Korean J Urol.
2011 May;52(5):317-322.
Expression of Claudin-1 and -7 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Clinical Significance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. chp@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the correlations between the expression of claudin-1 and claudin-7 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (clear cell RCC) and clinical parameters.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The subjects of this study were 119 patients with confirmed clear cell RCC between January 2000 and December 2007. Their RCC tissues were immunohistochemically stained for claudin-1 and claudin-7. The correlations between the expression of claudin and parameters such as sex, age, body mass index (BMI), tumor size, TNM stage, Furhman nuclear grade, postoperative distant metastasis, and cancer-specific survival were analyzed.
RESULTS
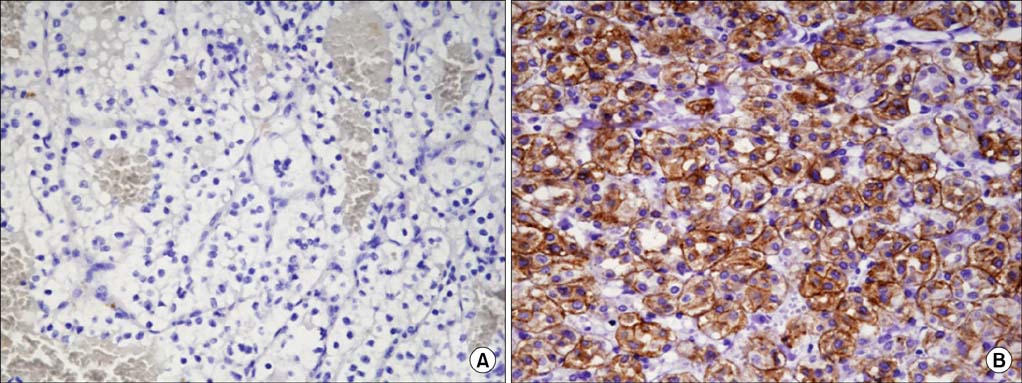
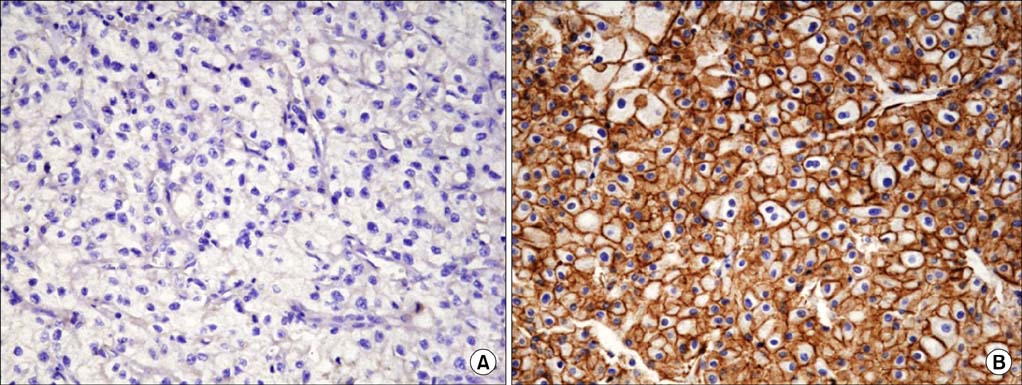
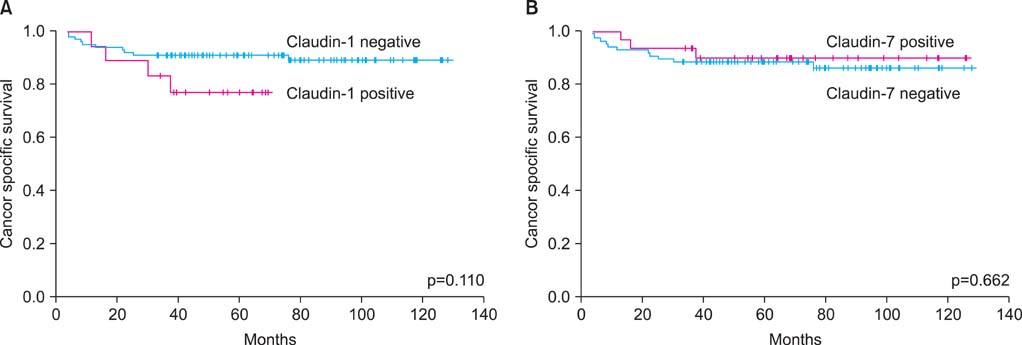
Among the total 119 subjects, claudin-1 was expressed in 18 (15.1%) and claudin- 7 in 31 (26.1%). Claudin-1 was expressed in patients who were older (p=0.007), who had a greater tumor size (p=0.001), who had a higher pathologic T stage (p=0.009), who had preoperative distant metastasis (p=0.035), and who had a higher Furhman nuclear grade (p=0.004). Claudin-7 was expressed only in patients who had a higher Furhman nuclear grade (p=0.031). The risk of postoperative distant metastasis was associated with the expression of claudin-1 (p<0.001) but not with the expression of claudin-7 (p=0.668). The expression of claudin-1 and -7 was not associated with cancer-specific survival (p>0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
In clear cell RCC, claudin-1 was expressed in patients who were older and who had a greater tumor size, who had higher T or M stages, and who had a higher Furhman nuclear grade. The expression of claudin-1 was associated with a higher risk of postoperative distant metastasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gumbiner BM. Cell adhesion: the molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 1996. 84:345–357.2. González-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE. Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003. 81:1–44.3. Matsuda M, Kubo A, Furuse M, Tsukita S. A peculiar internalization of claudins, tight junction-specific adhesion molecules, during the intercellular movement of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2004. 117:1247–1257.4. Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001. 2:285–293.5. Huo Q, Kinugasa T, Wang L, Huang J, Zhao J, Shibaguchi H, et al. Claudin-1 protein is a major factor involved in the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009. 29:851–857.6. Ohtani S, Terashima M, Satoh J, Soeta N, Saze Z, Kashimura S, et al. Expression of tight-junction-associated proteins in human gastric cancer: downregulation of claudin-4 correlates with tumor aggressiveness and survival. Gastric Cancer. 2009. 12:43–51.7. Comper F, Antonello D, Beghelli S, Gobbo S, Montagna L, Pederzoli P, et al. Expression pattern of claudins 5 and 7 distinguishes solid-pseudopapillary from pancreatoblastoma, acinar cell and endocrine tumors of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. 33:768–774.8. Lopez-Beltran A, Scarpelli M, Montironi R, Kirkali Z. 2004 WHO classification of the renal tumors of the adults. Eur Urol. 2006. 49:798–805.9. