Korean J Urol.
2010 Jan;51(1):30-33.
Learning Curve for Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy for Pathologic T2 Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urologic Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khrha@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
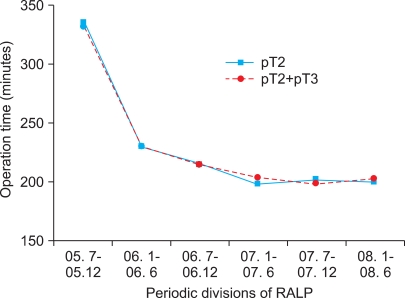
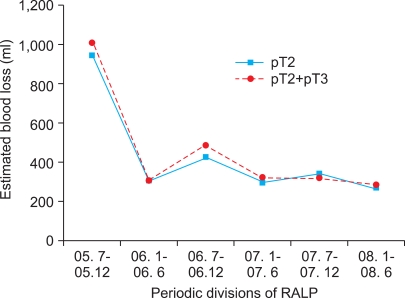
To investigate the learning curve for robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALP) for pathologic T2 disease, we examined differences in perioperative outcomes according to time period. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between July 2005 and June 2008, a total of 307 consecutive patients underwent RALP for prostate cancer and 205 patients had pathologic T2 disease. Patients were grouped into 6-month time periods. We collected and examined the patient's perioperative data including age, body mass index (BMI), prostate-specific antigen (PSA), operation time, estimated blood loss, and positive surgical margin. RESULTS: There were no significant differences among the groups in age (p=0.705), BMI (p=0.246), PSA (p=0.425), or prostate volume (p=0.380). Operation time (p<0.001) and estimated blood loss (p<0.001) decreased significantly with time. The positive surgical margin rate also showed a decreasing trend, but this was not significant (p=0.680). CONCLUSIONS: Operation time and estimated blood loss had a steep learning curve during the early 24 cases and then stabilized. A positive surgical margin rate, however, did not have a significant learning curve, although the positive surgical margin decreased continuously.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Binder J, Kramer W. Robotically-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2001; 87:408–410. PMID: 11251539.
Article2. Kong GS, Seong YK, Sung GT. Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy using da Vinci™ surgical robotic system: initial Korean experience. Korean J Urol. 2005; 46:353–359.3. Park SY, Ham WS, Choi YD, Rha KH. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: clinical experience of 200 cases. Korean J Urol. 2008; 49:215–220.
Article4. Pasticier G, Rietbergen JB, Guillonneau B, Fromont G, Menon M, Vallancien G. Robotically assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: feasibility study in men. Eur Urol. 2001; 40:70–74. PMID: 11528179.
Article5. Menon M, Tewari A, Baize B, Guillonneau B, Vallancien G. Prospective comparison of radical retropubic prostatectomy and robot-assisted anatomic prostatectomy: the Vattikuti Urology Institute experience. Urology. 2002; 60:864–868. PMID: 12429317.
Article6. Ahlering TE, Skarecky D, Lee D, Clayman RV. Successful transfer of open surgical skills to a laparoscopic environment using a robotic interface: initial experience with laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2003; 170:1738–1741. PMID: 14532766.
Article7. Zorn KC, Orvieto MA, Gong EM, Mikhail AA, Gofrit ON, Zagaja GP, et al. Robotic radical prostatectomy learning curve of a fellowship-trained laparoscopic surgeon. J Endourol. 2007; 21:441–447. PMID: 17451340.
Article8. Patel VR, Tully AS, Holmes R, Lindsay J. Robotic radical prostatectomy in the community setting--the learning curve and beyond: initial 200 cases. J Urol. 2005; 174:269–272. PMID: 15947662.
Article9. Wolfram M, Bräutigam R, Engl T, Bentas W, Heitkamp S, Ostwald M, et al. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: the Frankfurt technique. World J Urol. 2003; 21:128–132. PMID: 12851781.
Article10. Lee YS, Han WK, Yang SC, Rha KH. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Korean J Urol. 2006; 47:206–210.
Article11. Ahlering TE, Woo D, Eichel L, Lee DI, Edwards R, Skarecky DW. Robot-assisted versus open radical prostatectomy: a comparison of one surgeon's outcomes. Urology. 2004; 63:819–822. PMID: 15134953.
Article12. Tewari A, Srivasatava A, Menon M. A prospective comparison of radical retropubic and robot-assisted prostatectomy: experience in one institution. BJU Int. 2003; 92:205–210. PMID: 12887468.
Article13. Bentas W, Wolfram M, Jones J, Bräutigam R, Kramer W, Binder J. Robotic technology and the translation of open radical prostatectomy to laparoscopy: the early Frankfurt experience with robotic radical prostatectomy and one year follow-up. Eur Urol. 2003; 44:175–181. PMID: 12875935.
Article14. Jaffe J, Castellucci S, Cathelineau X, Harmon J, Rozet F, Barret E, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: a single-institutions learning curve. Urology. 2009; 73:127–133. PMID: 18952261.
Article15. Ban JH, Ko YH, Kang SH, Park HS, Cheon J. Learning curve with robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a prospective study. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:140–147.
Article16. Sim HG, Yip SK, Lau WK, Tan JK, Cheng CW. Early experience with robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Asian J Surg. 2004; 27:321–325. PMID: 15564188.
Article17. Hegarty NJ, Kaouk JH. Radical prostatectomy: a comparison of open, laparoscopic and robot-assisted laparoscopic techniques. Can J Urol. 2006; 13(Suppl 1):56–61. PMID: 16526984.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- A Case of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy in Primary Small Cell Prostate Cancer
- Learning Curve of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy for a Single Experienced Surgeon: Comparison with Simultaneous Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: the Learning Curve of the Initial 150 Cases
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy