Prog Med Phys.
2015 Mar;26(1):12-17. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.1.12.
Monte Carlo Simulation of the Carbon Beam Nozzle for the Biomedical Research Facility in RAON
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. jwkwak0301@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chengju, Korea.
- 3Proton Therapy Center, National Cancer Center, Ilsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2315773
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.1.12
Abstract
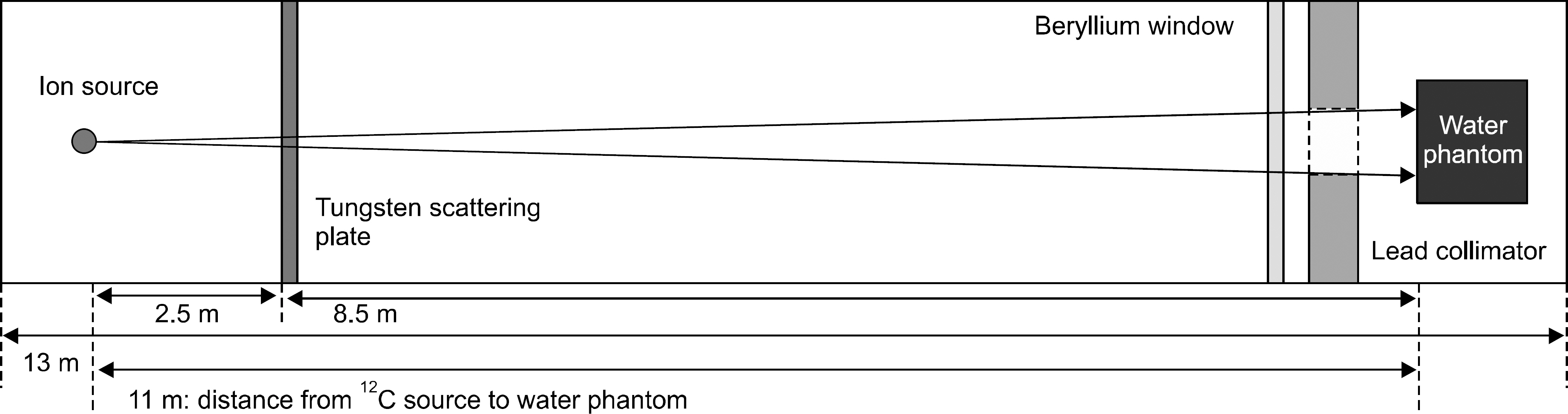
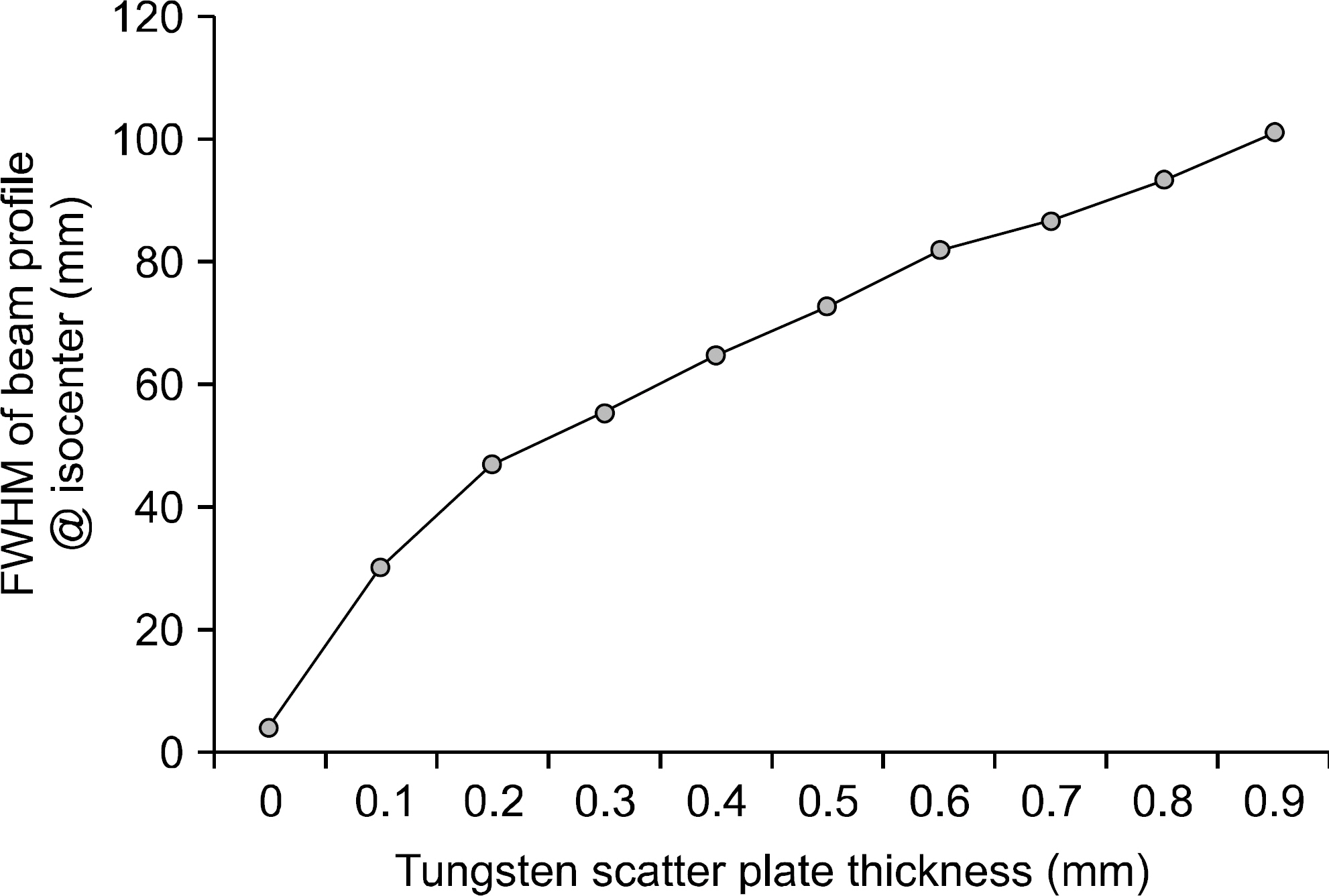
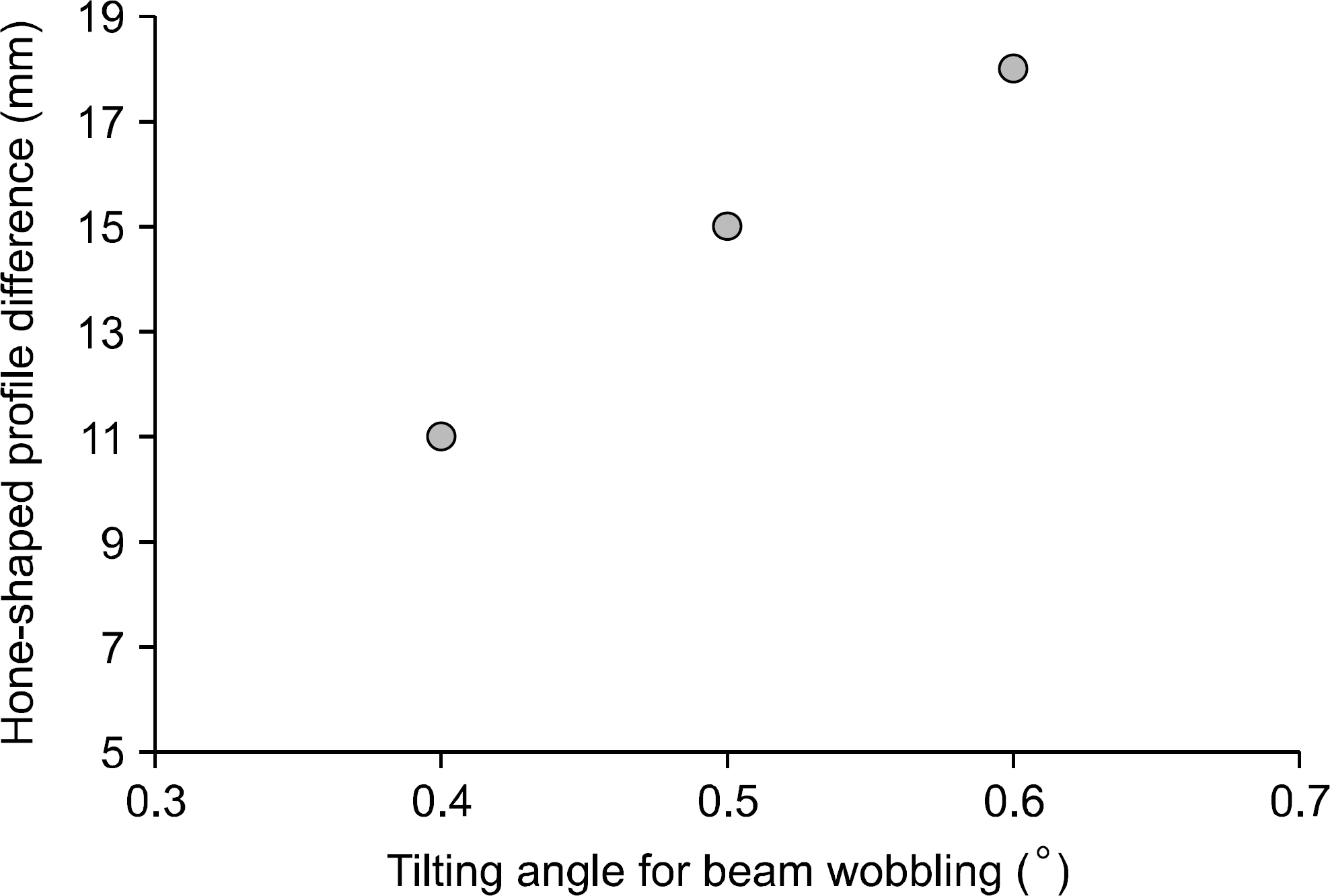
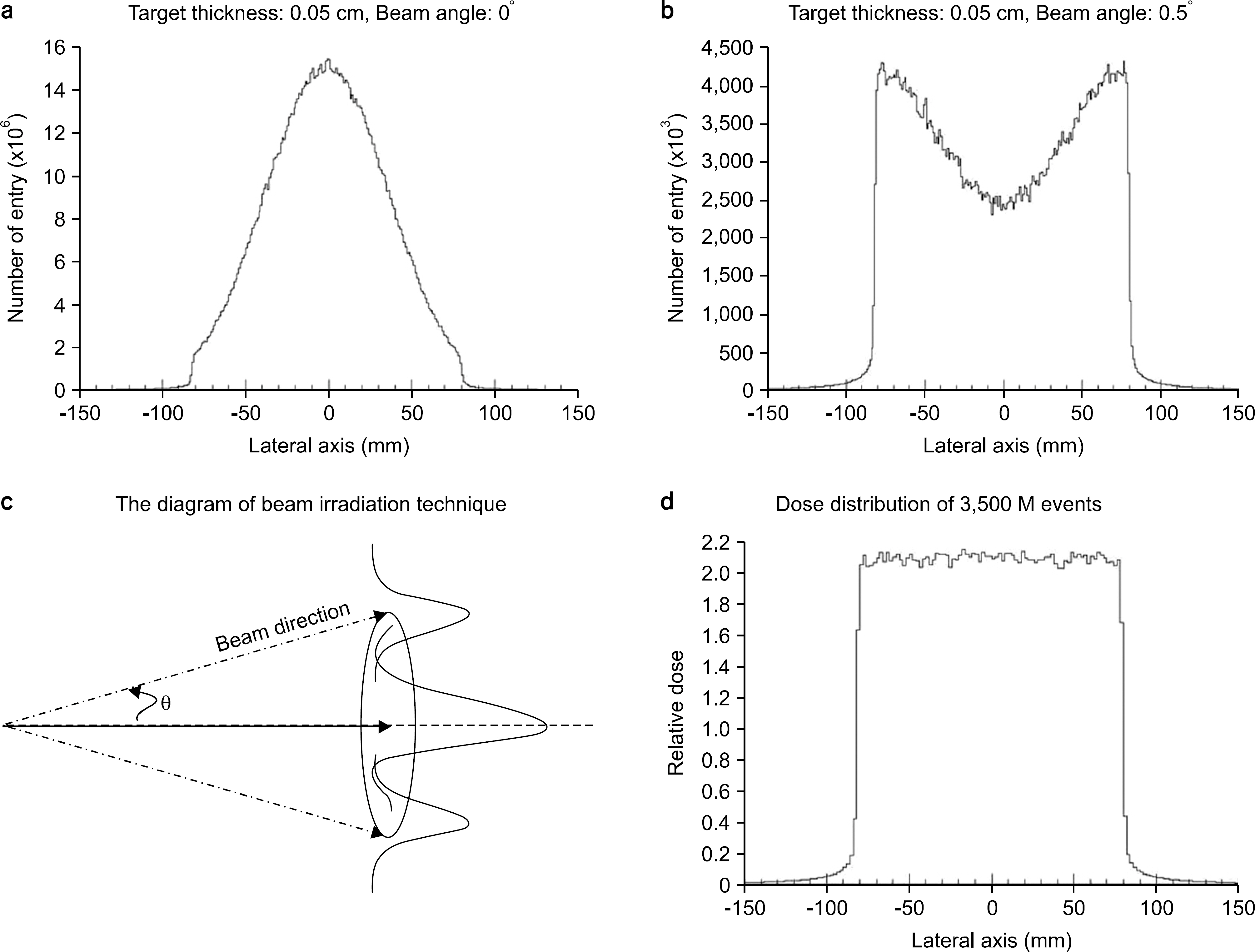
