Nutr Res Pract.
2015 Apr;9(2):192-198. 10.4162/nrp.2015.9.2.192.
Vitamin E status of 20- to 59-year-old adults living in the Seoul metropolitan area of South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Duksung Women's University, 33, Samyangro 114 Gill, Dobonggu, Seoul 132-714, Korea. yunokcho@duksung.ac.kr
- KMID: 2313829
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2015.9.2.192
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin and functions primarily as a lipid antioxidant. Inadequate vitamin E status may increase risk of several chronic diseases. Thus, the objectives of this study were to estimate intake and plasma concentration of each tocopherol and to evaluate vitamin E status of Korean adults.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
Three consecutive 24-h food recalls and fasting blood samples were collected from healthy 20- to 59-y-old adults (33 males and 73 females) living in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea. alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-tocopherol intakes and plasma concentrations of tocopherols (alpha-, delta-, and gamma-tocopherol) were analyzed by gender.
RESULTS
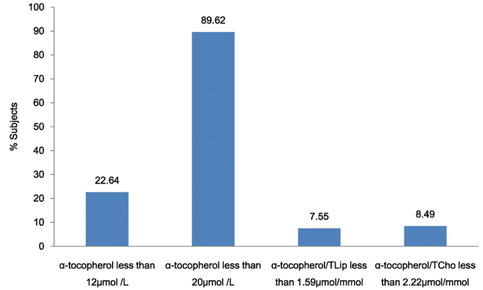
Dietary vitamin E and total vitamin E intake (dietary plus supplemental vitamin E) was 17.68 +/- 14.34 and 19.55 +/- 15.78 mg alpha-tocopherol equivalents, respectively. The mean daily alpha-tocopherol, and gamma-tocopherol intakes were 3.07 +/- 2.27 mg and 5.98 +/- 3.74 mg, respectively. Intakes of total vitamin E and each tocopherol of males were significantly higher than those of females (P < 0.05). Plasma alpha-tocopherol concentration was 15.45 +/- 10.16 of males and 15.00 +/- 4.54 micromol/L of females, respectively. There were no significant differences in plasma tocopherol concentrations by gender (P > or = 0.05). Plasma alpha-tocopherol was negatively correlated with gamma-tocopherol intake (P < 0.05). Twenty-three percent of the subjects had plasma alpha-tocopherol concentrations < 12 micromol/L indicating a biochemical deficiency of vitamin E. Approximately 8% and 9% of these participants had plasma alpha-tocopherol:total lipid ratio less than 1.59 micromol/mmol and plasma alpha-tocopherol:total cholesterol ratio less than 2.22 micromol/mmol, respectively, which are also indicative of vitamin E deficiency.
CONCLUSIONS
Vitamin E intakes of Korean adults were generally adequate with the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes for vitamin E. However, alpha-tocopherol intake was lower than that reported in other countries, and 23% of the subjects in the current study were vitamin E deficient based on plasma alpha-tocopherol concentrations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Folate food source, usual intake, and folate status in Korean adults
Young-Nam Kim, Youn-Ok Cho
Nutr Res Pract. 2018;12(1):47-51. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.1.47.Dietary intake and major source foods of vitamin E among Koreans: findings of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Jee-Seon Shim, Ki Nam Kim, Jung-sug Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutr Res Pract. 2022;16(5):616-627. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2022.16.5.616.α-Tocopherol and γ-tocopherol decrease inflammatory response and insulin resistance during the interaction of adipocytes and macrophages
Sella Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Nutr Res Pract. 2024;18(6):761-773. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.6.761.
Reference
-
1. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society;2010.2. McCullough ML, Feskanich D, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci EL, Rimm EB, Hu FB, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, Colditz GA, Willett WC. Diet quality and major chronic disease risk in men and women: moving toward improved dietary guidance. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002; 76:1261–1271.
Article3. Singh U, Devaraj S, Jialal I. Vitamin E, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Annu Rev Nutr. 2005; 25:151–174.
Article4. Constantinou C, Papas A, Constantinou AI. Vitamin E and cancer: an insight into the anticancer activities of vitamin E isomers and analogs. Int J Cancer. 2008; 123:739–752.
Article5. Sauberlich HE. Vitamin E (Tocopherols). Laboratory Tests for the Assessment of Nutritional Status. 2nd ed. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press;1999. p. 249–266.6. Burton GW, Traber MG, Acuff RV, Walters DN, Kayden H, Hughes L, Ingold KU. Human plasma and tissue alpha-tocopherol concentrations in response to supplementation with deuterated natural and synthetic vitamin E. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998; 67:669–684.
Article7. Behrens WA, Thompson JN, Madère R. Distribution of α-tocopherol in human plasma lipoproteins. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982; 35:691–696.
Article8. Horwitt MK, Harvey CC, Dahm CH Jr, Searcy MT. Relationship between tocopherol and serum lipid levels for determination of nutritional adequacy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972; 203:223–236.
Article9. Institute of Medicine (US). Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press;2000.10. Hensley K, Benaksas EJ, Bolli R, Comp P, Grammas P, Hamdheydari L, Mou S, Pye QN, Stoddard MF, Wallis G, Williamson KS, West M, Wechter WJ, Floyd RA. New perspectives on vitamin E: gamma-tocopherol and carboxyelthylhydroxychroman metabolites in biology and medicine. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004; 36:1–15.
Article11. Ju J, Picinich SC, Yang Z, Zhao Y, Suh N, Kong AN, Yang CS. Cancer-preventive activities of tocopherols and tocotrienols. Carcinogenesis. 2010; 31:533–542.
Article12. Bates CJ, Mishra GD, Prentice A. γ-tocopherol as a possible marker for nutrition-related risk: results from four National Diet and Nutrition Surveys in Britain. Br J Nutr. 2004; 92:137–150.
Article13. Baker H, Handelman GJ, Short S, Machlin LJ, Bhagavan HN, Dratz EA, Frank O. Comparison of plasma alpha and gamma tocopherol levels following chronic oral administration of either all-rac-alphatocopheryl acetate or RRR-alpha-tocopheryl acetate in normal adult male subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986; 43:382–387.
Article14. Cho SH, Lee OJ, Choi YS, Park WH. A study on serum lipid and vitamin E status and lifestyle factors in Korean men living in Taegu. J Appl Sci Res Inst. 1997; 5:181–190.15. Kim KJ, Lee HJ, Park YK, Kang MH. Association between plasma tocopherol levels and related factors in middle-aged Korean men. Korean J Nutr. 2006; 39:773–785.16. Kim CS, Kang HJ, Lee SH, Park YK, Kang MH. The effect of alpha-tocopherol supplementation on the improvement of antioxidant status and lymphocyte DNA damage in postmenopausal women. Korean J Nutr. 2007; 40:708–718.17. The Korean Nutrition Society. Computer Aided Nutritional Analysis Program for Professionals. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society;2011.18. Yonsei University, Research Institute of Food and Nutritional Sciences (KR). Phytonutrient Contents in Vegetable/Fruits/Legumes. Seoul: Shinkwang;2009.19. Kim YN, Giraud DW, Driskell JA. Tocopherol and carotenoid contents of selected Korean cooked combination foods consumed by young Korean children. Nutr Sci. 2006; 9:323–329.20. Kim YN, Giraud DW, Driskell JA. Tocopherol and carotenoid contents of selected Korean fruits and vegetables. J Food Compost Anal. 2007; 20:458–465.
Article21. United States Department of Agriculture, Agriculural Research Service. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 21. Washington, D.C.: Agriculural Research Service;2008. cited 2009 June-December. Available from: http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/search/.22. Giraud DW, Kim YN, Cho YO, Driskell JA. Vitamin E inadequacy observed in a group of 2- to 6-year-old children living in Kwangju, Republic of Korea. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2008; 78:148–155.
Article23. Gibson RS. Assessment of the status of vitamins A, D, and E. Principles of Nutritional Assessment. 2nd ed. New York (MY): Oxford University Press;2005. p. 477–528.24. Riemersma RA, Wood DA, Oliver MF, Elton RA, Macintyre CC, Gey KF. Risk of angina pectoris and plasma concentrations of vitamins A, C, and E and carotene. Lancet. 1991; 337:1–5.
Article25. Singh RB, Ghosh S, Niaz MA, Singh R, Beegum R, Chibo H, Shoumin Z, Postiglione A. Dietary intake, plasma levels of antioxidant vitamins, and oxidative stress in relation to coronary artery disease in elderly subjects. Am J Cardiol. 1995; 76:1233–1238.
