J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Jun;57(6):1022-1025. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.6.1022.
A Case of Fibrotic Obstruction of Scleral Orifice of Ex-PRESS Shunt
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. exo70@naver.com
- KMID: 2290510
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.6.1022
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of fibrotic obstruction of scleral orifice in Ex-PRESS shunt.
CASE SUMMARY
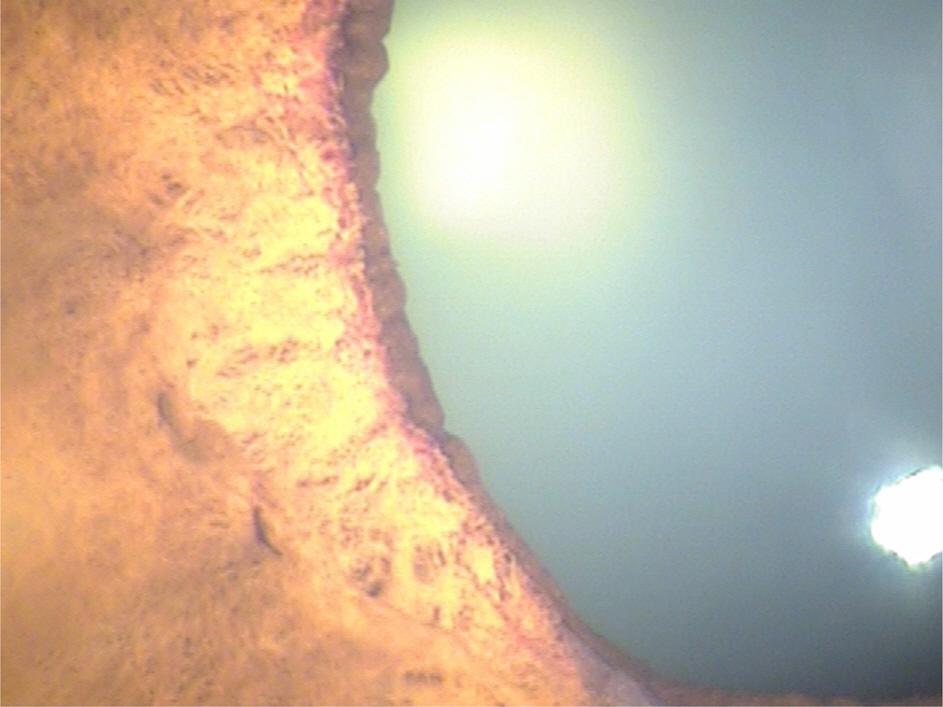
A 57-year-old male presented with elevated intraocular pressure in his left eye. In the past, laser photocoagulation was performed at a local clinic due to retinal venous occlusion in his left eye. During observation, he was transferred to our hospital due to uncontrolled intraocular pressure despite antiglaucoma medications. He was diagnosed with neovascular glaucoma in the left eye. Since intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor with maximal medical therapy did not lower the intraocular pressure, an Ex-PRESS shunt device was implanted. Two weeks postoperatively, the bleb was flat and diffuse with shallow anterior chamber and intraocular pressure was below 5 mm Hg. Therefore, we performed scleral flap revision and intraocular pressure was sustained between 10 and 15 mm Hg. Two months postoperatively, the patient experienced high intraocular pressure and no elevated bleb, thus we performed bleb revision. During the surgery, although we removed fibrotic adhesions between the conjunctiva and episclera using a 30-gauge needle, aqueous outflow was not observed. Therefore, we opened the scleral flap and found the scleral orifice of the Ex-PRESS shunt was obstructed by fibrous scar tissue. After scar tissue removal and achieving aqueous outflow through the scleral opening, intraocular pressure decreased to a satisfactory level.
CONCLUSIONS
In patients with elevated intraocular pressure after implantation of the Ex-PRESS shunt, the scleral opening of the Ex-PRESS shunt should be examined for obstruction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Samsudin A, Eames I, Brocchini S, Khaw PT. Evaluation of dimesional and flow properties of ExPRESS glaucoma drainage devices. J Glaucoma. 2015; Feb 25:[Epub ahead of print].2. Kanner EM, Netland PA, Sarkisian SR Jr, Du H. abdominal abdominal glaucoma device implanted under a scleral flap alone or abdominal with phacoemulsification cataract surgery. J Glaucoma. 2009; 18:488–91.3. Salim S. abdominal glaucoma filtration device-surgical technique and outcomes. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2011; 51:83–94.4. Dahan E, Carmichael TR. Implantation of a miniature glaucoma device under a scleral flap. J Glaucoma. 2005; 14:98–102.
Article5. Tanito M, Sano I, Ohira A. A case report of progressive obstruction of abdominal miniature glaucoma shunt after transient flat anterior chamber and treatment using Nd:YAG laser. BMC Ophthalmol. 2015; 15:2.
Article6. Holló G, Naghizadeh F. High magnification in vivo evaluation of the mechanism of failure of an abdominal shunt implanted under the sclera flap. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2014; 24:617–9.7. Yu XB, Sun XH, Dahan E, et al. Increased levels of transforming growth factor-betal and –beta2 in the aqueous humor of patients with neovascular glaucoma. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2007; 38:6–14.8. Mariotti C, Dahan E, Nicolai M, et al. abdominal outcomes and risk factors for failure with the Ex-press glaucoma drainage device. Eye (Lond). 2014; 28:1–8.