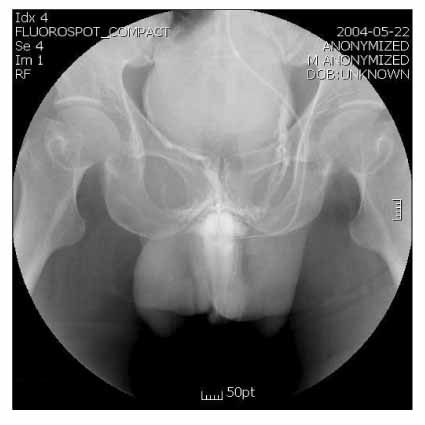
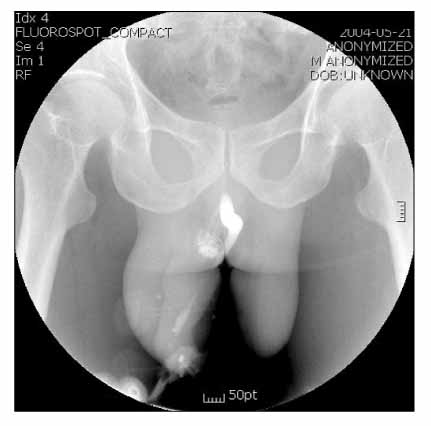
Korean J Urol.
2009 Feb;50(2):165-168.
Long-Term Results of Immediate Surgical Treatment of Penile Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chungj90@paran.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Penile fracture is a rare but serious urological condition. Immediate surgical repair is widely accepted as the treatment of choice in penile fracture. The aim of this study is to investigate the long-term outcome of immediate surgical treatment of penile fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a retrospective study of 12 men with penile fracture who were treated in the Department of Urology, Sanggyepaik Hospital, Seoul, Korea from January 2000 to June 2005. Diagnosis was made clinically and was confirmed by cavernosography in all our patients. All patients underwent immediate surgical repair, within two days after trauma, using a degloving incision. The long term results of the immediate surgical repair were evaluated using questionnaire on outpatient department visiting or telephoning.
RESULTS
The median patient age was 43 years (range, 18 to 57 years). The median follow-up was 32 months (range, 14 to 60 months). Of these patients, 8 (66.7%) patients were injured during sexual intercourse, whereas 4 (33.3%) patients were injured during masturbation. All patients were treated by immediate surgery. All patients reported satisfactory, painless erectile function; two developed penile curvature and one had a penile nodule.
CONCLUSIONS
Immediate surgical repair of penile fracture is effective, restores erectile function, and the incidence of complications is low.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dever DP, Saraf PG, Catanese RP, Feinstein MJ, Davis RS. Penile fracture: operative management and cavernosography. Urology. 1983. 22:394–396.2. Karadeniz T, Topsakal M, Ariman A, Erton H, Basak D. Penile fracture: differential diagnosis, management and outcome. Br J Urol. 1996. 77:279–281.3. Koga S, Saito Y, Arakaki Y, Nakamura N, Matsuoka M, Saita H, et al. Sonography in fracture of the penis. Br J Urol. 1993. 72:228–229.4. Shin DJ, Cheon MW, Kim MK, Park JK. The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of penile fracture. Korean J Urol. 2002. 43:49–51.5. Zargooshi J. Penile fracture in Kermanshah, Iran: report of 172 cases. J Urol. 2000. 164:364–366.6. Nicolaisen GS, Melamud A, Williams RD, McAninch JW. Rupture of the corpus cavernosum: surgical management. J Urol. 1983. 130:917–919.7. Wespes E, Libert M, Simon J, Schulman CC. Fracture of the penis: conservative versus surgical treatment. Eur Urol. 1987. 13:166–168.8. Fergany AF, Angermeier KW, Montague DK. Review of Cleveland Clinic experience with penile fracture. Urology. 1999. 54:352–355.9. Paparel P, Ruffion A. Rupture of copora cavernosa: clinical practice. Ann Urol. 2006. 40:267–272.10. Bae C, Lee YT. Penile fracture: a report of 6 cases. Korean J Urol. 1991. 32:623–628.11. Ko HS, Rha KC, Kim JS, Choi DY, Han YT. Penile fracture: a report of 4 cases. Korean J Urol. 1999. 40:245–249.12. Milles S, McAninch JW. Penile fracture and soft tissue injury in traumatic and reconstructive urology. 1996. 1st ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;693–698.13. Waller DA, Britton JP, Ferro MA. Rotational injury of the penis. Br J Urol. 1990. 65:425.14. Nehru-Babu M, Hendry D, Ai-Saffar N. Rupture of the dorsal vein mimicking fracture of the penis. BJU Int. 1999. 84:179–180.15. Mostafa H. Rupture of the dorsal artery of the penis as a result of sexual intercourse. J Urol. 1967. 97:314.16. Tsang T, Demby AM. Penile fracture with urethral injury. J Urol. 1992. 147:466–468.17. Jeong HH, Choi JB, Lee JB. Different clinical manifestations of penile fracture according to patients age. Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:168–172.18. Asgari MA, Hosseini SY, Safarinejad MR, Samadzadeh B, Bardideh AR. Penile fractures: evaluation, therapeutic approaches and long-term results. J Urol. 1996. 155:148–149.19. Morris SB, Miller MA, Anson K. Management of penile fracture. J R Soc Med. 1998. 91:427–428.20. Agrawal KS, Morgan BE, Shafique M, Shazely M. Experience with penile fractures in Saudi Arabia. Br J Urol. 1991. 67:644–646.21. Cortellini P, Ferretti S, Larosa M, Peracchia G, Arena F. Traumatic injury of the penis: surgical management. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1996. 30:517–519.22. Mydlo JH. Surgeon experience with penile fracture. J Urol. 2001. 166:526–529.23. Zargooshi J. Penile fracture in Kermanshah, Iran: the long-term results of surgical treatment. BJU Int. 2002. 89:890–894.24. Cheon J, Kim JJ. Fracture of the penis: results of early surgical treatment. Korean J Urol. 1991. 32:428–430.25. Hwang SW, Cho SP, Lee JB. Penile injury during erection: the clinical manifestations and results of operative treatment. Korean J Urol. 1997. 38:1229–1234.26. El Atat R, Sfaxi M, Benslama MR, Amine D, Ayed M, Mouelli SB, et al. Fracture of the penis: management and long-term results of surgical treatment. Experience in 300 cases. J Trauma. 2008. 64:121–125.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Penile Fracture: 2 Cases
- Risk Factors for Development of Long-term Complications after Surgical Repair of Penile Fracture
- Penile fracture: a report of 6 cases
- Penile fracture: experiences with conservative and surgical treatment
- Long-term Treatment Outcomes Between Surgical Correction and Conservative Management for Penile Fracture: Retrospective Analysis