Article26. Department of Health (GB). The Nutrition of Elderly People. Report on Health and Social Subjects No.43. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office;1992.27. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2009: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-3). Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2010.28. Shim JE, Paik HY, Lee SY, Moon HK, Kim YO, Kwon HH, Kim JH. Assessment of vitamin A and E status in Korean rural adult population by dietary intake and serum levels. Korean J Nutr. 2001; 34:213–221.29. Oh HM, Yoon JY, Cho SH, Yoon JS. Vitamin A and vitamin E status of diabetic patients and normal adults in Korea. Korean J Nutr. 2009; 42:318–326.
Article30. The Korean Nutrition Society. Improvement of Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans: Final report. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2009.31. Jenab M, Salvini S, van Gils CH, Brustad M, Shakya-Shrestha S, Buijsse B, Verhagen H, Touvier M, Biessy C, Wallström P, Bouckaert K, Lund E, Waaseth M, Roswall N, Joensen AM, Linseisen J, Boeing H, Vasilopoulou E, Dilis V, Sieri S, Sacerdote C, Ferrari P, Manjer J, Nilsson S, Welch AA, Travis R, Boutron-Ruault MC, Niravong M, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, van der Schouw YT, Tormo MJ, Barricarte A, Riboli E, Bingham S, Slimani N. Dietary intakes of retinol, β-carotene, vitamin D and vitamin E in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition cohort. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009; 63:Suppl 4. S150–S178.
Article32. Rural Resources Development Institute (KR). R.D.A. Food Composition Table. 7th rev. Wanju: Rural Resources Development Institute;2006.33. Zou Y, Wang DH, Sakano N, Sato Y, Iwanaga S, Taketa K, Kubo M, Takemoto K, Masatomi C, Inoue K, Ogino K. Associations of serum retinol, α-tocopherol, and γ-tocopherol with biomarkers among healthy Japanese men. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014; 11:1647–1660.
Article34. Bailey RL, Fulgoni VL 3rd, Keast DR, Dwyer JT. Examination of vitamin intakes among US adults by dietary supplement use. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012; 112:657–663.e4.
Article35. Talegawkar SA, Johnson EJ, Carithers T, Taylor HA Jr, Bogle ML, Tucker KL. Total α-tocopherol intakes are associated with serum α-tocopherol concentrations in African American adults. J Nutr. 2007; 137:2297–2303.
Article36. Lee HJ, Lee DH, Kim KO, Kim YJ, Lee HS. Analysis of serum antioxidant materials concentration and their relation with blood lipids and anthropometric indices in middle-aged adults in Korea. Korean J Nutr. 2009; 42:464–473.
Article37. Ford ES, Sowell A. Serum alpha-tocopherol status in the United States population: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Epidemiol. 1999; 150:290–300.
Article38. Thurnham DI, Davies JA, Crump BJ, Situnayake RD, Davis M. The use of different lipids to express serum tocopherol: lipid ratios for the measurement of vitamin E status. Ann Clin Biochem. 1986; 23:514–520.
Article39. Traber MG. Mechanisms for the prevention of vitamin E excess. J Lipid Res. 2013; 54:2295–2306.
Article40. Gao X, Martin A, Lin H, Bermudez OI, Tucker KL. α-Tocopherol intake and plasma concentration of Hispanic and non-Hispanic white elders is associated with dietary intake pattern. J Nutr. 2006; 136:2574–2579.
Article41. Ascherio A, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Rimm EB, Litin L, Willett WC. Correlations of vitamin A and E intakes with the plasma concentrations of carotenoids and tocopherols among American men and women. J Nutr. 1992; 122:1792–1801.
Article42. Friedrich MJ. To "E" or not to "E", vitamin E's role in health and disease is the question. JAMA. 2004; 292:671–673.
Article43. Khalil A, Gaudreau P, Cherki M, Wagner R, Tessier DM, Fulop T, Shatenstein B. Antioxidant-rich food intakes and their association with blood total antioxidant status and vitamin C and E levels in community-dwelling seniors from the Quebec longitudinal study NuAge. Exp Gerontol. 2011; 46:475–481.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vitamin A status of 20- to 59-year-old adults living in Seoul and the metropolitan area, Korea
- Evaluation of vitamin B6 intake and status of 20- to 64-year-old Koreans
- Vitamin A and Vitamin E Status of Diabetic Patients and Normal Adults in Korea
- Association between Vitamin D Status and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Korean Adults
- Assessment of Nutritional Status and Food Sources of Significant Nutrients with Picky Eating Behavior in Preschoolers