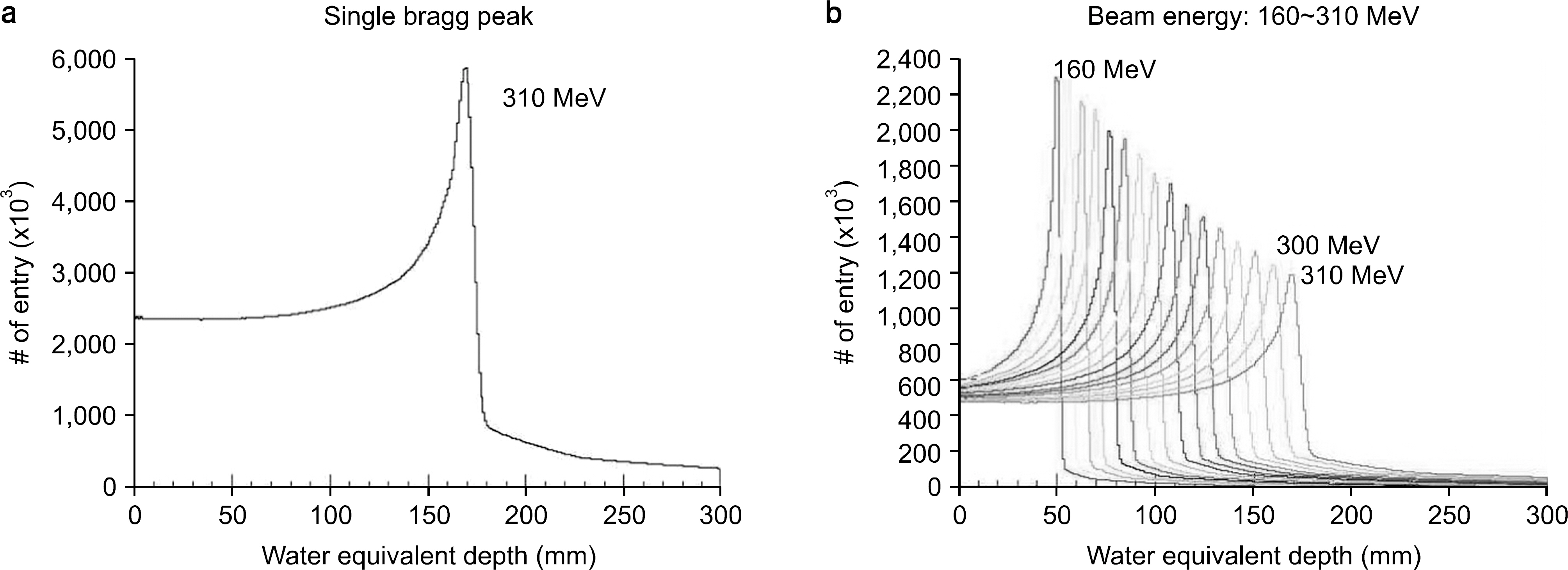
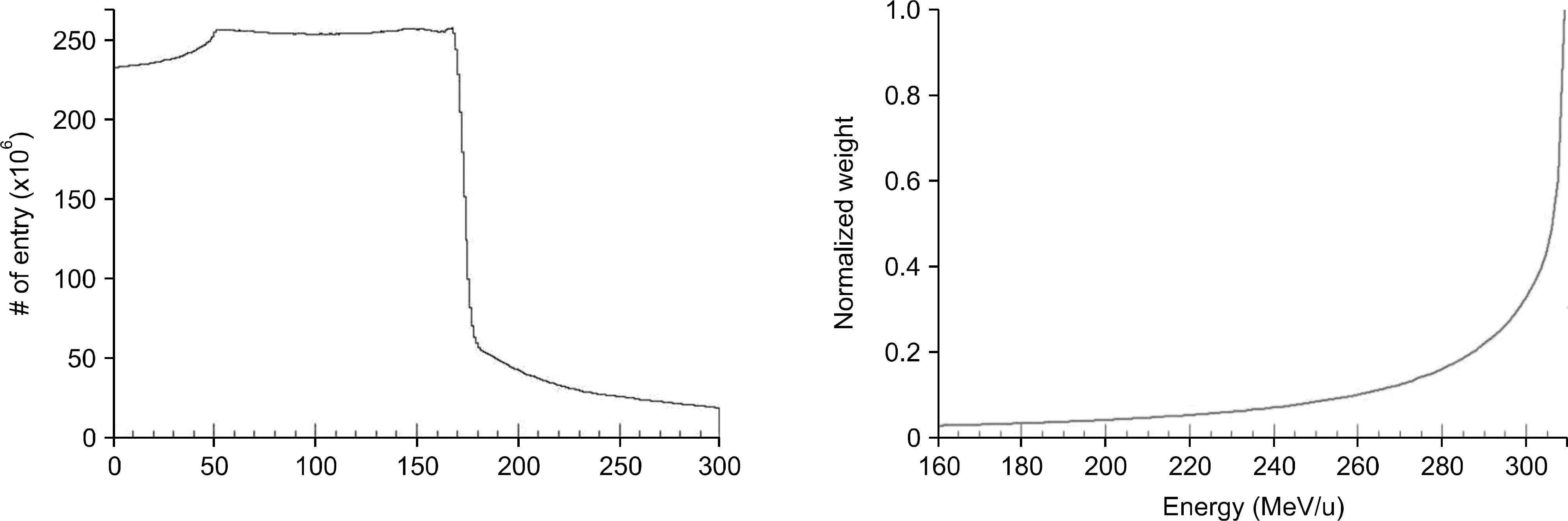
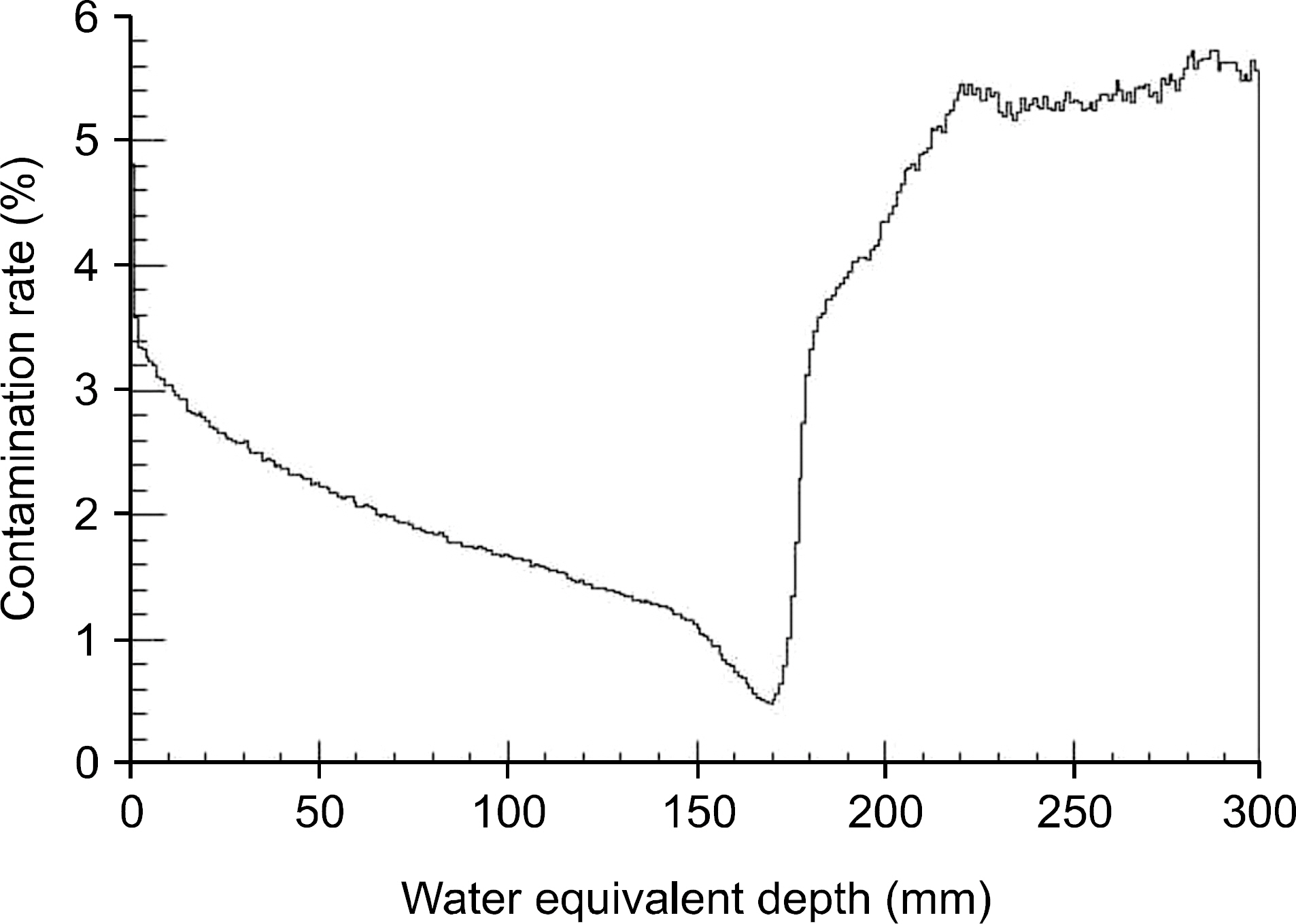
- The purpose of the Monte Carlo simulation study was to provide the optimized nozzle design to satisfy the beam conditions for biomedical researches in the Korean heavy-ion accelerator, RAON. The nozzle design was required to produce C12 beam satisfying the three conditions; the maximum field size, the dose uniformity and the beam contamination. We employed the GEANT4 toolkit in Monte Carlo simulation to optimize the nozzle design. The beams for biomedical researches were required that the maximum field size should be more than 15x15 cm2, the dose uniformity was to be less than 3% and the level of beam contamination due to the scattered radiation from collimation systems was less than 5% of total dose. For the field size, we optimized the tilting angle of the circularly rotating beam controlled by a pair of dipole magnets at the most upstream of the user beam line unit and the thickness of the scatter plate located downstream of the dipole magnets. The values of beam scanning angle and the thickness of the scatter plate could be successfully optimized to be 0.5degrees and 0.05 cm via this Monte Carlo simulation analysis. For the dose uniformity and the beam contamination, we introduced the new beam configuration technique by the combination of scanning and static beams. With the combination of a central static beam and a circularly rotating beam with the tilting angle of 0.5degrees to beam axis, the dose uniformity could be established to be 1.1% in 15x15 cm2 sized maximum field. For the beam contamination, it was determined by the ratio of the absorbed doses delivered by C12 ion and other particles. The level of the beam contamination could be achieved to be less than 2.5% of total dose in the region from 5 cm to 17 cm water equivalent depth in the combined beam configuration. Based on the results, we could establish the optimized nozzle design satisfying the beam conditions which were required for biomedical researches.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. International Science and Business Belt. http://www.isbb.or.kr/.2. Institute for Basic Science. http://www.ibs.re.kr/.3. Kwon YK, Choi BH, Chung YS, Han JE, et al. Status of Rare Isotope Science Project in Korea. Few-Body Syst. 54:961–966. 2013.
Article4. Amaldi U, Kraft G. Radiotherapy with beams of carbon ions. Rep Prog Phys. 68:1861–1882. 2005.
Article5. Noda K, Furukawa T, Fujisawa T, Iwata Y, et al. New Accelerator Facility for Carbon-Ion Cancer-Therapy. J Radiat Res. 48:43–54. 2007.
