Korean J Adult Nurs.
2013 Dec;25(6):597-609.
Adaptation Experience to Work of Nurses with Low Back Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Inje University, Busan, Korea. jhyang@inje.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Health Science, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was to explore work experience among nurses with low back pain. Specific aims were to identify problems nurses face as workers at a hospital and how they interact with other workers.
METHODS
Grounded theory methodology was utilized. Data were collected from iterative fieldwork with individual in-depth interviews from 9 nurses with low back pain as key informants, and a head nurse and a charge nurse who had experiences working with nurses with low back pain as general informants.
RESULTS
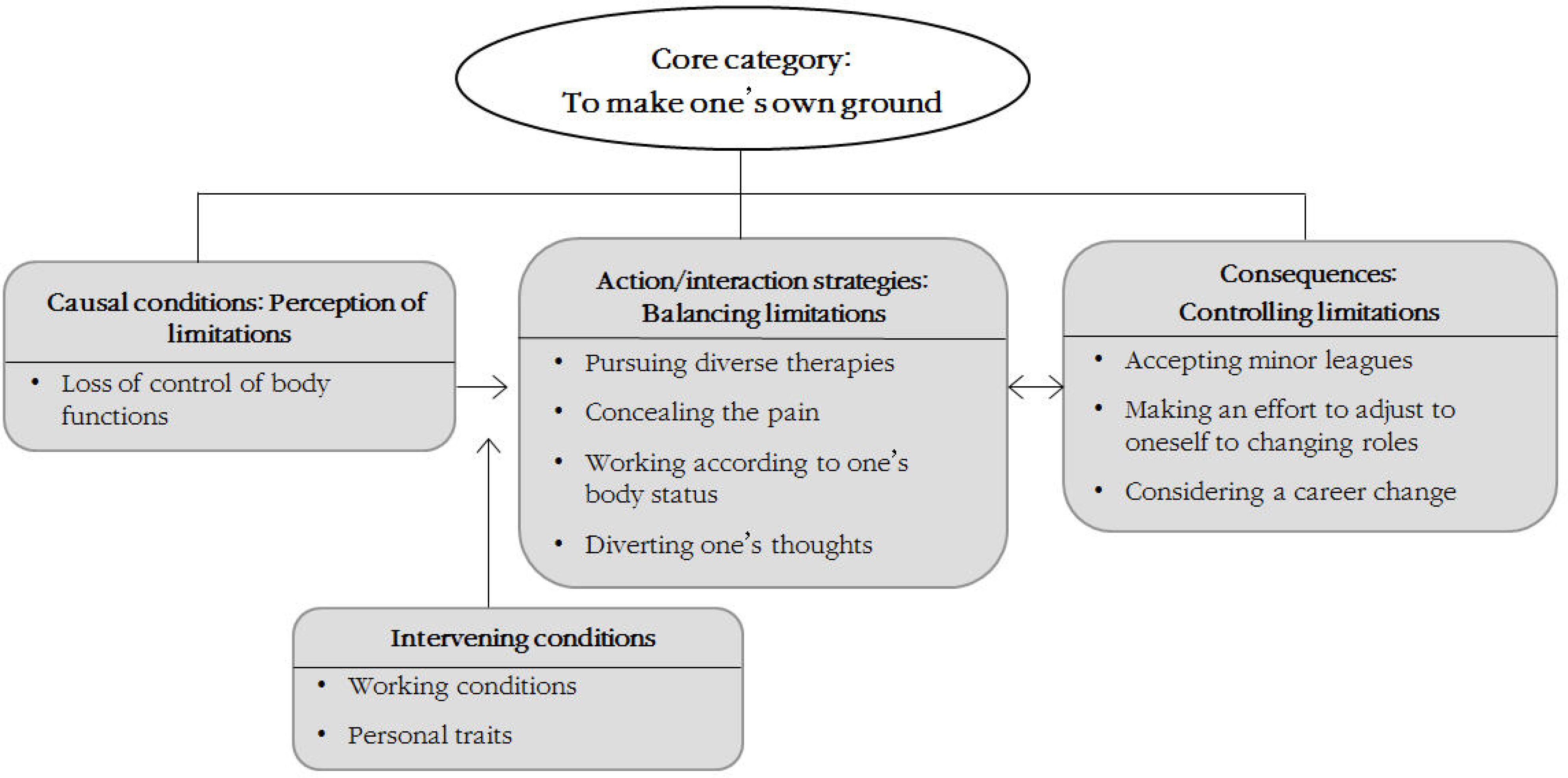
Through constant comparative analysis, a core category emerged as "to make one's own ground". The process of "to make one's own ground" was identified as four categories: perception of limitations, intervening conditions, balancing limitations, and controlling limitations. Intervening conditions were identified as 'working conditions' and 'personal traits'.
CONCLUSION
Findings of the study indicate that there is a need for health professionals and administrators to understand limitations to working experience among nurses with low back pain. In addition, institutional and psychological support program is needed to improve an adaptation to working environment among nurses with low back pain.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
Buijs P. C.., Lambeek L. C.., Koppenrade V.., Hooftman W. E.., Anema J. R.2009. Can workers with chronic back pain shift from pain elimination to function restore at work? Qualitative evaluation of an innovative work related multidisciplinary programme. Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. 22:65–73. http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/BMR-2009-0215.Coole C.., Drummond A.., Watson P. J.., Radford K.2010. What concerns workers with low back pain? Findings of a qualitative study of patients referred for rehabilitation. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation. 20:472–480. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10926-010-9237-5.
