Korean J Adult Nurs.
2014 Dec;26(6):681-692. 10.7475/kjan.2014.26.6.681.
Qualitative Study on Clinical Nurses' Intention to Stay in Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Sunchon National Universtiy, Suncheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea. jongkimk@dankook.ac.kr
- 3Department of Nursing, Changwon University, Changwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2298158
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2014.26.6.681
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the experience of hospital nurses regarding their intention to stay at hospital.
METHODS
Experiential data were collected from 10 experienced nurses through in-depth interviews. The main question was "Could you describe your experience and your work during your years at the hospital?" Qualitative data from the field and transcribed notes were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory methodology.
RESULTS
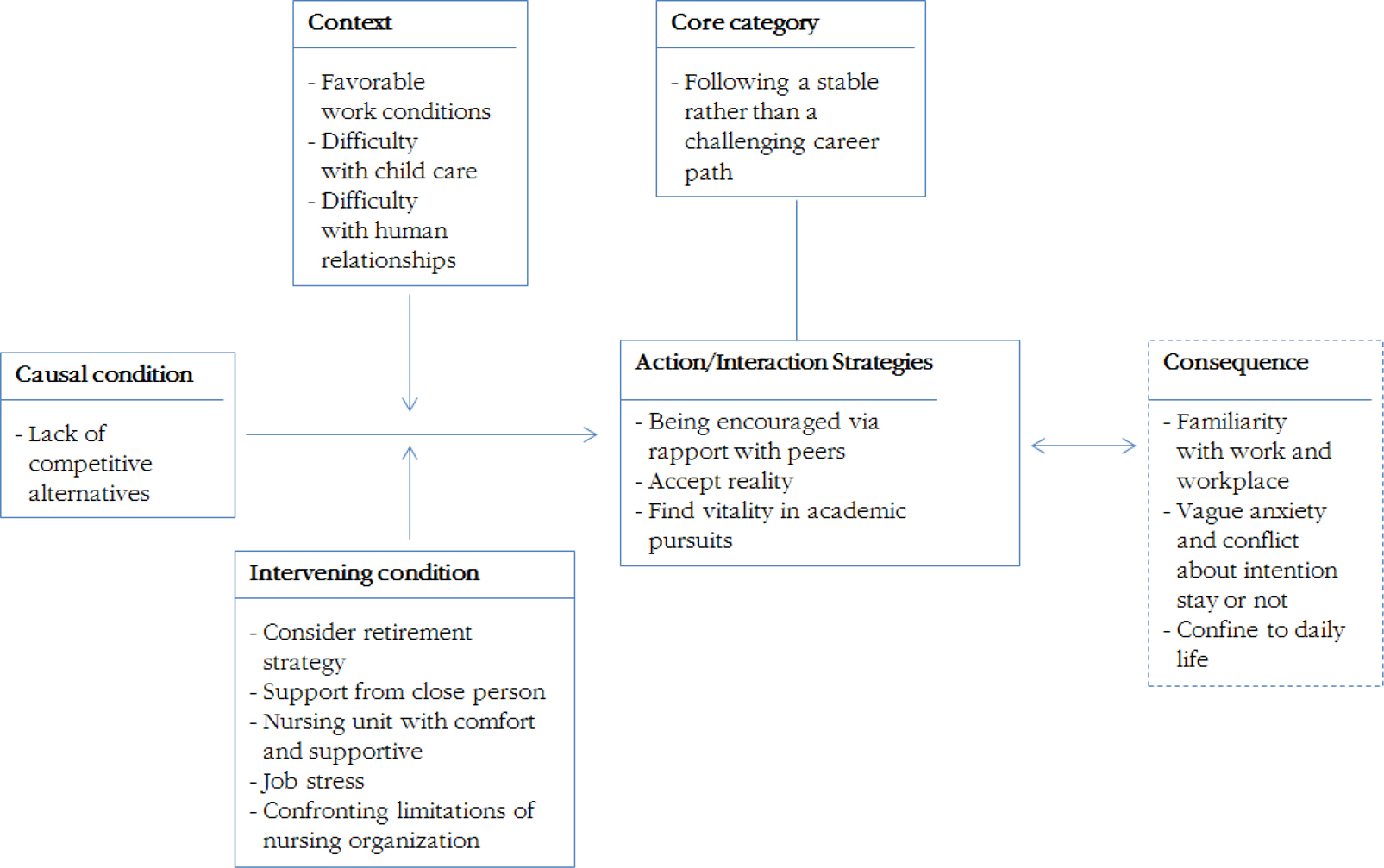
The core category of experience regarding hospital nurses' intention to stay was 'following a stable rather than a challenging path'. Participants used three interactional strategies: 'being encouraged via rapport with peers', 'accept reality', and 'find vitality in academic pursuits'.
CONCLUSION
The retention of experienced nurses is critical to human resource management in nursing departments. This study found that experienced nurses have a vague uncertainty about their future in the hospital. Therefore, nursing managers should support experienced nurses by providing them with the opportunities needed to develop their careers, by managing conflicts in nursing units, and by implementing new programs to increase confidence.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Factors Influencing Korean Nurses’ Intention to Stay: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sunhee Park, Taewha Lee
J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2018;24(2):139-148. doi: 10.11111/jkana.2018.24.2.139.
