J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Jun;57(6):905-916. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.6.905.
Comparison of Intraocular Lens Calculation Formulas Measured by Immersion-Type A-Scan Ultrasound and Partial Coherence Interferometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. yhs0816@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2290492
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.6.905
Abstract
- PURPOSE
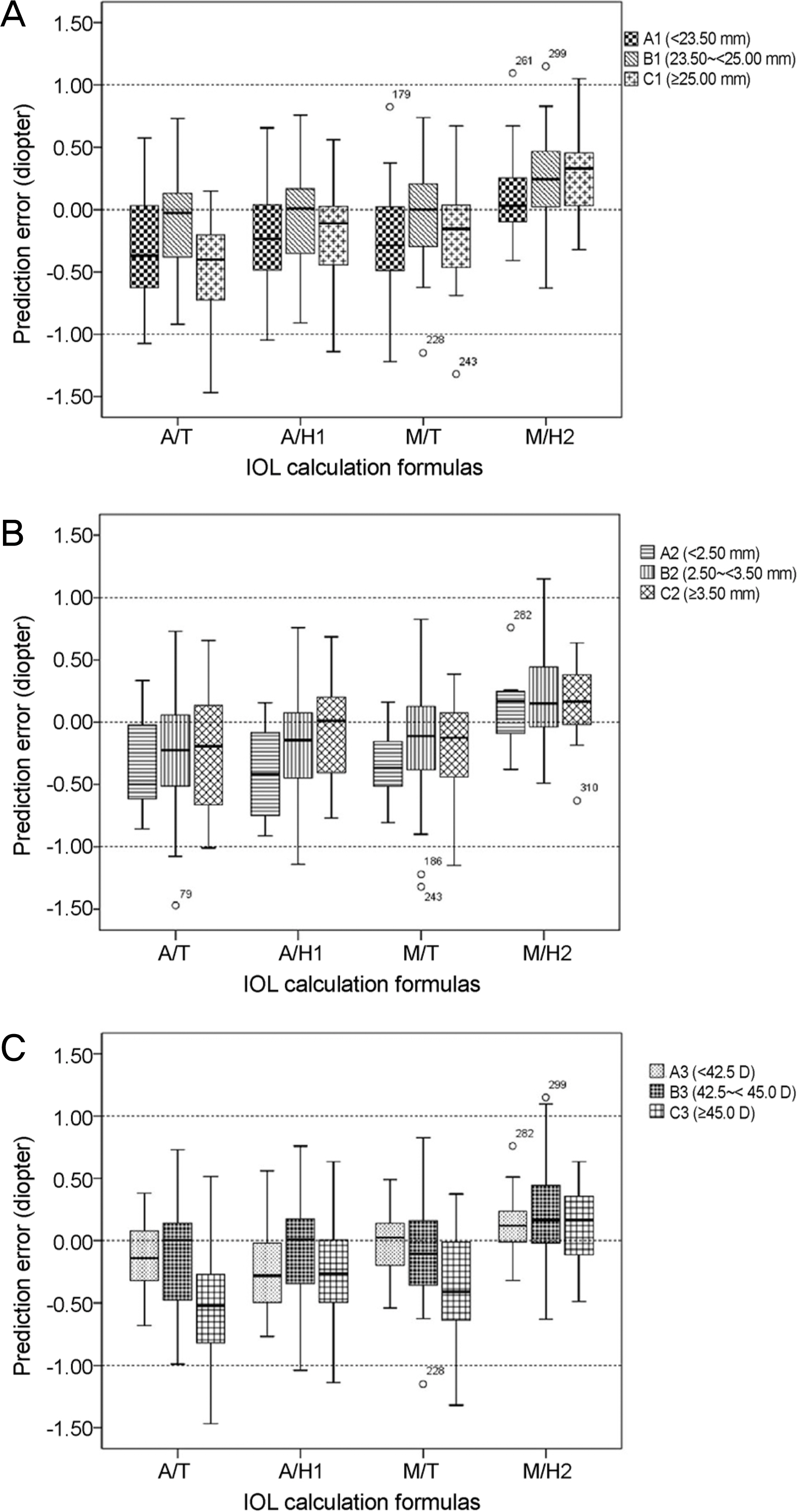
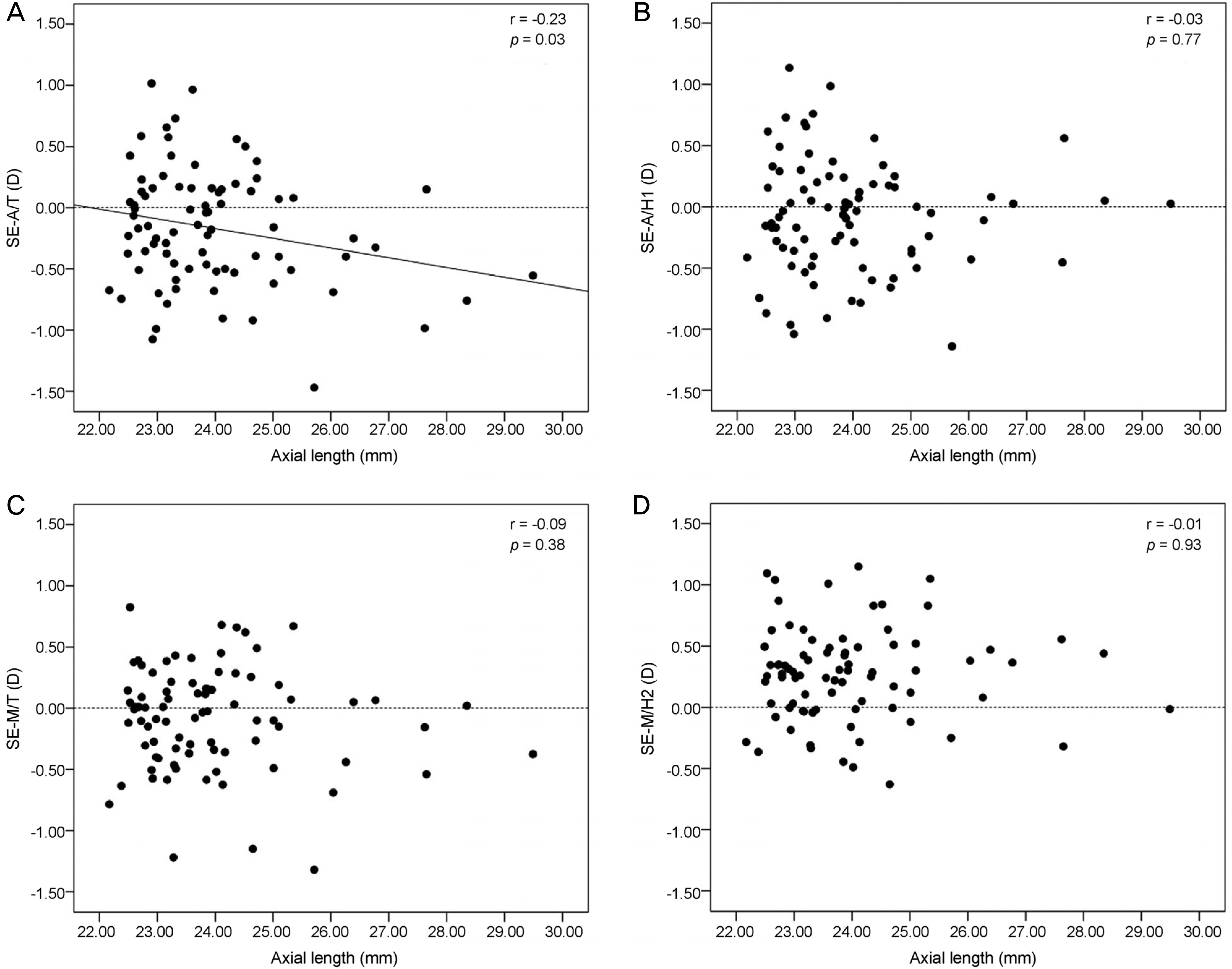
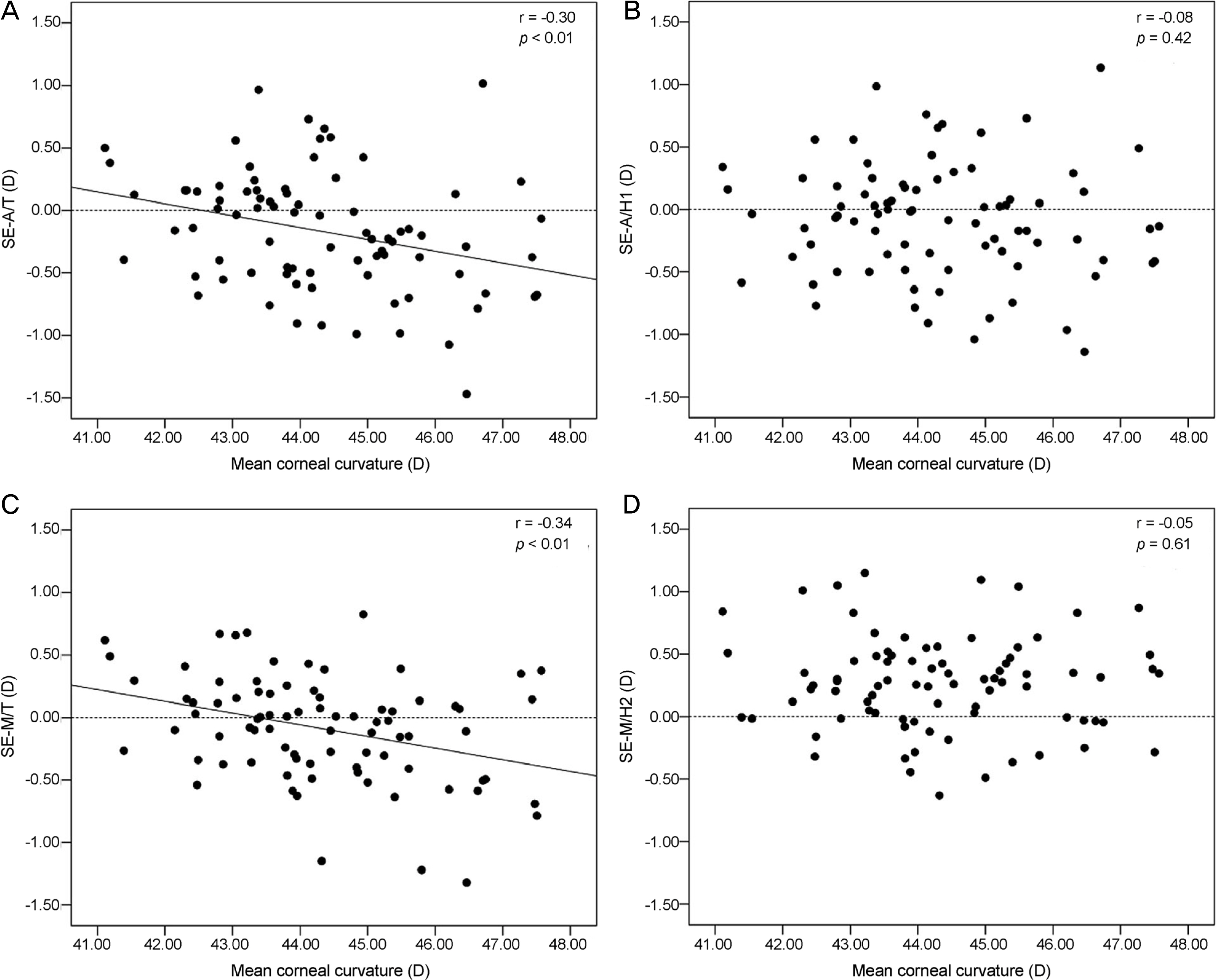
To report the accuracy of intraocular lens (IOL) formulas according to axial length, anterior chamber depth, and mean corneal curvature when performing biometry with an immersion type A-scan with mannual keratomery and an IOL Master®.
METHODS
Retrospective medical chart reviews were carried out for 82 eyes of 65 patients who underwent cataract surgery performed by a single surgeon. Biometry was performed using IOL Master®, mannual keratometry, and immersion type A-scan ultrasound in sequence. Prediction diopter was obtained using Sanders-Retzlaff-Kraff/Theoretical (SRK-T) and Holladay 1 formulas calculated with the biometric value measured by mannual keratomery and A-scan, and using SRK-T and, Holladay 2 formulas with IOL Master®. The final refractive outcome was determined as manifested refraction at least 7 weeks after the surgery, and it was compared with the preoperative prediction dipoter (D) of the IOL formulas.
RESULTS
Mean axial length and mean keratomtric measurements as determined by A-scan with mannual keratomery showed significant statistical differences from those of IOL Master®. However, there was no difference in postoperative mean absolute error between biometric measurements, or among formulas according to axial length, anterior chamber depth, or mean corneal curvature. However, the percentage of actual refraction within ±0.50 D of the intended refraction was dirrerent among the four formalas according to axial length, anterior chamber dept, mean corneal curvature.
CONCLUSIONS
Biometry measurement using the immersion-type A-scan with mannual keratomery is as accurate as that using IOL Master® for predicting the postoperative refractive state of cataract surgery. However, it is suggested that the best IOL formula be chosen according to axial length, anterior chamber depth, and mean corneal curvature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Németh J, Fekete O, Pesztenlehrer N. Optical and ultrasound measurement of axial length and anterior chamber depth for abdominal lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:85–8.2. Abulafia A, Barrett GD, Rotenberg M, et al. Intraocular lens power calculation for eyes with an axial length greater than 26.0 mm: comparison of formulas and methods. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:548–56.
Article3. Narváez J, Zimmerman G, Stulting RD, Chang DH. Accuracy of intraocular lens power prediction using the Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, Holladay 2, and SRK/T formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2050–3.
Article4. Aristodemou P, Knox Cartwright NE, Sparrow JM, Johnston RL. Intraocular lens formula constant optimization and partial abdominal interferometry biometry: refractive outcomes in 8108 eyes abdominal cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:50–62.5. Kim DY, Kim MJ, Kim JY, Tchah H. Comparison of formulas for intraocular lens power calculation installed in a partial coherence interferometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:523–8.
Article6. Yi CH, Choi SH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Accuracy of the Haigis abdominal based on axial length and anterior chamber depth. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:175–81.7. Olsen T, Olesen H, Thim K, Corydon L. Prediction of abdominal intraocular lens chamber depth. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:587–90.8. Srivannaboon S, Chirapapaisan C, Chirapapaisan N, et al. Accuracy of Holladay 2 formula using IOLMaster parameters in the absence of lens thickness value. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:2563–7.
Article9. Kiss B, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Biometry of cataractous eyes using partial coherence interferometry: clinical feasibility study of a commercial prototype I. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:224–9.10. Vogel A, Dick HB, Krummenauer F. Reproducibility of optical biometry using partial coherence interferometry: intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1961–8.
Article11. Shin DH, Lim DH, You JY, et al. Formula comparison for abdominal lens power calculation using IOL master and ultrasound for the ZCB00 IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:527–33.12. Hwang JS, Lee JH. Comparison of the IOL master(R) and A-scan ultrasound: refractive results of 96 consecutive cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:27–32.13. Song BY, Yang KJ, Yoon KC. Accuracy of partial coherence abdominal in intraocular lens power calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:775–80.14. Hennessy MP, Franzco , Chan DG. Contact versus immersion abdominal of axial length before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:2195–8.15. Giers U, Epple C. Comparison of A-scan device accuracy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:235–42.
Article16. Olsen T, Nielsen PJ. Immersion versus contact technique in the measurement of axial length by ultrasound. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1989; 67:101–2.
Article17. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS, et al. Immersion A-scan abdominal with partial coherence interferometry: outcomes analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:239–42.18. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.
Article19. Kim BH, Wee WR, Kim MK. Analysis of factors that influence on accuracy of intraocular lens power calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:173–81.
Article20. Park KH, Cho YM, Lee JS. The clinical efficacy of the Haigis abdominal using A-scan contact ultrasound biometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1793–9.21. Kim JW, Lee H, Jung JW, et al. Comparison of ocular biometry abdominal low-coherence reflectometry with other devices for intraocular lens power calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:1558–65.22. Elder MJ. Predicting the refractive outcome after cataract surgery: the comparison of different IOLs and SRK-II v SRK-T. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:620–2.
Article23. Aristodemou P, Knox Cartwright NE, Sparrow JM, Johnston RL. Formula choice: Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, or SRK/T and refractive outcomes in 8108 eyes after cataract surgery with biometry by abdominal coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:63–71.24. Iwase T, Tanaka N, Sugiyama K. Postoperative refraction changes in phacoemulsification cataract surgery with implantation of abdominal types of intraocular lens. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2008; 18:371–6.25. Patel RP, Pandit RT. Comparison of anterior chamber depth abdominals from the Galilei Dual Scheimpflug Analyzer with IOLMaster. J Ophthalmol. 2012; 2012:430249.26. Kim SI, Kang SJ, Oh TH, et al. Accuracy of ocular biometry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients with AL-Scan(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1688–93.27. Elbaz U, Barkana Y, Gerber Y, et al. Comparison of different abdominals of anterior chamber depth and keratometric measurements. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:48–53.28. Shirayama M, Wang L, Weikert MP, Koch DD. Comparison of abdominal powers obtained from 4 different devices. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 148:528–35.e1.29. Lee AC, Qazi MA, Pepose JS. Biometry and intraocular lens power calculation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:13–7.
Article30. Bang S, Edell E, Yu Q, et al. Accuracy of intraocular lens abdominals using the IOLMaster in eyes with long axial length and a comparison of various formulas. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:503–6.31. Trivedi RH, Wilson ME, Reardon W. Accuracy of the Holladay 2 intraocular lens formula for pediatric eyes in the absence of pre-operative refraction. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1239–43.
Article32. Lüchtenberg M, Kuhli-Hattenbach C, Fronius M, et al. Predictability of intraocular lens calculation using the Holladay II formula after in-the-bag or optic captured posterior chamber intraocular lens abdominalation in paediatric cataracts. Ophthalmologica. 2008; 222:302–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Accuracy of Partial Coherence Interferometry in Intraocular Lens Power Calculation
- Comparison of Formulas for Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Installed in a Partial Coherence Interferometer
- Biometry with Partial Coherence Interferometry and Ultrasonography in High Myopes
- Comparison of Accuracy of Six Modern Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas
- Comparison of the SRK and SRKII Formulas with Revision of Constant A in Intraocular Lens Power Calculation