J Korean Fract Soc.
2007 Apr;20(2):196-201. 10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.196.
Comparison of the Surgical Treatment Results of Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament between Children and Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Joint Disease, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. park5962@paran.com
- KMID: 2295580
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.196
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the clinical and radiological results after surgical treatments of the avulsion fractures of ACL between children and adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
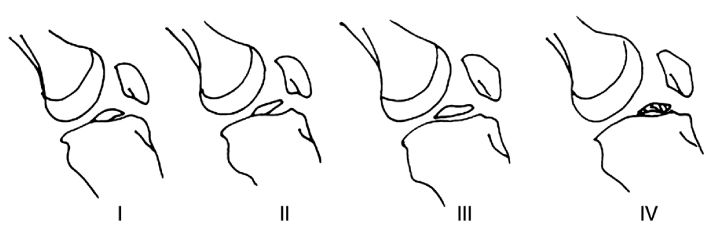
40 cases (18 cases of children, 22 cases of adults), who underwent surgical treatments after avulsion fractures of the ACL and followed up more than one year, were enrolled. Fractures were classified by modified Meyers & McKeever criteria. Range of motion, LK score, Lachman test, Pivot-Shift test, quadriceps muscle atropy and Telos® stress arthrometer were compared.
RESULTS
The types of fracture in children were categorized into 8 cases of type II, 10 cases of type III, and 2, 15, 5 cases of type II, III, IV each in adult group. Mean LK score showed significant difference between 99.3 points in children and 89.5 points in adults (p<0.05). In addition, accompanied injuries and the high degree of fracture leaded low LK score. However, there was no significant difference in range of motion, Lachman test and Pivot-Shift test. Anterior laxity by Telos® device showed an average of 2.0 mm in children, 2.5 mm in adults (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Children group showed better treatment results of avulsion fracture of ACL. Higher incidence of type II fractures and less combined injuries considered to be factors for better results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baxter MP, Wiley JJ. Fracture of the tibial spine in children. An evaluation of knee stability. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988; 70:228–230.2. Burstein DB, Viola A, Fulkerson JP. Entrapment of the medial meniscus in a fracture of the tibial eminence. Arthroscopy. 1988; 4:47–50.
Article3. Grönkvist H, Hirsch G, Johansson L. Fracture of the anterior tibial spine in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984; 4:465–468.
Article4. Hess T, Rupp S, Hopf T, Gleitz M, Liebler J. Lateral tibial avulsion fractures and disruptions to the anterior cruciate ligament. A clinical study of their incidence and correlation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; 303:193–197.5. Iobst CA, Stanitski CL. Acute knee injuries. Clin Sports Med. 2000; 19:621–635.
Article6. Kendall NS, Hsu SY, Chan KM. Fracture of the tibial spine in adults and children. A review of 31 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992; 74:848–852.
Article7. Keys GW, Walters J. Nonunion of intercondylar eminence fracture of the tibia. J Trauma. 1988; 28:870–871.
Article8. Lubowitz JH, Grauer JD. Arthroscopic treatment of anterior cruciate ligament avulsion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (294):242–246.
Article9. McLennan JG. The role of arthroscopic surgery in the treatment of fractures of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982; 64:477–480.
Article10. McNair PJ, Marshall RN, Matheson JA. Important features associated with acute anterior cruciate ligament injury. N Z Med J. 1990; 103:537–539.11. Meyers MH, Mckeever FM. Fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52:1677–1684.
Article12. Song EK, Seol JY, Choi J. The surgical treatment of chronic avulsion fracture of the anterior curciate ligament. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2002; 6:31–36.13. Wiley JJ, Baxter MP. Tibial spine fractures in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 255:54–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Avulsion Fracture of Femoral Attachment of Anterior Cruciate Ligament in a 7-Year-Old Girl
- Avulsion Fractures of the Anterior Cruciate and Posterior Cruciate Ligaments in a Skeletally Immature Child
- Bilateral PCL Avulsion Fracture from Tibial Attatchment Site in a 16-years-old Male : A Case Report
- Avulsion of the Femoral Attachment of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Associated with Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft Fracture in Skeletally Mature Patient: A Case Report
- Avulsion Fracture of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament from Femoral Insertion Occurred in a Patient with Residual Poliomyelitis: A Case Report