Reference
-
1.Kim JH. The effect of job embeddeddness on turnover intention and organizational citizenship behavior in hospital employee-focusing on moderating effect of personality traits. [dissertation]. Pusan: Kyungsung University;2009. p. 1–132.2.Park KW. The system and policy related to nursing program. Nursing Inquiry. 2006. 15:5–17.3.Ingersoll GL., Olsan T., Drew-Cates J., Devinney BC., Davis J. Nurses' job satisfaction, organizational commitment and career intent. Journal of Nursing Administration. 2002. 32(5):250–63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005110-200205000-00005.
Article4.Shin YG. Management principle -system approach-. Seoul: Dasan Publication;2011. p. 10–20.5.Kim JK., Kim MJ. A review of research on hospital nurses' turnover intention. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2011. 17(4):538–50.
Article6.Cotton JL., Tuttle JM. Employee turnover: a meta analysis and review with implication for research. The Academy of Management Review. 1986. 11(1):57–70. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/258331.7.Lee MA. Effect of nurses'perception of reward and organizational commitment on their turnover intention. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2009. 15(3):434–43.8.Reitz OE., Anderson MA. An overview of job embeddedeness. Journal of Professional Nursing. 2011. 27(5):320–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.profnurs.2011.04.004.9.Mitchell TR., Holtom BC., Thomas W., Lee TW., Sablynski CJ., Erez M. Why people stay: using job embeddedness to predict voluntary turnover. The Academy of Management Journal. 2001. 44(6):1102–21. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3069391.
Article10.Halfer D. Job embeddedness factors and retention of nurses with 1 to 3 years of experience. A Journal for Continuing Education. 2011. 42(10):468–76. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/00220124-20110601-02.
Article11.Price JL., Mueller CW. A causal model of turnover for nurses. The Academy of Management Journal. 1981. 24(3):543–65. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/255574.
Article12.Lee TW., Mowday RT. Voluntarily leaving an organization: an empirical investigation of Steers and Mowday's model of turnover. Academy of Management Journal. 1987. 30(4):721–43.
Article13.Ryu JR. (A) Study on the effects of job embeddedness on staying in organization [master's thesis]. Busan: Pusan University;2005. p. 1–109.14.Shin KR., Kim MY. Basic of qualitative research. Seoul: Hyoon-moonsa;2009.15.Strauss A., Corbin JM. Basics of qualitative research: grounded theory procedures and techniques. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications;1990.16.Che GS., Noe WJ., Park MM., Jeong EJ., Cho YY. Survey about placement of hospital nursing. Report. Hospital Nurses Association. 2013. 103.17.Lee EH., Cho KS., Son HM. A study of hospital nurse's intention to keep nursing job. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2014. 20(1):15–27.18.Park KO., Kim SY., Kim JK. Hospital nurses' experience of bullying in the workplace and burnout, organizational commitment, turnover intention and nursing productivity. Journal of Clinical Nursing Research. 2013. 19(2):169–80.19.Kim SY., Kim JK., Park KO. The role experience of preceptor nurses in hospitals. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2012. 18(1):33–45.
Article20.Kim HS., Yim HW., Jeong SH., Jo SJ. An association among verbal abuse, social support and turnover intention for special unit nurses in a hospital. The Korean Journal of occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2009. 12(4):388–95.
Article21.Lee YJ., Kim KB. Experience of nurse turnover. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008. 38(2):248–57.22.Lee Sy., Oh EJ., Sung KM. The experience of turnover intention in early stage nurses. Journal of East-West Nursing Research. 2013. 19(2):168–76.23.Son HM., Kim HS., Koh MH., Yu SJ. Analysis of the communication education in the undergraduate nursing curriculum of Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Social Nursing Education. 2001. 17(3):426–34. http://dx.doi.org/10.5977/JKASNE.2011.17.3.424.
Article24.Hayburst A., Saylor C., Stuenkel D. Work environmental factors and retention of nurses. Journal of Nursing Care Quality. 2005. 29(3):283–8.
Article25.Park YL., Yang S. Nurses manager's facilitative communication and nurses's organizational commitment, job satisfaction and empowerment. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2008. 17(3):342–52.26.Kang KH., Han YH., Kang SJ. Relationship between organizational communication satisfaction and organizational commitment among hospital nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2012. 18(1):13–22.
Article27.Kwon JA. Clinical nurses' working environment and intention of retention. [master's thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang University;2009. p. 1–59.28.Kim SY., Park KO., Kim JK. Nurses'experience of incivility in general hospitals. Journal of Korean Academy Nursing. 2013. 43(4):453–67. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.453.29.Kim MA., Park KO., You SJ., Kim MJ., Kim ES. A survey of nursing activities in small and medium-size hospitals: reasons for turnover. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2009. 15(1):149–65.30.Han YH., Sohn IS., Park KO., Kang KH. The relationships between professionalism, job involvement, organizational commitment and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2010. 16(2):17–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationships among Grit, Job Satisfaction, and the Intention to Stay of Clinical Nurses in Korea
- Effect of Preceptors' Teaching Behavior on New Graduate Nurses' Intention to Stay: The Mediating Effect of Resilience and Organizational Socialization
- Affecting Factors on Intention to Stay of Nurses Working at a University Hospital
- Effects of Job Embeddedness, Professional Self-concept, and Work-life Balance on Clinical Nurses’ Intention to Stay
- The Mediating Effect of Grit on the Relationship between Work Environment and Intention to Stay at Work among Regional Trauma Center Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study