J Korean Fract Soc.
2007 Apr;20(2):178-183. 10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.178.
Joint Depression Type of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures Treated with Essex-Lopresti Method
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Handong University Sunlin Hospital, Pohang, Korea. docos@naver.com
- KMID: 2295577
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.178
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the result of joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures treated with Essex-Lopresti method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 2001 to February 2005, Thirty two patients' joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures which treated with Essex-Lopresti method were clinically and radiographically evaluated retrospectively.
RESULTS
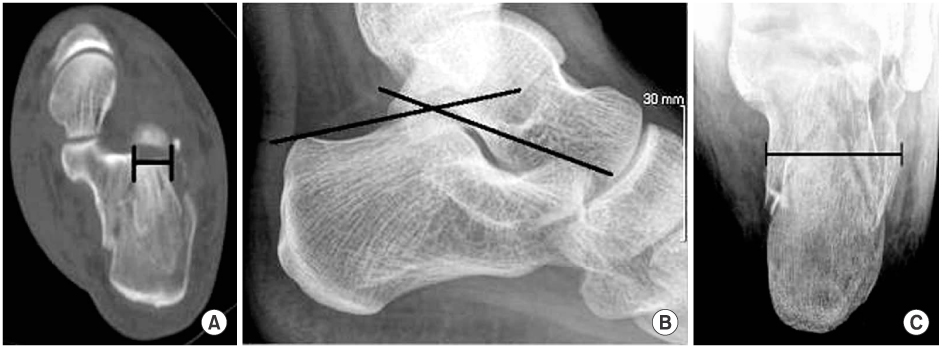
According to Creighton-Nebraska Health Foundation Assessment Score (C-N score), there were 5 excellent, 11 good, 6 fair and 10 poor results. Böhler angle was corrected from 10.3 degrees to 24.5 degrees. There was a positive correlation between size of depressed fragment and C-N score (p<0.01).
CONCLUSION
Essex-Lopresti method can substitute open reduction methods in joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures which have relatively large depressed joint fragments.
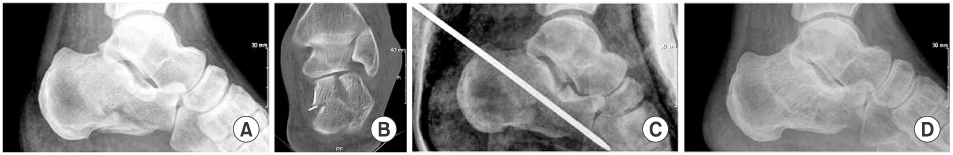
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment of Calcaneus Fractures: Recent Trend for Acute Fractures and Complications
Woo-Chun Lee
J Korean Fract Soc. 2007;20(4):361-367. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.361.
Reference
-
1. Bernstein SA. Late sequelae of calcaneal fractures. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2000; 17:81–96.2. Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T. Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72:852–859.
Article3. Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T. Intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results of closed treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 290:47–54.
Article4. Essex-Lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique and results of os calcis. Br J Surg. 1952; 39:395–419.5. Kwak KD, Cho HO, Lim DH, Ahn SM, Jang JH. Modified Essex-Lopresti reduction for the displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Soc Foot Surg. 2003; 7:109–114.6. Lance EM, Carey EJ Jr, Wade PA. Fractures of the os calcis treatment by early mobilization. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1963; 30:76–90.7. Miller WE. Pain and impairment considerations following treatment of disruptive os calcis fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; (177):82–86.
Article8. Myerson M, Quill GE Jr. Late complications of fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75:331–341.
Article9. Pozo JL, Kirwan EO, Jackson AM. The long-term results of conservative management of the severely displaced fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66:386–390.10. Ross SD, Sowerby MR. The operative treatment of fractures of the os calcis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; 199:132–143.
Article11. Sanders R. Displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:225–250.
Article12. Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 290:87–95.13. Sung CH, Park BM, Song KS, Kim HG, Kim JM, Kim TE. Operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures-comparison of outcomes between open reduction and closed reduction. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:170–175.
Article14. Tornetta P 3rd. The Essex-Lopresti reduction for calcaneal fractures revisited. J Orthop Trauma. 1998; 12:469–473.
Article15. Yoon HK, Jeon KP, Kang KH, Kim JI, Kim DS, Song KS. Essex-Loprestis axial pinning in the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999; 12:344–350.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Essex-Lopresti Axial Fixation for Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures
- Calcaneal Fractures-Extended Lateral Approach
- The prognostic factors in Tongue shaped calcaneal fractures treated by Essex-Lopresti method
- Prediction of Peroneal Tenosynovitis in the Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures Using Computed Tomography
- Entrapment of Sural Nerve in Essex-Lopresti Axial Fixation for Calcaneal Fracture: A Case Report