann A, Gratzke C, et al. Preliminary evaluation of a novel side-fire diode laser emitting light at 940 nm, for the potential treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: ex-vivo and in-vivo investigations. BJU Int. 2009; 103:770–775.28. Seitz M, Reich O, Gratzke C, Schlenker B, Karl A, Bader M, et al. High-power diode laser at 980 nm for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: ex vivo investigations on porcine kidneys and human cadaver prostates. Lasers Med Sci. 2009; 24:172–178.29. Ruszat R, Wyler SF, Seitz M, Lehmann K, Abe C, Bonkat G, et al. Comparison of potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser vaporization of the prostate and transurethral resection of the prostate: update of a prospective non-randomized two-centre study. BJU Int. 2008; 102:1432–1438.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Initial Experiences with a 980 nm Diode Laser for Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Outcome of 980 nm diode laser vaporization for benign prostatic hyperplasia: A prospective study
- The Evolution of KTP Laser Vaporization of the Prostate
- The Effect of 5-alpha Reductase Inhibitors on the Efficacy of Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate with 120 W GreenLight HPS Laser
- Long-Term Follow-Up Results of Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate with the 120 W Greenlight HPS Laser for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia