Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis.
2011 Jun;21(2):131-136.
A Case of Laryngeal Neurofibroma with Sleep Obstructive Apnea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjhong@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
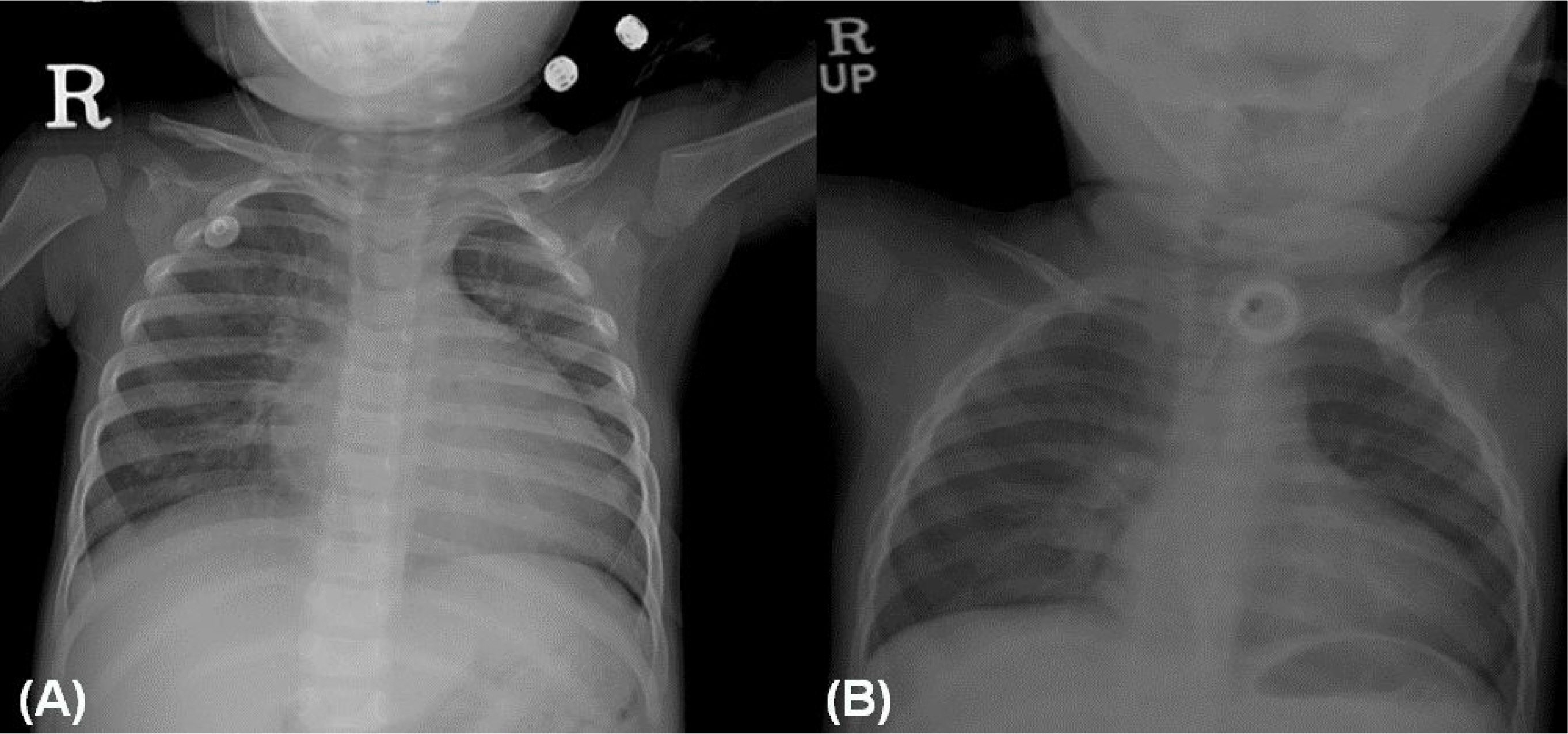
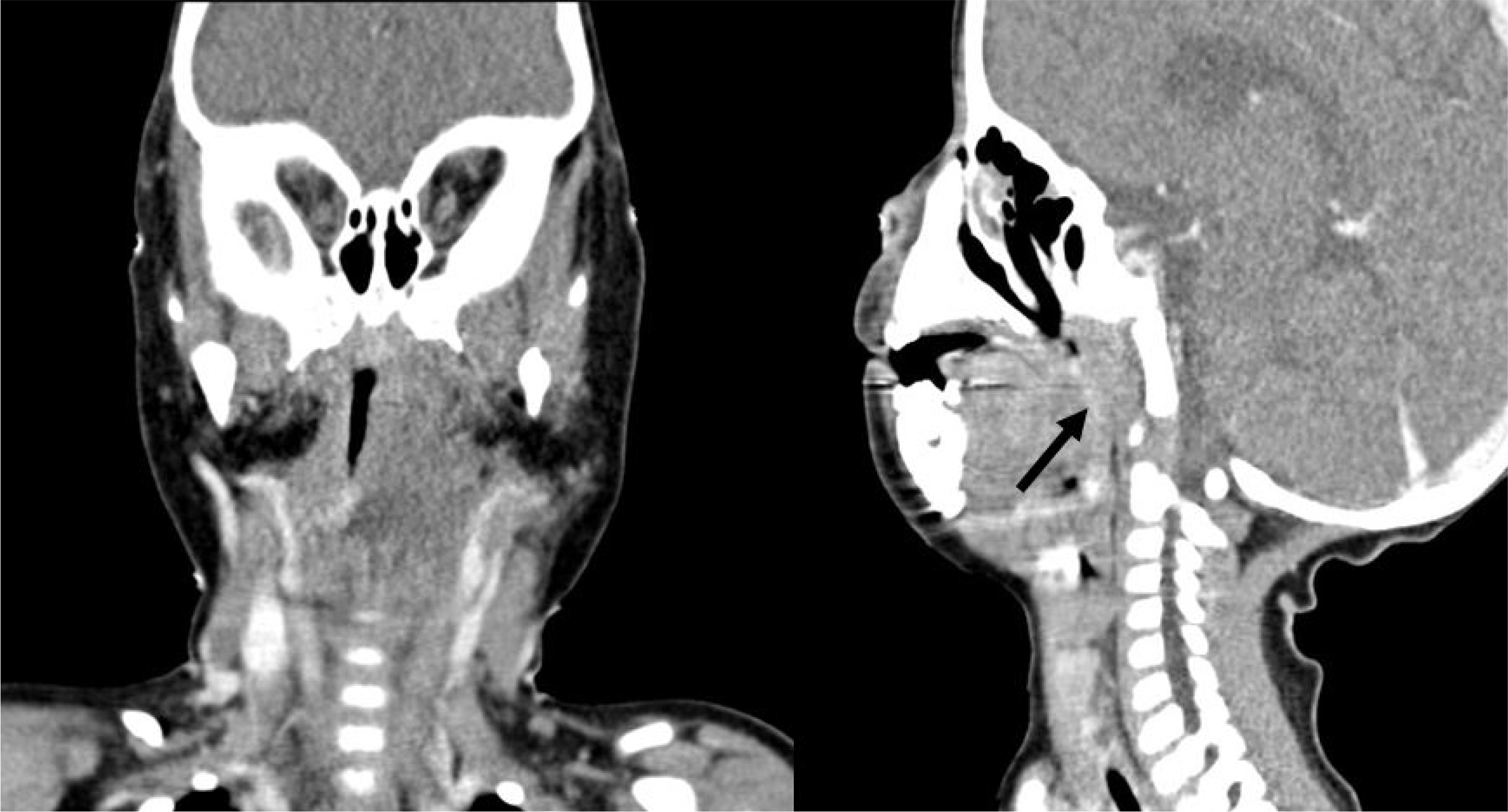
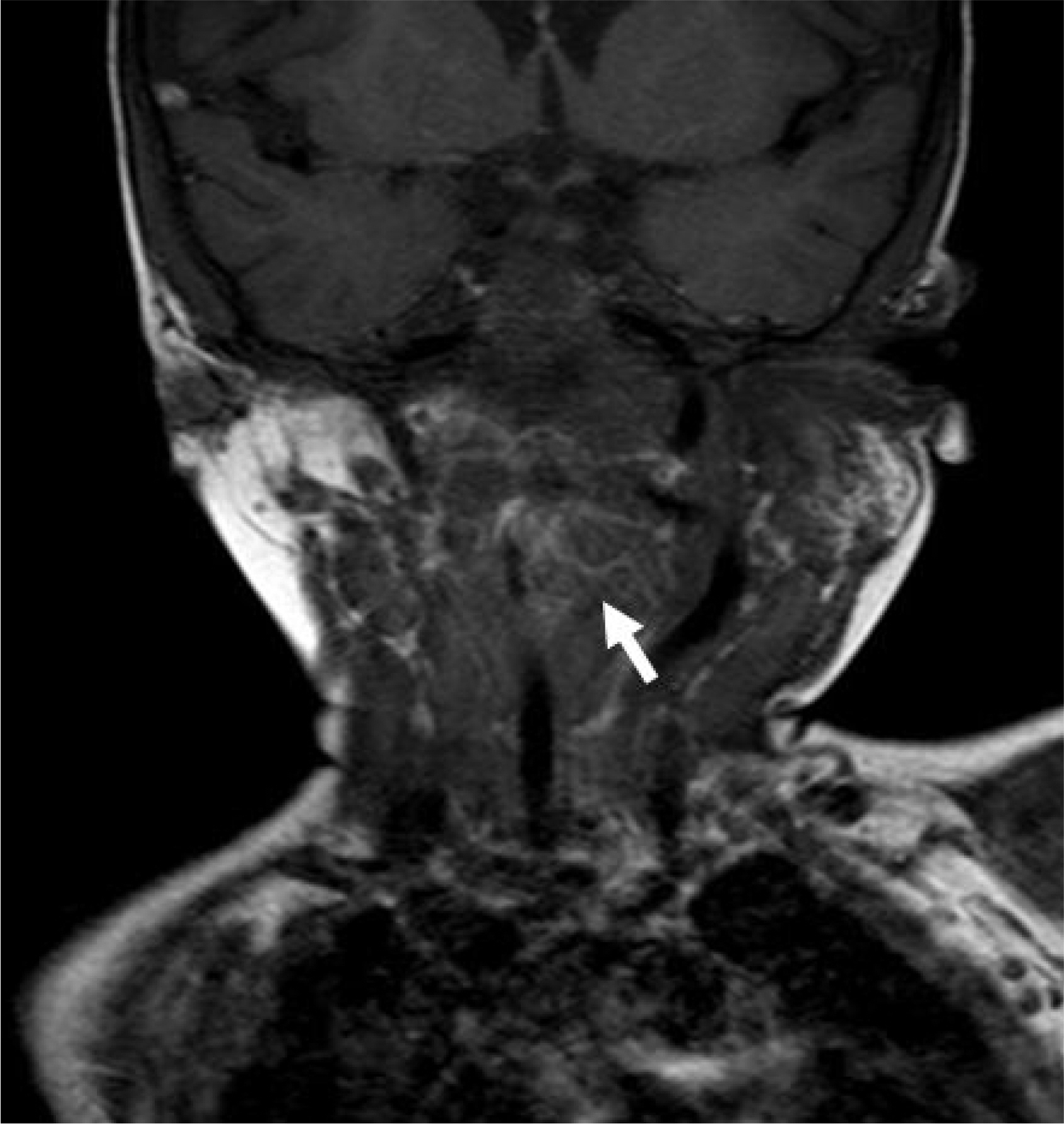
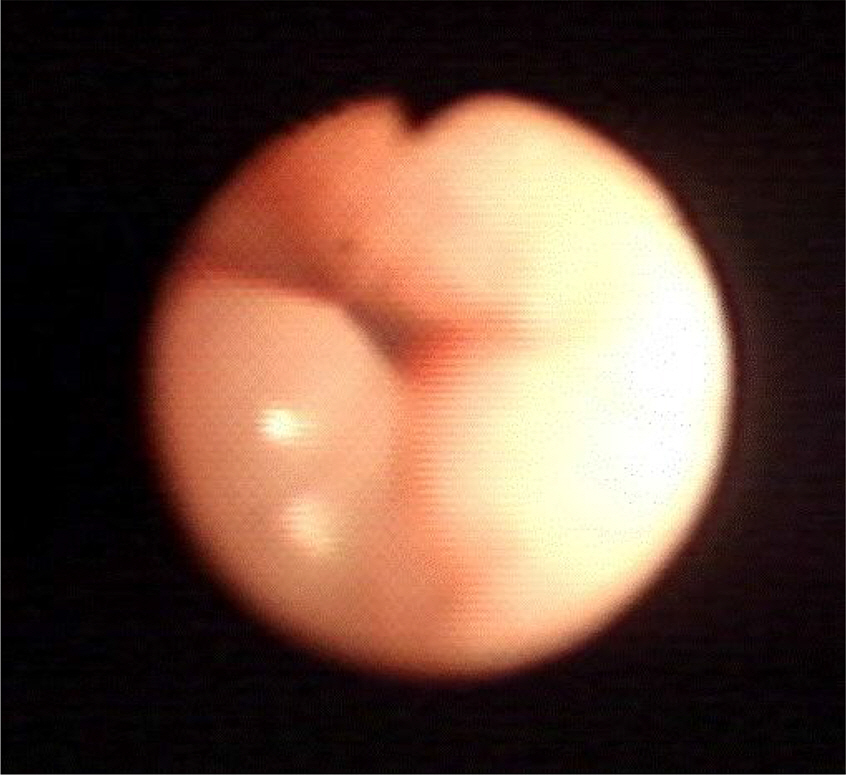
- Most patients with neurofibromas suffer from neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen's disease), which is characterized by cafe-au-lait spots and cutaneous neurofibromas. Neurofibromas in the laryngeal area are extremely rare. Most patients with a laryngeal neurofibroma present with dyspnea, dysphagia, stridor, or hoarseness, depending on the location and size of the tumor. We present a case of a laryngeal neurofibroma in a boy with neurofibromatosis type 1. A 30-month-old boy with neurofibromatosis presented to our hospital with respiratory difficulty and obstructive sleep apnea. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a round mass over the left carotid space, and its location made surgical resection impossible. Hence, tracheostomy was performed to maintain airway patency. The patient's symptoms improved after tracheostomy. Long-term follow-up is essential owing to the possibility of recurrence. The patient has thus far shown no obstructive airway symptoms for one year after closure of the tracheostomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sabol Z, Kipke-Sabol L. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen's disease or peripheral neurofibromatosis): from phenotype to gene. Lijec Vjesn. 2005; 127:303–11.2. Evans GR, Lloyd SK, Ramsden RT. Neurofibromatosis type 2. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011; 70:91–8.
Article3. Boudewyns A, Claes J, Van de Heyning P. Clinical practice: an approach to stridor in infants and children. Eur J Pediatr. 2010; 169:135–41.4. Chen YW, Fang TJ, Li HY. A solitary laryngeal neurofibroma ina pediatric patient. Chang Gung Med J. 2004; 27:930–3.5. Shah KN. The diagnostic and clinical significance of café-au-lait macules. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010; 57:1131–53.
Article6. Polgár N, Komlósi K, Hadzsiev K, Illés T, Me-legh B. Molecular genetic diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type I. Orv Hetil. 2011; 152:415–9.
Article7. Suchanek E. Neurinom des kehlkopfeinganges. Monatsschr Orhenheilkd Laryngo-Rhinol. 1925; 50:613–7.8. Willcox TO Jr, Rosenberg SI, Handler SD. Laryngeal involvement in neurofibromatosis. Ear Nose Throat J. 1993; 72:811–2. 815.
Article9. Masip MJ, Esteban E, Alberto C, Menor F, Cortina H. Laryngeal involvement in pediatric neurofibromatosis: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol. 1996; 26:488–92.
Article10. Powell S, Kubba H, O'Brien C, Tremlett M. Paediatric obstructive sleep apnoea. BMJ. 2010; 340:c1918.11. Marcus CL, Carroll JL, Koerner CB, Hamer A, Lutz J, Loughlin GM. Determinants of growth in children with the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Pediatr. 1994; 125:556–62.
Article12. Bland RM, Bulgarelli S, Ventham JC, Jackson D, Reilly JJ, Paton JY. Total energy expenditure in children with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J. 2001; 18:164–9.
Article13. Amin RS, Kimball TR, Bean JA, Jeffries JL, Willging JP, Cotton RT, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy and abnormal ventricular geometry in children and adolescents with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:1395–9.
Article14. Enright PL, Goodwin JL, Sherrill DL, Quan JR, Quan SF. Tucson Children's Assessment of Sleep Apnea study. Blood pressure elevation associated with sleep-related breathing disorder in a community sample of white and Hispanic children: the Tucson Children's Assessment of Sleep Apnea study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003; 157:901–4.15. Kraiczi H, Caidahl K, Samuelsson A, Peker Y, Hedner J. Impairment of vascular endothelial function and left ventricular filling: association with the severity of apnea-induced hypoxemia during sleep. Chest. 2001; 119:1085–91.16. Needle MN, Cnaan A, Dattilo J, Chatten J, Phillips PC, Shochat S, et al. Prognostic signs in the surgical management of plexiform neurofibroma: the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia experience, 1974–1994. J Pediatr. 1997; 131:678–82.
Article17. Sidman J, Wood RE, Poole M, Postma DS. Management of plexiform neurofibroma of the larynx. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1987; 96(1 Pt 1):53–5.
Article18. Rahbar R, Litrovnik BG, Vargas SO, Robson CD, Nuss RC, Irons MB, et al. The biology and management of laryngeal neurofibroma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 130:1400–6.
Article19. Ransom ER, Yoon C, Manolidis S. Single stage near total resection of massive pediatric head and neck plexiform neurofibromas. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 70:1055–61.
Article