Korean J Urol.
2012 Apr;53(4):248-252.
alpha-Blocker Monotherapy and alpha-Blocker Plus 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitor Combination Treatment in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia; 10 Years' Long-Term Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. cikim@dsmc.or.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We compared the effects of alpha-adrenergic receptor blocker (alpha-blocker) monotherapy with those of combination therapy with alpha-blocker and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor (5-ARI) on benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) progression for over 10 years.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 620 patients with BPH who received alpha-blocker monotherapy (alpha-blocker group, n=368) or combination therapy (combination group, n=252) as their initial treatment were enrolled from January 1989 to June 2000. The incidences of acute urinary retention (AUR) and BPH-related surgery were compared between the two groups. Incidences stratified by follow-up period, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and prostate volume (PV) were compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
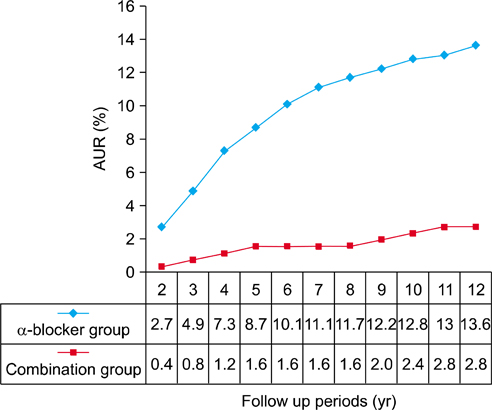
The incidence of AUR was 13.6% (50/368) in the alpha-blocker group and 2.8% (7/252) in the combination group (p<0.001). A total of 8.4% (31/368) and 3.2% (8/252) of patients underwent BPH-related surgery in the alpha-blocker and combination groups, respectively (p=0.008). According to the follow-up period, the incidence of AUR was significantly decreased in combination group. However, the incidence of BPH-related surgery was significantly reduced after 7 years of combination therapy. Cutoff levels of PSA and PV for reducing the incidences of AUR and BPH-related surgery were 2.0 ng/ml and 35 g, respectively (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Long-term combination therapy with alpha-blocker and 5-ARI can suppress the progression of BPH more efficiently than alpha-blocker monotherapy. For patients with BPH with PSA >2.0 ng/ml or PV >35 ml, combination therapy promises a better effect for reducing the risk of BPH progression.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Djavan B, Fong YK, Harik M, Milani S, Reissigl A, Chaudry A, et al. Longitudinal study of men with mild symptoms of bladder outlet obstruction treated with watchful waiting for four years. Urology. 2004. 64:1144–1148.2. McConnell JD, Bruskewitz Z, Walsh P, Andriole G, Lieber M, Holtgrewe HL, et al. The effect of finasteride on the risk of acute urinary retention and the need for surgical treatment among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:557–563.3. Roehrborn CG, McConnell JD, Lieber M, Kaplan S, Geller J, Malek GH, et al. PLESS Study Group. Serum prostate-specific antigen concentration is a powerful predictor of acute urinary retention and need for surgery in men with clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 1999. 53:473–480.4. Lepor H, Willford WO, Barry MJ, Brawer MK, Dixon CM, Gormley G, et al. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Study Group. The efficacy of terazosin, finasteride, or both in benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335:533–539.5. Kirby RS, Roehrborn C, Boyle P, Bartsch G, Jardin A, Cary MM, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of doxazosin and finasteride, alone or in combination, in treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Prospective European Doxazosin and Combination Therapy (PREDICT) trial. Urology. 2003. 61:119–126.6. McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole GL Jr, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al. The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:2387–2398.7. Kim CI, Chang HS, Kim BK, Park CH. Long-term results of medical treatment in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2006. 68:1015–1019.8. Welch G, Weinger K, Barry MJ. Quality-of-life impact of lower urinary tract symptom severity: results from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. Urology. 2002. 59:245–250.9. Breum L, Klarskov P, Munck LK, Nielsen TH, Nordestgaard AG. Significance of acute urinary retention due to intravesical obstruction. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1982. 16:21–24.10. Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Gould AL, Waldstreicher J. Serum prostate-specific antigen as a predictor of prostate volume in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 1999. 53:581–589.11. Roehrborn CG, McConnell J, Bonilla J, Rosenblatt S, Hudson PB, Malek GH, et al. Serum prostatic specific antigen is a strong predictor of future prostate growth in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. PROSCAR long-term efficacy and safety study. J Urol. 2000. 163:13–20.12. Jacobsen SJ, Jacobson DJ, Girman CJ, Roberts RO, Rhodes T, Guess HA, et al. Natural history of prostatism: risk factors for acute urinary retention. J Urol. 1997. 158:481–487.13. Bartsch G, Fitzpaatrick JM, Schalken JA, Isaacs J, Nordling J, Roehrborn CG. Consensus statement: the role of prostate-specific antigen in managing the patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2004. 93:Suppl 1. 27–29.14. Kaplan SA, McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Meehan AG, Lee MW, Noble WR, et al. Combination therapy with doxazosin and finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and a baseline total prostate volume of 25 ml or greater. J Urol. 2006. 175:217–220.15. Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damiao R, Major-Walker K, Morrill B, et al. The effects of dutasteride, tamsulosin and combination therapy on lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic enlargement: 2-year results from the CombAT study. J Urol. 2008. 179:616–621.16. Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damião R, Major-Walker K, Nandy I, et al. The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study. Eur Urol. 2010. 57:123–131.17. Lee JY, Lee SH, Kim SJ, Kim CS, Lee HM, Kim CI, et al. Change in International Prostate Symptom storage subscore after long-term medical therapy in BPH patients: finasteride and Alpha-blocker combination therapy in men with moderate-to-severe LUTS/BPH in Korea. Urology. 2011. 77:171–176.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the Long Term Effect of Alpha-Blocker Only and 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitor Combination Treatment on Acute Urinary Retention and Prostatic Surgery for Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- The Efficacy of Combination Therapy of 5 alpha -Reductase Inhibitor and of-Adrenergic Blocker in Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
- The Effect of alpha-Blocker Treatment for Nocturia with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Effect of 5-alpha Reductase Inhibitor on Storage Symptoms in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Prospective Factor Analysis of Alpha Blocker Monotherapy Failure in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia