Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis.
2012 Dec;22(4):336-343.
Changes in the Indices of Bronchial Reversibility Assessed by the Office Spirometry and Their Relationship to Asthma Symptoms after Discontinuing Controller Medication in Children with Controlled Asthma: Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dongins0@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
It is important to assess the level of control in asthmatic children who were well-controlled and thus discontinued controller medications. Office spirometry has been regarded to provide objective measures. We aimed to see time changes in lung function indices measured by the office spirometry and their relationship to clues for asthma exacerbation after discontinuation of controller medications.
METHODS
As a pilot study, a total of 20 well-controlled children with persistent asthma were included. After discontinuing controller medications, each made follow-up visits at the 2nd, 6th, and 12th week. At each visit, spirometric values before and after bronchodilators were evaluated by the office-based spirometer. Time changes and their relationship to clues for asthma exacerbation were assessed.
RESULTS
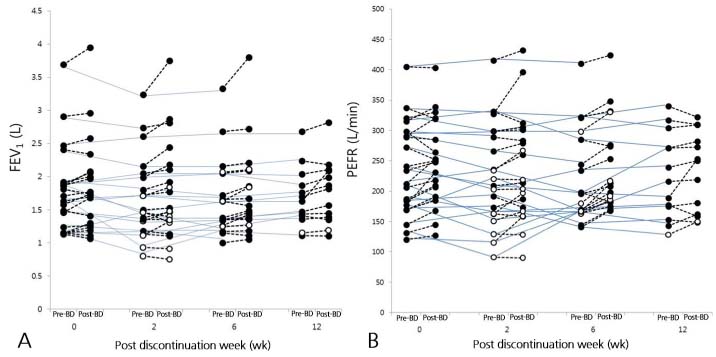
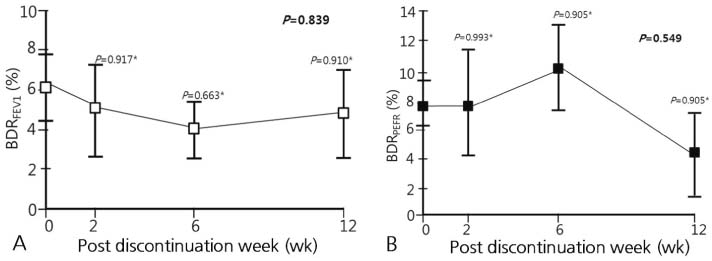
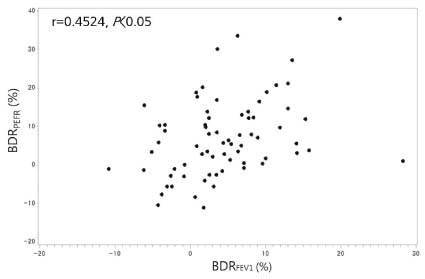
Among 20 children, 13 (65%) were successfully followed-up for 12 weeks with asthma kept stable. They presented similar spirometric values (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1], peak expiratory flow rate [PEFR], bronchodilator responses [BDRs] based on the FEV1 and PEFR) across all time-points. No differences in spirometric values were found between those who were stable and those who exhibited clues for asthma exacerbation. BDRs calculated from FEV1 values (BDRFEV1) correlated well with those calculated from PEFR values (BDRPEFR).
CONCLUSION
When controller medications were discontinued in children with well-controlled asthma, many of them were able to maintain the stable condition. Since the spirometric measures including BDR failed to differentiate clues for asthma exacerbation, the usefulness of office spirometry needs to be reevaluated by the larger population of children with controlled asthma after discontinuing medications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert panel report 3 (EPR-3): guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma-summary report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 120:5 Suppl. S94–S138.2. Guilbert TW, Morgan WJ, Zeiger RS, Mauger DT, Boehmer SJ, Szefler SJ, et al. Long-term inhaled corticosteroids in preschool children at high risk for asthma. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:1985–1997.
Article3. Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2005 Korean Guideline for Asthma Management. 2005. Seoul: Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology;77–108.4. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: 2008 update [Internet]. c2012. cited 2012 Aug 19. [place unknown]: The Global Initiative For Asthma;Available from: http://www.ginasthma.org/Guidelines/guidelines-resources.html.5. Deykin A, Lazarus SC, Fahy JV, Wechsler ME, Boushey HA, Chinchilli VM, et al. Sputum eosinophil counts predict asthma control after discontinuation of inhaled corticosteroids. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 115:720–727.
Article6. Leuppi JD, Salome CM, Jenkins CR, Anderson SD, Xuan W, Marks GB, et al. Predictive markers of asthma exacerbation during stepwise dose reduction of inhaled corticosteroids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 163:406–412.
Article7. Pijnenburg MW, Hofhuis W, Hop WC, De Jongste JC. Exhaled nitric oxide predicts asthma relapse in children with clinical asthma remission. Thorax. 2005. 60:215–218.
Article8. Prosperini G, Rajakulasingam K, Cacciola RR, Spicuzza L, Rorke S, Holgate ST, et al. Changes in sputum counts and airway hyperresponsiveness after budesonide: monitoring anti-inflammatory response on the basis of surrogate markers of airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 110:855–861.
Article9. Anderson SD. Provocative challenges to help diagnose and monitor asthma: exercise, methacholine, adenosine, and mannitol. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008. 14:39–45.
Article10. Linna O. Spirometry, bronchodilator test or symptom scoring for the assessment of childhood asthma. Acta Paediatr. 1996. 85:564–569.
Article11. Degryse J, Buffels J, Van Dijck Y, Decramer M, Nemery B. Accuracy of office spirometry performed by trained primary-care physicians using the MIR Spirobank hand-held spirometer. Respiration. 2012. 83:543–552.
Article12. Mortimer KM, Fallot A, Balmes JR, Tager IB. Evaluating the use of a portable spirometer in a study of pediatric asthma. Chest. 2003. 123:1899–1907.
Article13. Yoon KA, Lim HS, Koh YY, Kim H. Normal predicted values of pulmonary function test in Korean school-aged children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1993. 36:25–37.14. Lim DH, Kim JH, Park JH, Choi JW, Kim SK, Son BK. Normal predicted values of pulmonary function test in Korean primary school-aged children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1994. 37:240–249.15. Song DJ, Han YN, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Lim JY, Pee DH, et al. Lung function reference values in healthy Korean children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2002. 12:105–113.16. Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease. Normal predicted values of PEFR [Internet]. c2009. cited 2012 Aug 19. Seoul: Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease;Available from: http://www.kapard.or.kr/member/member08.html.17. Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F, Casaburi R, et al. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J. 2005. 26:948–968.
Article18. Dundas I, Chan EY, Bridge PD, McKenzie SA. Diagnostic accuracy of bronchodilator responsiveness in wheezy children. Thorax. 2005. 60:13–16.
Article19. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005. 26:319–338.
Article20. Bland JM, Altman DG. Calculating correlation coefficients with repeated observations: Part 1: Correlation within subjects. BMJ. 1995. 310:446.
Article21. Perera BJ. Successful withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids in childhood asthma. Respirology. 2005. 10:385–388.
Article22. Bahçeciler NN, Barlan IB, Nuhoğlu Y, Başaran MM. Which factors predict success after discontinuation of inhaled budesonide therapy in children with asthma? J Asthma. 2002. 39:37–46.
Article23. Dekker FW, Schrier AC, Sterk PJ, Dijkman JH. Validity of peak expiratory flow measurement in assessing reversibility of airflow obstruction. Thorax. 1992. 47:162–166.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacologic Treatment of Childhood Asthma
- Relevance of Exhaled Nitric Oxide Levels to Asthma Control Test Scores and Spirometry Values in Children with Atopic Asthma
- Use of Office Spirometry in Primary-Care Clinics
- Is It Necessary to Re-Evaluate Airway Hyperresponsiveness During Treatment of Mild Asthma?
- School-aged asthma children with high fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels and lung dysfunction are at high risk of prolonged lung dysfunction