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Aster JC. Robbins and Cotran: pathologic basis of disease. 2010. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;964–965.10. Letang N, Cabaniols L, Pouessel D, Robert M, Iborra F, Culine S, et al. Prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Bull Cancer. 2009. 96:475–484.11. Jiang WG, Puntis MC, Hallett MB. Molecular and cellular basis of cancer invasion and metastasis: implications for treatment. Br J Surg. 1994. 81:1576–1590.12. Langbein L, Grund C, Kuhn C, Praetzel S, Kartenbeck J, Brandner JM, et al. Tight junctions and compositionally related junctional structures in mammalian stratified epithelia and cell cultures derived therefrom. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002. 81:419–435.13. Tsukita S, Furuse M. Pores in the wall: claudins constitute tight junction strands containing aqueous pores. J Cell Biol. 2000. 149:13–16.14. Seo KW, Kwon YK, Kim BH, Kim CI, Chang HS, Choe MS, et al. Correlation between claudins expression and prognostic factors in prostate cancer. Korean J Urol. 2010. 51:239–244.15. Morohashi S, Kusumi T, Sato F, Odagiri H, Chiba H, Yoshihara S, et al. Decreased expression of claudin-1 correlates with recurrence status in breast cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2007. 20:139–143.16. Sheehan GM, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman RP Jr, Ross JS. Loss of claudins-1 and -7 and expression of claudins-3 and -4 correlate with prognostic variables in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2007. 38:564–569.17. Tzelepi VN, Tsamandas AC, Vlotinou HD, Vagianos CE, Scopa CD. Tight junctions in thyroid carcinogenesis: diverse expression of claudin-1, claudin-4, claudin-7 and occludin in thyroid neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2008. 21:22–30.18. Higashi Y, Suzuki S, Sakaguchi T, Nakamura T, Baba S, Reinecker HC, et al. Loss of claudin-1 expression correlates with malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2007. 139:68–76.19. Osunkoya AO, Cohen C, Lawson D, Picken MM, Amin MB, Young AN. Claudin-7 and claudin-8: immunohistochemical markers for the differential diagnosis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma. Hum Pathol. 2009. 40:206–210.20. Hornsby CD, Cohen C, Amin MB, Picken MM, Lawson D, Yin-Goen Q, et al. Claudin-7 immunohistochemistry in renal tumors: a candidate marker for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma identified by gene expression profiling. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007. 131:1541–1546.21. Fritzsche FR, Oelrich B, Johannsen M, Kristiansen I, Moch H, Jung K, et al. Claudin-1 protein expression is a prognostic marker of patient survival in renal cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. 14:7035–7042.22. Choi HJ, Jung JH, Yoo J, Kang SJ, Lee KY. Expression of claudin-1 and -4 in benign lesions and invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast. Korean J Pathol. 2007. 41:232–237.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Claudin-7 is Highly Expressed in Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Oncocytoma
- Diagnostic Utility of AMACR and Claudin-7 for the Classification of Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Differentiation of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Using Helical CT
- A Case of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma to the Gallbladder
- Expression of claudin-1, claudin-4 and zonula occludens-1 in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive squamous cell carcinoma