Korean J Urol.
2013 Nov;54(11):778-782.
An Evidence-Based Evaluation of Health Information on Erectile Dysfunction From 10 Nationwide Daily Newspapers in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Severance Hospital, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. youngd74@yuhs.ac
- 2Clinical Trial Center for Medical Devices, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Robot and Minimal Invasive Surgery Center, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
A rapid growth in the socioeconomic status of Koreans has triggered an unprecedented explosion of health information for the general population. Despite its obvious benefits, this increase in information could also result in potentially harmful effects for both consumers and professionals who do not use it appropriately. Thus, this study was conducted to evaluate the quality and accuracy of health information on erectile dysfunction from 10 nationwide daily newspapers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study analyzed health information from 10 nationwide daily newspapers in Korea from January 2011 through December 2011. We reviewed the health information for quality by using evidence-based medicine tools and evaluated the accuracy of the information provided. Articles that simply summarized scientific congresses or journal articles and that did not include direct quotations were excluded, as were advertisements.
RESULTS
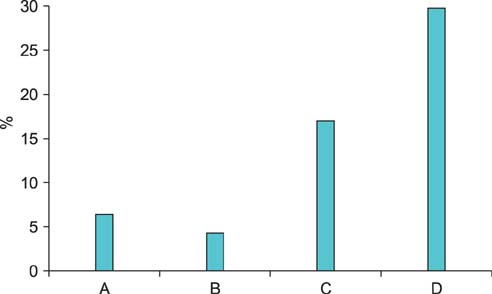
A total of 47 articles were gathered. Among them, 27 (57.4%) contained inaccurate or misleading statements on the basis of an evidence-based medicine evaluation. These statements included using inappropriate surrogate outcomes as clinical endpoints (three cases, 6.4%), extrapolating nonhuman results to humans (two cases, 4.3%), exaggerating the significance of results (eight cases, 17.0%), and using incorrect words (14 cases, 29.8%). The rate of error was higher in the information from Korean sources than in that from international sources (22 cases vs. 5 cases).
CONCLUSIONS
Approximately 57% of all articles on erectile dysfunction from 10 nationwide daily newspapers were found to contain inaccuracies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. LOcal Campaign on Antibiotics ALliance (LOCAAL) study group. Doctors and local media: a synergy for public health information?: a controlled trial to evaluate the effects of a multifaceted campaign on antibiotic prescribing (protocol). BMC Public Health. 2011; 11:816.2. Lee JY, Kang DH, Moon HS, Kim YT, Yoo TK, Choi HY, et al. Analysis of content legibility for smartphones of websites of the korean urological association and other urological societies in Korea. Korean J Urol. 2011; 11:142–146.3. Knudsen AK, Omenas AN, Harvey SB, Lovvik CM, Lervik LV, Mykletun A. Chronic fatigue syndrome in the media: a content analysis of newspaper articles. JRSM Short Rep. 2011; 2:42.4. Lee JY, Cho SY, Oh CY, Ha US, Lee SH, Park SY, et al. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with mirodenafil and α1-blocker for benign prostatic hyperplasia-induced lower urinary tract symptoms accompanied by erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, open-label, prospective study. Int J Impot Res. 2011; 23:249–256.5. Lee JY, Park SY, Jeong TY, Moon HS, Kim YT, Yoo TK, et al. Combined tadalafil and α-blocker therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia in patients with erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, prospective study. J Androl. 2012; 33:397–403.6. Kang DH, Lee JY, Park SY, Moon HS, Jeong TY, Yoo TK, et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil 5 mg administered once daily in Korean men with erectile dysfunction: a prospective, multicenter study. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:647–652.7. Tan HM, Tong SF, Ho CC. Men's health: sexual dysfunction, physical, and psychological health: is there a link? J Sex Med. 2012; 9:663–671.8. Sugita M, Miyakawa M. Economic analysis of use of counterfeit drugs: health impairment risk of counterfeit phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor taken as an example. Environ Health Prev Med. 2010; 15:244–251.9. Hwang YW, Byun JS, Lee KW, Hwang IH, Kim SY. Evidence based evaluation of health information in the television news. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2006; 27:523–528.10. Lavallee LT, Montori VM, Canfield SE, Breau RH. Advanced topics in evidence-based urologic oncology: surrogate endpoints. Urol Oncol. 2011; 29:447–453.11. Nobre MR, Bernardo WM, Jatene FB. Evidence based clinical practice. Part III: critical appraisal of clinical research. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2004; 50:221–228.12. Carducci A, Alfani S, Sassi M, Cinini A, Calamusa A. Mass media health information: quantitative and qualitative analysis of daily press coverage and its relation with public perceptions. Patient Educ Couns. 2011; 82:475–478.13. Tan HM, Low WY, Ng CJ, Chen KK, Sugita M, Ishii N, et al. Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction (ED) and treatment seeking for ED in Asian men: the Asian Men's Attitudes to Life Events and Sexuality (MALES) study. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:1582–1592.14. Tannenbaum C. Effect of age, education and health status on community dwelling older men's health concerns. Aging Male. 2012; 15:103–108.15. Ahn TY, Park JK, Lee SW, Hong JH, Park NC, Kim JJ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Korean men: results of an epidemiological study. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:1269–1276.16. Kang DH, Lee JY, Chung JH, Cho HJ, Cho JM, Moon HS, et al. Analysis of prescriptions of alpha-blockers and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors from the urology department and other departments. Int Neurourol J. 2011; 15:216–221.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Child Health Information Articles in Newspapers
- Analysis of Food and Nutrition Informations for Articles and Advertisements in the Daily Newspapers(year 2002)
- The Relationship between Benign Prostate Hyperplasia and Erectile Dysfunction: What is Reality?
- Trends in Reports on Climate Change in 2009-2011 in the Korean Press Based on Daily Newspapers' Ownership Structure
- Analysis of Dietary Informations in Newspapers and Magazine for Children (2002)