Korean J Urol.
2011 Apr;52(4):284-288.
The Learning Curve for Flank Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Kidney Calculi: A Single Surgeon's Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea. hanwk@yuhs.ac
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is conventionally conducted in the prone position. However, the prone position increases anesthesia-related morbidity and position changes lengthen the operation time. We report perioperative outcomes and the learning curve for flank PCNL on the basis of a single surgeon's experience.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study investigated 53 cases of flank PCNL performed for renal stones at our institution from April 2008 to September 2010. We compared mean operative time, stone-free rate, drop in hemoglobin level, length of hospital stay, complications, and need for additional procedures after the surgery. The 53 cases were divided into three groups by case number to compare therapeutic effect, stability, and the learning curve for flank position PCNL.
RESULTS
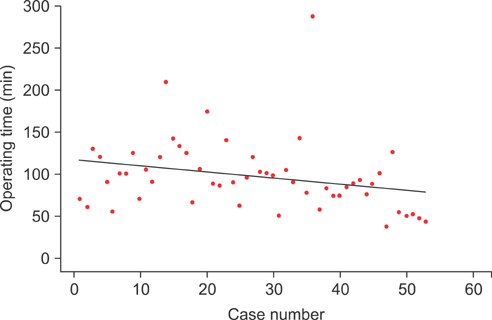
The mean operation time for the 53 patients was 97.3+/-43.1 minutes. The mean operation time gradually decreased as the surgeon accumulated experience. From the 36th case, the mean operation time showed a statistically significant decrease to 72.2+/-24.1 minutes (p=0.003). The overall stone-free rate was 64.2% for all procedures (range, 61.1-76.5%). There were no significant differences in the drop in hemoglobin level, stone-free rate, re-treatment, hospital stay, or complication rate. There was no injury to the bowel or renal vessels, and no other major complications occurred.
CONCLUSIONS
Flank PCNL can be used to remove renal stones effectively while overcoming the disadvantages of the existing prone position PCNL. After 36 cases, the learning curve showed acquisition of surgical competence. The clinical experience reported here suggests that flank PCNL is a safe and feasible technique.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fernström I, Johansson B. Percutaneous pyelolithotomy. A new extraction technique. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1976. 10:257–259.2. Valdivia Uría JG, Valle Gerhold J, López López JA, Villarroya Rodriguez S, Ambroj Navarro C, Ramirez Fabián M, et al. Technique and complications of percutaneous nephroscopy: experience with 557 patients in the supine position. J Urol. 1998. 160:1975–1978.3. Kerbl K, Clayman RV, Chandhoke PS, Urban DA, De Leo BC, Carbone JM. Percutaneous stone removal with the patient in a flank position. J Urol. 1994. 151:686–688.4. Stambough JL, Dolan D, Werner R, Godfrey E. Ophthalmologic complications associated with prone positioning in spine surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007. 15:156–165.5. Segura JW, Patterson DE, LeRoy AJ, May GR, Smith LH. Percutaneous lithotripsy. J Urol. 1983. 130:1051–1054.6. Peces-Barba G, Rodriguez-Nieto MJ, Verbanck S, Paiva M, González-Mangado N. Lower pulmonary diffusing capacity in the prone vs. supine posture. J Appl Physiol. 2004. 96:1937–1942.7. Pump B, Talleruphuus U, Christensen NJ, Warberg J, Norsk P. Effects of supine, prone, and lateral positions on cardiovascular and renal variables in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2002. 283:R174–R180.8. Edgcombe H, Carter K, Yarrow S. Anaesthesia in the prone position. Br J Anaesth. 2008. 100:165–183.9. Walick KS, Kragh JE Jr, Ward JA, Crawford JJ. Changes in intraocular pressure due to surgical positioning: studying potential risk for postoperative vision loss. Spine. 2007. 32:2591–2595.10. Falahatkar S, Moghaddam AA, Salehi M, Nikpour S, Esmaili F, Khaki N. Complete supine percutaneous nephrolithotripsy comparison with the prone standard technique. J Endourol. 2008. 22:2513–2517.11. Rana AM, Bhojwani JP, Junejo NN, Das Bhagia S. Tubeless PCNL with patient in supine position: procedure for all seasons?--with comprehensive technique. Urology. 2008. 71:581–585.12. Karami H, Rezaei A, Mohammadhosseini M, Javanmard B, Mazloomfard M, Lotfi B. Ultrasonography-guided percutaneous nephrolithotomy in the flank position versus fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous nephrolithotomy in the prone position: a comparative study. J Endourol. 2010. 24:1357–1361.13. LeRoy AJ, Williams HJ Jr, Bender CE, Segura JW, Patterson DE, Benson RC. Colon perforation following percutaneous nephrostomy and renal calculus removal. Radiology. 1985. 155:83–85.14. Rodrigues Netto N Jr, Lemos GC, Fiuza JL. Colon perforation following percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urology. 1988. 32:223–224.15. Hadar H, Gadoth N. Positional relations of colon and kidney determined by perirenal fat. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984. 143:773–776.16. Jeong WJ, Jeon HG, Yang SC, Han WK. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a semi-lateral position. Korean J Urol. 2009. 50:892–896.17. Tanriverdi O, Boylu U, Kendirci M, Kadihasanoglu M, Horasanli K, Miroglu C. The learning curve in the training of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Eur Urol. 2007. 52:206–211.18. Allen D, O'Brien T, Tiptaft R, Glass J. Defining the learning curve for percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Endourol. 2005. 19:279–282.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The experiences of endourologic management and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy to the complications in horseshoe kidneys
- Experience in the treatment of complete staghorn calculi
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Causes of Failure and Complications
- Percutaneous management of staghorn renal calculi
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: 52 Cases