Prog Med Phys.
2014 Dec;25(4):281-287. 10.14316/pmp.2014.25.4.281.
Isocenter Check and QA of Tactic Radiosurgery Devices Using EPID
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. amiran@hanmail.net
- 2Research Center, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2315768
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2014.25.4.281
Abstract
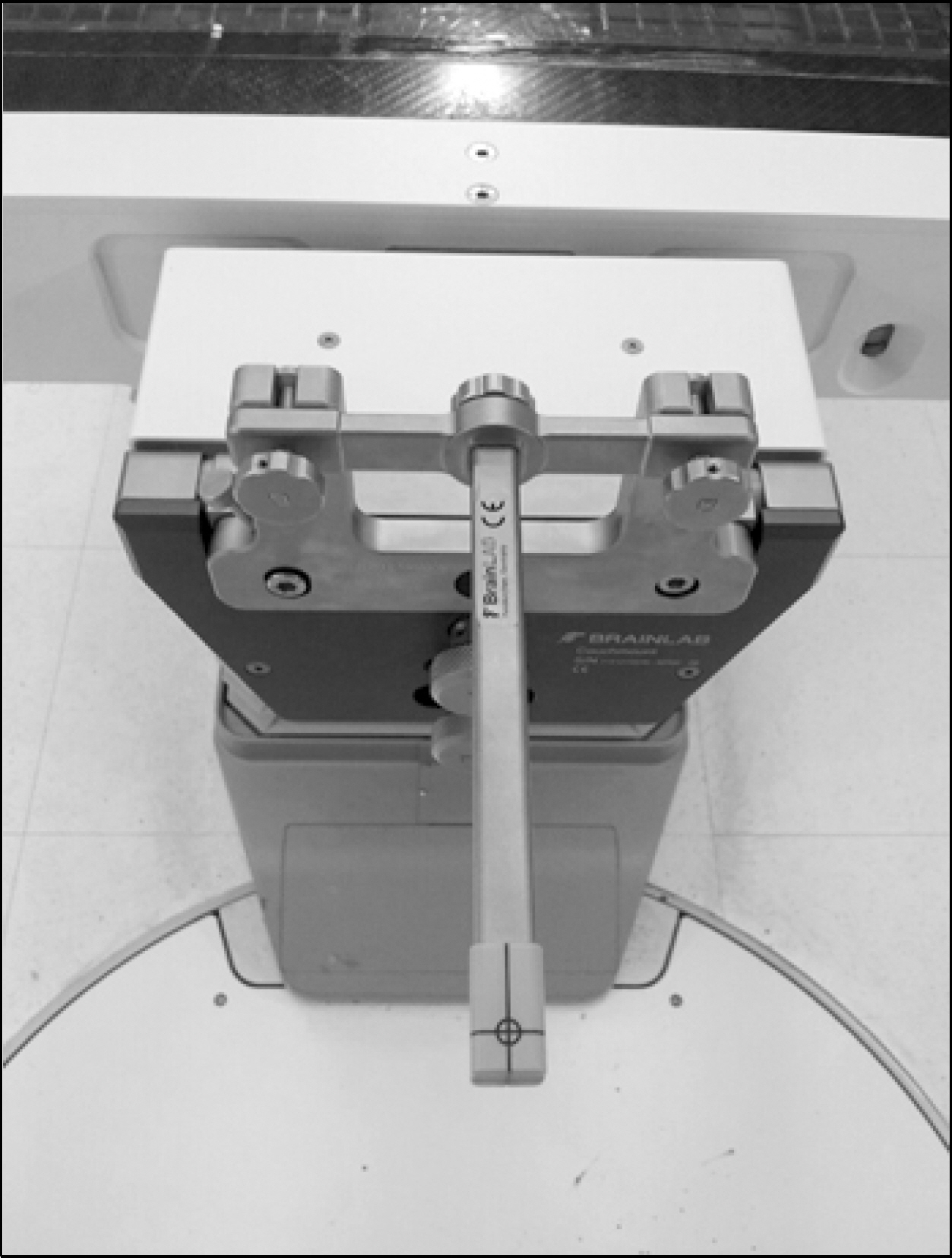
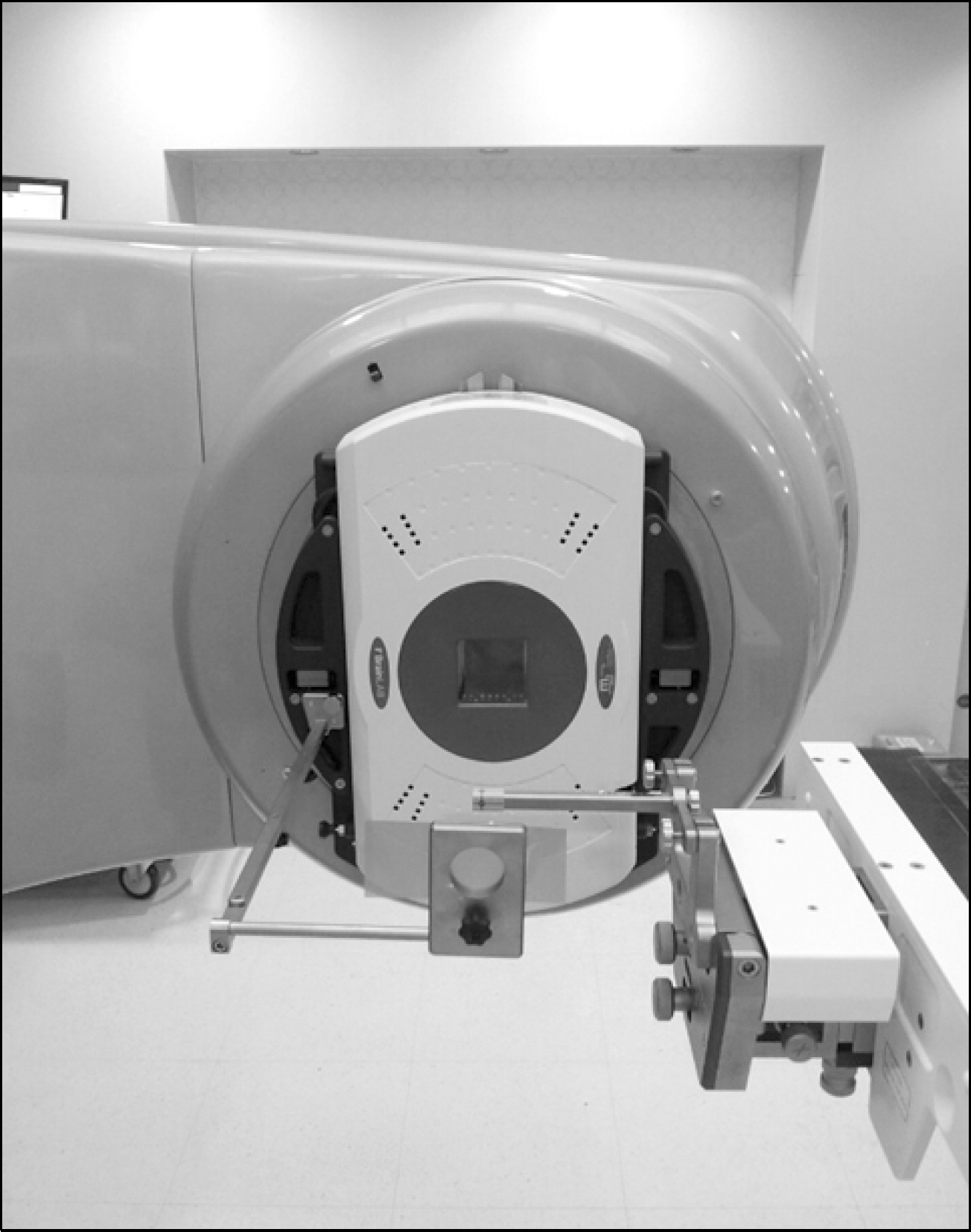
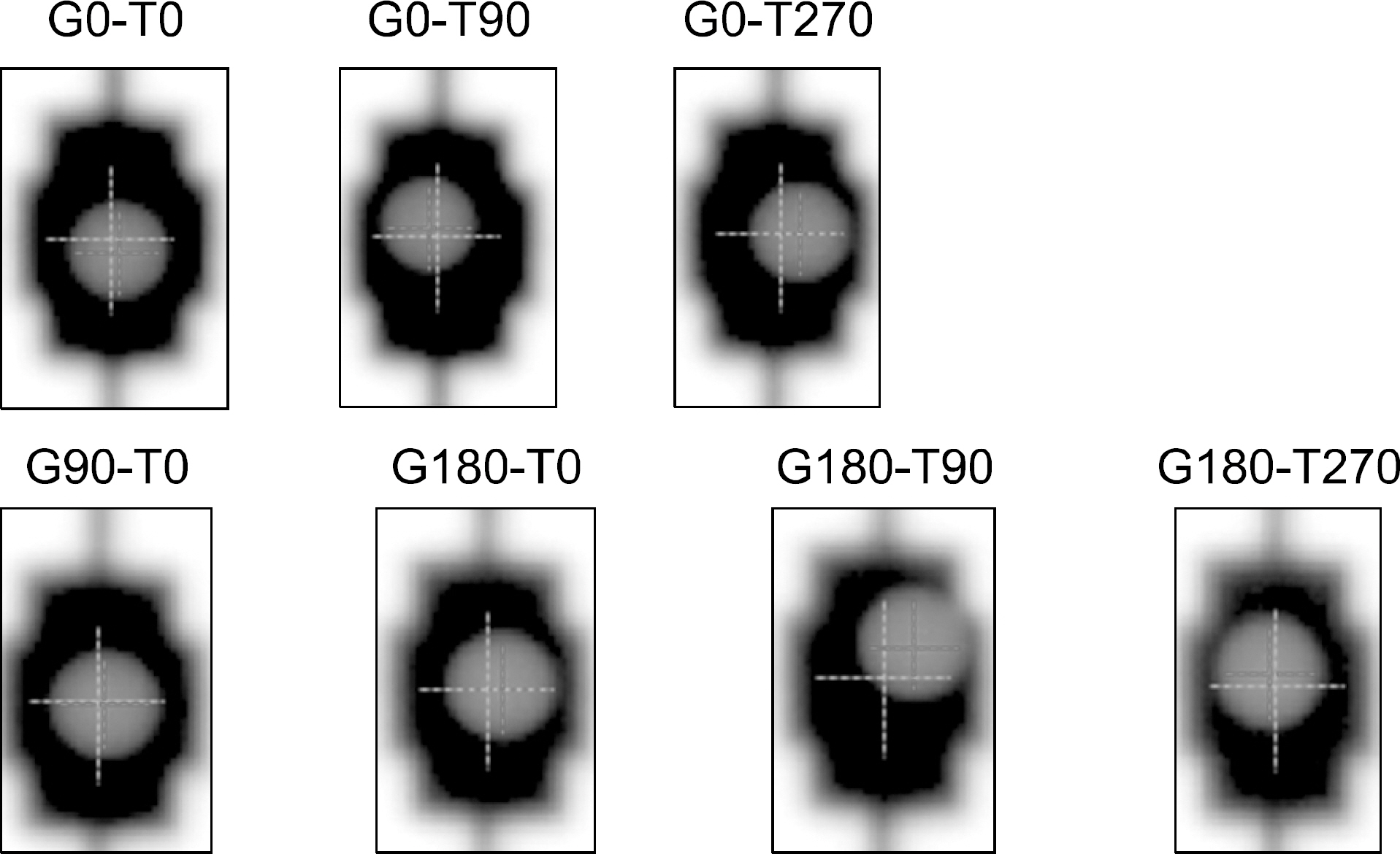
- The Winston Lutz test, which checks the accuracy of the isocenter for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), was performed with the commercial electronic portal imaging device (EPID). The usual Winston Lutz test with film was also performed for comparison with the test with EPID. The maximum difference in isocenter between the two methods was 0.32 mm. The Winston Lutz test using EPID is practical as it can reduce time and avoid human errors compared to the test with film.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lutz W, Winston KR, Maleki N. A system for stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988; 14(2):373–81.
Article2. Podgorsak EB, Pike GB, Olivier A, Pla M, Souhami L. Radiosurgery with high energy photon beams: a comparison among techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989; 16(3):857–65.
