Korean J Endocr Surg.
2016 Jun;16(2):25-30. 10.16956/kaes.2016.16.2.25.
Risk Factors for Distant Metastasis in Patients with Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gsyoon@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2308566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16956/kaes.2016.16.2.25
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The major issue of follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC) diagnosed after hemithyroidectomy is whether to undergo further treatments. The aim of this study is to examine the clinico-pathological characteristics of FTC and to evaluate the risk factors for distant metastasis.
METHODS
From 1993 to 2010, 274 patients underwent initial thyroid surgery and were subsequently diagnosed as FTC. After review of the histological sections by an experienced pathologist, 211 patients were confirmed as FTC and were enrolled in this study. Clinicopathological features were compared based on the presence or absence of distant metastases, and the risk factors for distant metastases and distant metastases-free survival (DMFS) rates were analyzed.
RESULTS
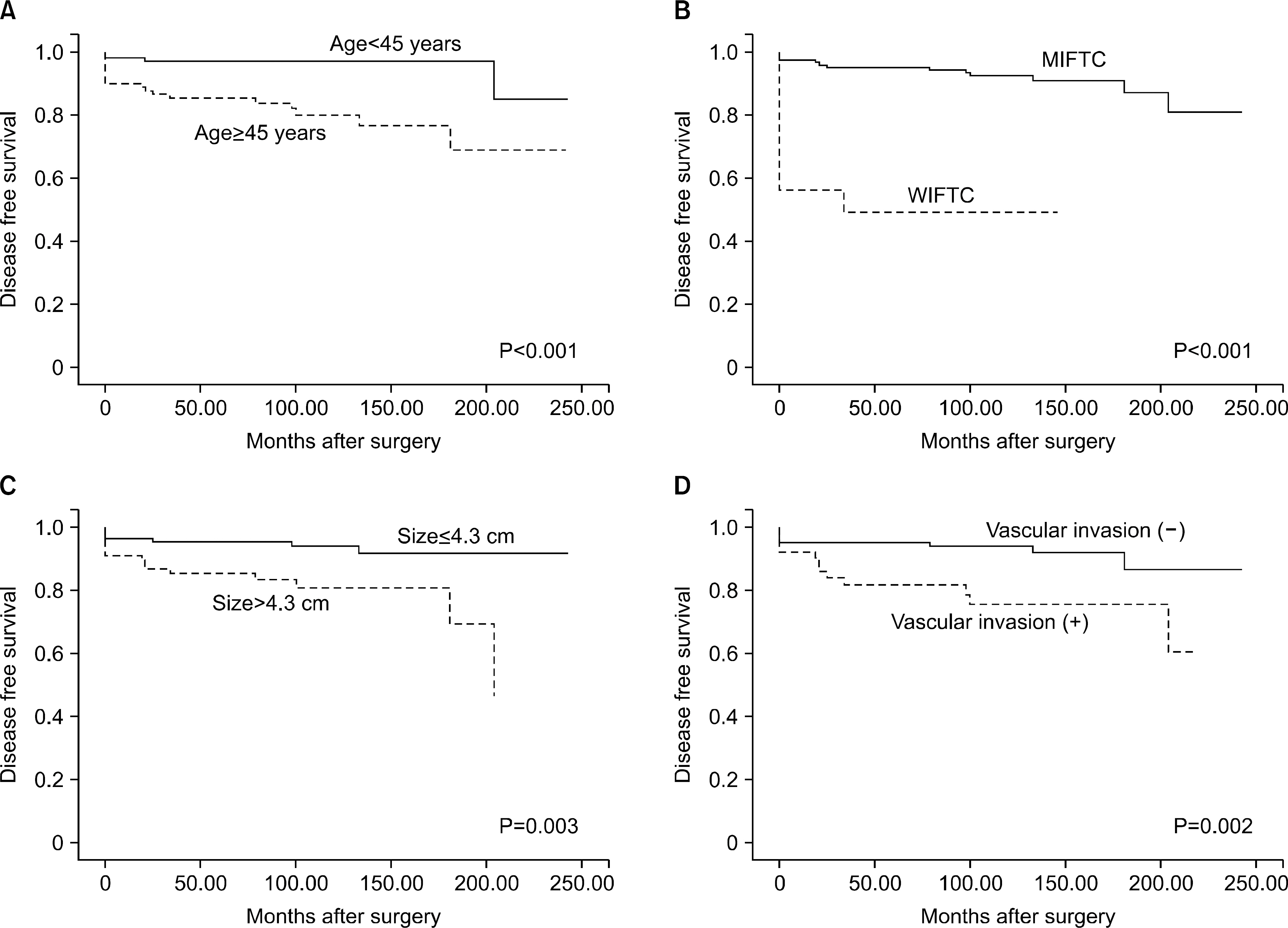
The patients included 39 males (18.5%) and 172 females (81.5%), with a mean age of 44.0±14.5 years. The median follow-up period was 99.5 months (range, 13.0~222.0). Distant metastases were detected in 23 patients (10.9%), including 15 synchronous distant metastases and 8 metachronous distant metastases. In multivariate analysis, age ≥45 years, widely invasive FTC, tumor size ≥4.3 cm, and vascular invasion were independent risk factors for distant metastasis. DMFS rates in patients with these risk factors were significantly poorer than those in patients without these risk factors.
