Korean J Schizophr Res.
2015 Apr;18(1):28-34. 10.16946/kjsr.2015.18.1.28.
A Comparison of Magical Ideation in Nonclinical Adolescent and Adult Groups : An Item Response Theory Based Differential Item Functioning Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Psychiatry, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hyjung@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Adolescent Psychiatry, National Center for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Seoul National Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Psychiatry and Institute of Clinical Psychopharmacology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 5Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Science, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2288315
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2015.18.1.28
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
We examined magical ideation in adolescent and adult group by Magical Ideation Scale (MIS). We also explored how adolescents and adults respond differently to each items of MIS.
METHODS
310 nonclinical adults and 310 Year 10 students participated in this study, and completed MIS and Symptom Checklist 90-revision (SCL-90-R). Total scores of MIS were compared between adults and adolescents. The item characteristics of MIS were evaluated by item response theory (IRT). Differential item functioning (DIF) was detected using the parameters of IRT.
RESULTS
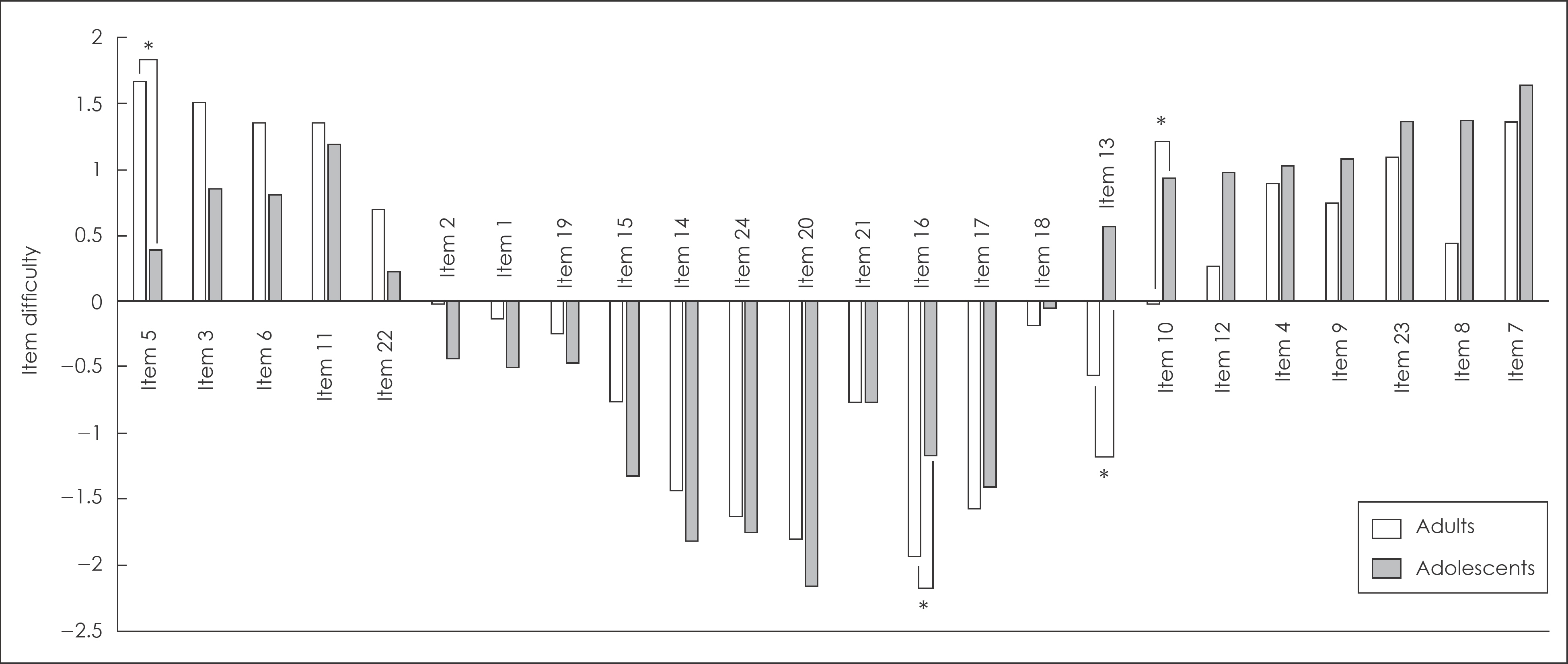
Total score of MIS was higher in adolescents than in adults, but there was no statistical significance. Item 5, 10, 13, and 16 showed significant difference on item difficulty parameters and were identified as DIF. Among DIF items, item 5 was more difficult for adolescents than adults. Item 10, 13, and 16 were more difficult for adults than adolescents. The modified MIS score excluding 4 DIF items was significantly higher in adolescents than adults.
CONCLUSION
The influence of age on response to DIF items should be considered when comparing MIS scores between adolescents and adults.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Johns LC, van Os J. The continuity of psychotic experiences in the general population. Clin Psychol Rev. 2001; 21:1125–1141.
Article2). Chapman LJ, Chapman JP, Miller EN. Reliabilities and intercorrelations of eight measures of proneness to psychosis. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1982; 50:187–195.
Article3). Eckblad M, Chapman LJ. Magical ideation as an indicator of schizotypy. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1983; 51:215–225.
Article4). Chapman LJ, Chapman JP, Kwapil TR, Eckblad M, Zinser MC. Putatively psychosis-prone subjects 10 years later. J Abnorm Psychol. 1994; 103:171–183.
Article5). Kwapil TR, Miller MB, Zinser MC, Chapman J, Chapman LJ. Magical ideation and social anhedonia as predictors of psychosis proneness: A partial replication. J Abnorm Psychol. 1997; 106:491–495.
Article6). Yang IH. A psychometric study of the psychosis proneness scale [dis-sertation]. Seoul: Graduate School of Hanyang Univ.;1996.7). Jung HY, Chang JS, Yi JS, Hwang S, Shin HK, Kim JH, et al. Measuring psychosis proneness in a nonclinical korean population: Is the peters et al delusions inventory useful for assessing high-risk individuals? Compr Psychiatry. 2008; 49:202–210.8). Kim Y, Chang JS, Hwang S, Yi JS, Cho IH, Jung HY. Psychometric properties of peters et al. Delusions inventory-21 in adolescence. Psychiatry Res. 2013; 207:189–194.
Article9). Claridge G, McCreery C, Mason O, Bentall R, Boyle G, Slade P, et al. The factor structure of “schizotypal' traits: A large replication study. Br J Clin Psychol. 1996; 35(Pt 1):103–115.
Article10). Peters ER, Joseph SA, Garety PA. Measurement of delusional ideation in the normal population: Introducing the pdi (peters et al. Delusions inventory). Schizophr Bull. 1999; 25:553–576.
Article11). Venables P, Bailes K. The structure of schizotypy, its relation to sub-diagnoses of schizophrenia and to sex and age. Br J Clin Psychol. 1994; 33:277–294.
Article12). Verdoux H, Van Os J, Maurice-Tison S, Gay B, Salamon R, Bourgeois M. Is early adulthood a critical developmental stage for psychosis proneness? A survey of delusional ideation in normal subjects. Schizophr Res. 1998; 29:247–254.
Article13). Eckblad M, Chapman LJ. Magical ideation as an indicator of schizotypy. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1983; 51:215.
Article14). Yang I, Choi M. Mmpi response study on psychology prone group. J Korean Educ Psychol. 1997; 11:255–289.15). Derogatis LR. Scl-90: Administration, scoring and procedures manual-i for the r evised version and other instruments of the psychopathology rating scale series. Baltimore: John Hopkins University;1977.16). Kim J, Kim K. The standardization study of symptom checklist-90-revision in korea iii. Ment Health Res. 1984; 2:278–311.17). Hambleton RK. Fundamentals of item response theory. Sage publications. 1991.18). Holland PW, Thayer D. Test validity. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.;1988.19). Baker FB. The basics of item response theory. Portsmouth (NH): Heinemann;1985.20). Scheuneman JD. A theoretical framework for the exploration of causes and effects of bias in testing. Educational Psychologist. 1984; 19:219–225.
Article21). Vollema MG, van den Bosch RJ. The multidimensionality of schizotypy. Schizophr Bull. 1995; 21:19–31.
Article22). Casey BJ, Getz S, Galvan A. The adolescent brain. Dev Rev. 2008; 28:62–77.
Article23). Spear LP. The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2000; 24:417–463.
Article24). Lewis DA. Development of the prefrontal cortex during adolescence: Insights into vulnerable neural circuits in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1997; 16:385–398.
Article25). Walker E, Bollini AM. Pubertal neurodevelopment and the emergence of psychotic symptoms. Schizophr Res. 2002; 54:17–23.
Article26). Harrop C, Trower P. Why does schizophrenia develop at late adolescence? Clin Psychol Rev. 2001; 21:241–265.
Article27). Fonseca-Pedrero E, Lemos-Giraldez S, Muniz J, Garcia-Cueto E, Campil-lo-Alvarez A. Schizotypy in adolescence: The role of gender and age. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2008; 196:161–165.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of item analysis results of Korean Medical Licensing Examination according to classical test theory and item response theory
- Psychometric Evaluation of the Korean Version of PROMIS SelfEfficacy for Managing Symptoms Item Bank: Item Response Theory
- Why Do Older Korean Adults Respond Differently to Activities of Daily Living and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living? A Differential Item Functioning Analysis
- Where Can I Find the Free Item Analysis Program Based on Item Response Theory, Computer-Based Testing and Computerized Adaptive Testing?
- Item analysis of the Korean version of the Intensive Care Experience Questionnaire: Using the Rasch Model based on Item Response Theory