Article3. Podgorsak EB, Pike GB, Pla M, Olivier A, Souhami L. Radiosurgery with photon beams: physical aspects and adequacy of linear accelerators. Radiother Oncol. 1990; 17(4):349–58.
Article4. Ramaseshan R and Heydarian M. Comprehensive quality assurance for stereotactic radiosurgery treatments. Phys Med Biol. 2003; 48(14):N199–N205.5. Verellen D, Linthout N, Bel A, et al. Assessment of the uncertainties in dose delivery of a commercial system for linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 44(2):421–33.
Article6. Serago ChF. Lewin AA, Houdek PV, et al. Radiosurgery target point alignment errors detected with portal film verification. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992; 24(4):777–80.7. Leksell L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 1951; 102(4):316–19.8. Pejman Rowshanfarzad, Mahsheed Sabet, Daryi J. OConnor, Peter B. Greer, et, al: Isocenter verification for linac-based stereotactic radiation therapy: review of principles and techniques. J of Appl. Clini. Med. Phy. 2011; 12(4):9. E. Shaw, C. Scott, L. Souhami, et al: Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: Final report of RTOG protocol 90–05 Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 47 (. 2000. ), pp.291–298.10. L. Walton, A. Hampshire, A. Roper, et al: Development of a relocatable frame technique for gamma knife radiosurgery: Technical note J Neurosurg, 93 (. 2000. ), pp.198–202.11. H. Shirato, T. Sakamoto, N. Takeuchi, et al: Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma (vs): Comparison between cystic-type and solid-type vs, Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 48 (. 2000. ), pp.1395–1401.12. J.A. Williams: Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for acoustic neuromas, Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 54 (. 2002. ), pp.500–504.13. Zheng C, Zhiheng W, Jinli M, et al. Six degree-of-freedom image guidance for frameless intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery with kilovoltage cone-beam CT, J Nucl Med Radiat Ther. 2010; 1:101.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Novalis Quality Assurance Protocol for Radiosurgery
- Evaluation of Real-time Target Positioning Accuracy in Spinal Radiosurgery
- Comparison of the Efficacy of 2D Dosimetry Systems in the Pre-treatment Verification of IMRT
- A Comparison Study of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Quality Assurances Using Portal Dosimetry and MapCHECK 2
- Radiation Dose Accuracy at the Isocenter: Standard Stereotactic Radiosurgery Technique Developed at Seoul National University Hospital