Article6. Suzuki M, Kase Y, Yamaguchi H, Kanai T, Ando K. Relative Biological Effectiveness for Cell-killing Effect on Various Human Cell Lines Irradiated with heavy-ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC) Carbon-ion Beams. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys. 48(1):241–250. 2000.
Article7. Rare Isotope Science Project. http://risp.ibs.re.kr.8. Amaldi U, Bonomi R, Braccini S, Crescenti M, et al. Accelerators for hadrontherapy: From Lawrence cyclotrons to linacs. Nucl Instr And Meth A. 620:563–577. 2010.
Article9. Yonai S, Kanematsu N, Komori M, Kanai T, Takei Y, et al. Evaluation of beam wobbling methods for heavy-ion radiotherapy. Med Phys. 35(3):927–38. 2008.
Article10. GEANT4. http://geant4.cern.ch.11. Agostinelli S, Allison J, Amako K, Apostolakis J, Araujo H, et al. GEANT4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl Instr And Meth A. 506:250–303. 2003.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Monte Carlo Simulation Study of a Therapeutic Proton Beam Delivery System Using the Geant4 Code
- Monte Carlo Simulation Codes for Nuclear Medicine Imaging
- The Comparative Analysis of External Dose Reconstruction in EPID and Internal Dose Measurement Using Monte Carlo Simulation
- Measurement and Monte Carlo Simulation of 6 MV X-rays for Small Radiation Fields
- Monte Carlo Photon and Electron Dose Calculation Time Reduction Using Local Least Square Denoising Filters