ArticleCorbin J.., Strauss A.2008. Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.Crowe M.., Whitehead L.., Gagan M. J.., Baxter D.., Panck-hurst A.2010-a. Self-management and chronic low back pain: A qualitative study. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 66:1478–1486. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05316.x.
ArticleCrowe M.., Whitehead L.., Gagan M. J.., Baxter G. D.., Pankhurst A.., Valledor V.2010-b. Listening to the body and talking to myself - the impact of chronic lower back pain: A qualitative study. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 47:586–592. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.09.012.
ArticleGeiger-Brown J.., Trinkoff A. M.., Nielsen K.., Lirtmunlikaporn S.., Brady B.., Vasquez E. I.2004. Nurses' perception of their work environment, health, and well-being: A qualitative perspective. Official Journal of the American Association of Occupational Health Nurses. 52:16–22.Griffiths F.., Borkan J.., Byrne D.., Crabtree B. F.., Dowrick C.., Gunn J., et al. 2010. Developing evidence for how to tailor medical interventions for the individual patient. Qualitative Health Research. 20:1629–1641. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049732310377453.
ArticleHolloway I.., Sofaer-Bennett B.., Walker J.2007. The stigmatisation of people with chronic back pain. Disability and Rehabilitation. 29:1456–1464.
ArticleHsieh L. L.., Kuo C. H.., Yen M. F.., Chen T. H.2004. A randomized controlled clinical trial for low back pain treated by acupressure and physical therapy. Preventive Medicine. 39:168–176.
ArticleJun K. J.2009. Occupational diseases and injuries among Korean nurses. Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing. 18:194–204.Kim E. A.2010. Occupational diseases of health care works. Hanyang Medical Reviews. 30:265–273.Kim J.., Lee J. A.., Choi S. H.., Hwang S. S.., Jung M. H.2007. Nurses and low back pain: A literature reviews. Journal of the Korean Society of Living Environmental system. 14:298–312.Kim K. S.., Park J. K.., Kim D. S.2010. Status and characteristics of occurrence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders. Journal of the Ergonomics Society of Korea. 29:405–422. http://dx.doi.org/10.5143/JESK.2010.29.4.405.
ArticleKim Y. H.., Kim Y. S.., Ahn Y. H.2007. Low back pain and job stress in hospital nurses. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 14:5–12.Ko J. K.2007. Comparing the effects of drug therapy, physical therapy, and exercise on pain, disability, and depression in patients with chronic low back pain. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 37:645–654.
ArticleKorean Statistical Information Service. 2011. Survey on working environment. Retrieved March 25, 2013, from. http://kosis.kr/wnsearch/totalSearch.jsp.Lee J. K.1999. A Phenomenological Study on the exercise experience of patients with low back pain. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 6:114–129.Lipscomb J. A.., Trinkoff A. M.., Geiger-Brown J.., Brady B.2002. Work-schedule characteristics and reported musculoskeletal disorders of registered nurses. Scandinavian. Journal of Work, Environment & Health. 28:394–401.Matthias M. S.., Miech E. J.., Myers L. J.., Sargent C.., Bair M. J.2012. An expanded view of self-management: Patients' perceptions of education and support in an intervention for chronic musculoskeletal pain. Pain Medicine. 13:1018–1028. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2012.01433.x.
ArticleMay S.2007. Patients' attitudes and beliefs about back pain and its management after physiotherapy for low back pain. Physiotherapy Research International. 12:126–135.
ArticleNelson A.., Owen B.., Lloyd J. D.., Fragala G.., Matz M. W.., Ama-to M., et al. 2003. Safe patient handling and movement. The American Journal of Nursing. 103(3):32–43.
ArticlePark J. K.., Jang S. H.., Kim D. S.., Hur K. H.., Lee H. Y.., Choi E. Y., et al. 2010. Musculoskeletal disorders and job stress risk factors in general hospital nurses: Nursing tasks and musculoskeletal disorder symptoms. Paper presented at the meeting of the Ergonomics Society of Korea, 2010 (10). 86–89.Shaw W. S.., Huang Y. H.2005. Concerns and expectations about returning to work with low back pain: Identifying themes from focus groups and semi-structured interviews. Disability and Rehabilitation. 27:1269–1281.
ArticleSoklaridis S.., Ammendolia C.., Cassidy D.2010. Looking upstream to understand low back pain and return to work: Psychosocial factors as the product of system issues. Social Science & Medicine. 71:1557–1566. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2010.08.017.
ArticleSong R.., Ahn S.2008. Effect of lumbar stabilization exercise on back pain, physical fitness, sleep, and depression in middle-aged women with chronic back pain. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 20:269–279.Sung M. H.., Seo D. H.., Eum O. B.2010. Factors affecting low back pain in nurses in intensive care unit. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 17:343–350.Wiitavaara B.., Lundman B.., Barnekow-Bergkvist M.., Brulin C.2007. Striking a balance—health experiences of male ambulance personnel with musculoskeletal symptoms: A grounded theory. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 44:770–779.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Risk Factors of Low Back Pain in General Hospital Nurses
- A Survey on Low Back Pain of General Hospital Nurses
- New Nurses’ Work Adaptation Experience
- Win-Win Partnership in the Clinical Setting: Female Nurses' Adaptive Experience to Male Nurses
- The Risk Factors of Industrial Low Back Pain among Shipyard Workers