CONCLUSION
Older age, aggressive histological classification, larger tumor size, and vascular invasion were independent risk factors for distant metastasis. FTC patients with these risk factors may be candidates for further treatments after diagnostic thyroid hemithyroidectomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Risk Factors for Distant Metastasis in Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma in Korea
Shin Dol Jo, Joon-Hyop Lee, Suk Ha Kang, Yun Yeong Kim, Yong Soon Chun, Heung Kyu Park, Sang Tae Choi, Jin Mo Kang, Yoo Seung Chung
J Endocr Surg. 2019;19(1):1-10. doi: 10.16956/jes.2019.19.1.1.
Reference
-
References
1. DeLellis R, Lloyd R, Heitz P, Eng C. WHO Classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of endocrine organs. Lyon: IARC Press;2004. p. 73–6.2. Lo CY, Chan WF, Lam KY, Wan KY. Follicular thyroid carcinoma: the role of histology and staging systems in predicting survival. Ann Surg. 2005; 242:708–15.3. Ito Y, Hirokawa M, Higashiyama T, Takamura Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, et al. Prognosis and prognostic factors of follicular carcinoma in Japan: importance of postoperative pathological examination. World J Surg. 2007; 31:1417–24.
Article4. Goffredo P, Cheung K, Roman SA, Sosa JA. Can minimally invasive follicular thyroid cancer be approached as a benign lesion?: a population-level analysis of survival among 1,200 patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:767–72.5. Sugino K, Kameyama K, Nagahama M, Kitagawa W, Shibuya H, Ohkuwa K, et al. Does completion thyroidectomy improve the outcome of patients with minimally invasive follicular carcinoma of the thyroid? Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:2981–6.
Article6. Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Tomoda C, Hirokawa M, Kobayashi K, Miya A. Prognostic significance of patient age in minimally and widely invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma: investigation of three age groups. Endocr J. 2014; 61:265–71.
Article7. Ban EJ, Andrabi A, Grodski S, Yeung M, McLean C, Serpell J. Follicular thyroid cancer: minimally invasive tumours can give rise to metastases. ANZ J Surg. 2012; 82:136–9.
Article8. Sugino K, Kameyama K, Ito K, Nagahama M, Kitagawa W, Shibuya H, et al. Outcomes and prognostic factors of 251 patients with minimally invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 2012; 22:798–804.
Article9. Delbridge L, Parkyn R, Philips J, Barraclough B, Robinson B. Minimally invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma: completion thyroidectomy or not? ANZ J Surg. 2002; 72:844–5.
Article10. O'Neill CJ, Vaughan L, Learoyd DL, Sidhu SB, Delbridge LW, Sywak MS. Management of follicular thyroid carcinoma should be individualised based on degree of capsular and vascular invasion. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2011; 37:181–5.11. Ito Y, Hirokawa M, Masuoka H, Yabuta T, Kihara M, Higashiyama T, et al. Prognostic factors of minimally invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma: extensive vascular invasion significantly affects patient prognosis. Endocr J. 2013; 60:637–42.
Article12. D'Avanzo A, Treseler P, Ituarte PH, Wong M, Streja L, Greenspan FS, et al. Follicular thyroid carcinoma: histology and prognosis. Cancer. 2004; 100:1123–9.13. Collini P, Sampietro G, Pilotti S. Extensive vascular invasion is a marker of risk of relapse in encapsulated non-Hürthle cell follicular carcinoma of the thyroid gland: a clinicopathological study of 18 consecutive cases from a single institution with a 11-year median follow-up. Histopathology. 2004; 44:35–9.14. Lang BH, Lo CY, Chan WF, Lam KY, Wan KY. Staging systems for follicular thyroid carcinoma: application to 171 consecutive patients treated in a tertiary referral centre. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007; 14:29–42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Definition and Prognostic Factor of Minimally Invasive Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
- A Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma Presenting as Single Bone Metastasis to Distal Femur with Pathologic Fracture: a Case Report
- Tremendous Skull Metastasis from Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Case Reort
- Successful Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Metastasis from Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma with Lenvatinib
- Solitary metastasis to the kidney from follicular carcinoma of the thyroid