J Clin Neurol.
2008 Mar;4(1):51-57. 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.1.51.
Multiple Sclerosis and Peripheral Multifocal Demyelinating Neuropathies Occurring in a Same Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. pkd1165@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2287687
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2008.4.1.51
Abstract
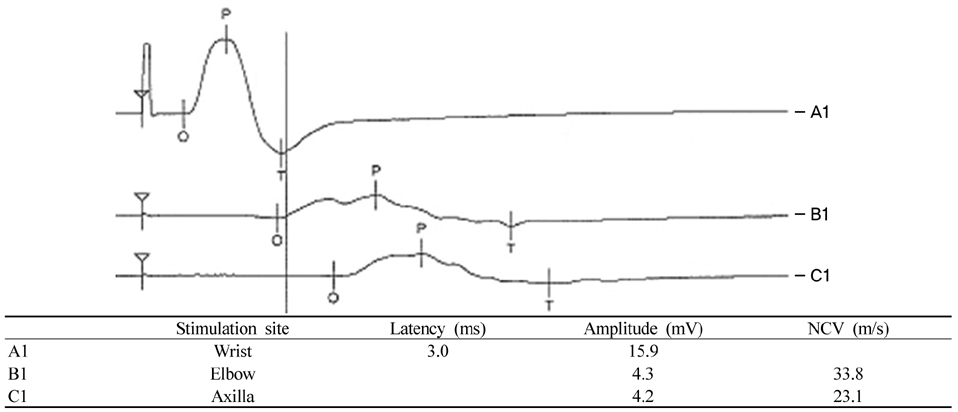
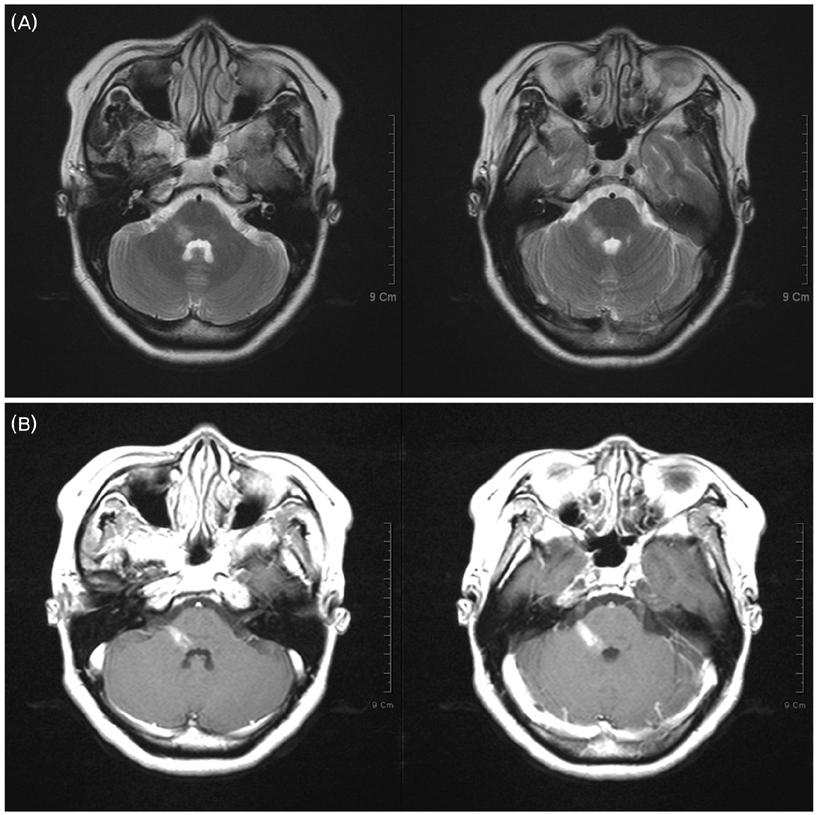
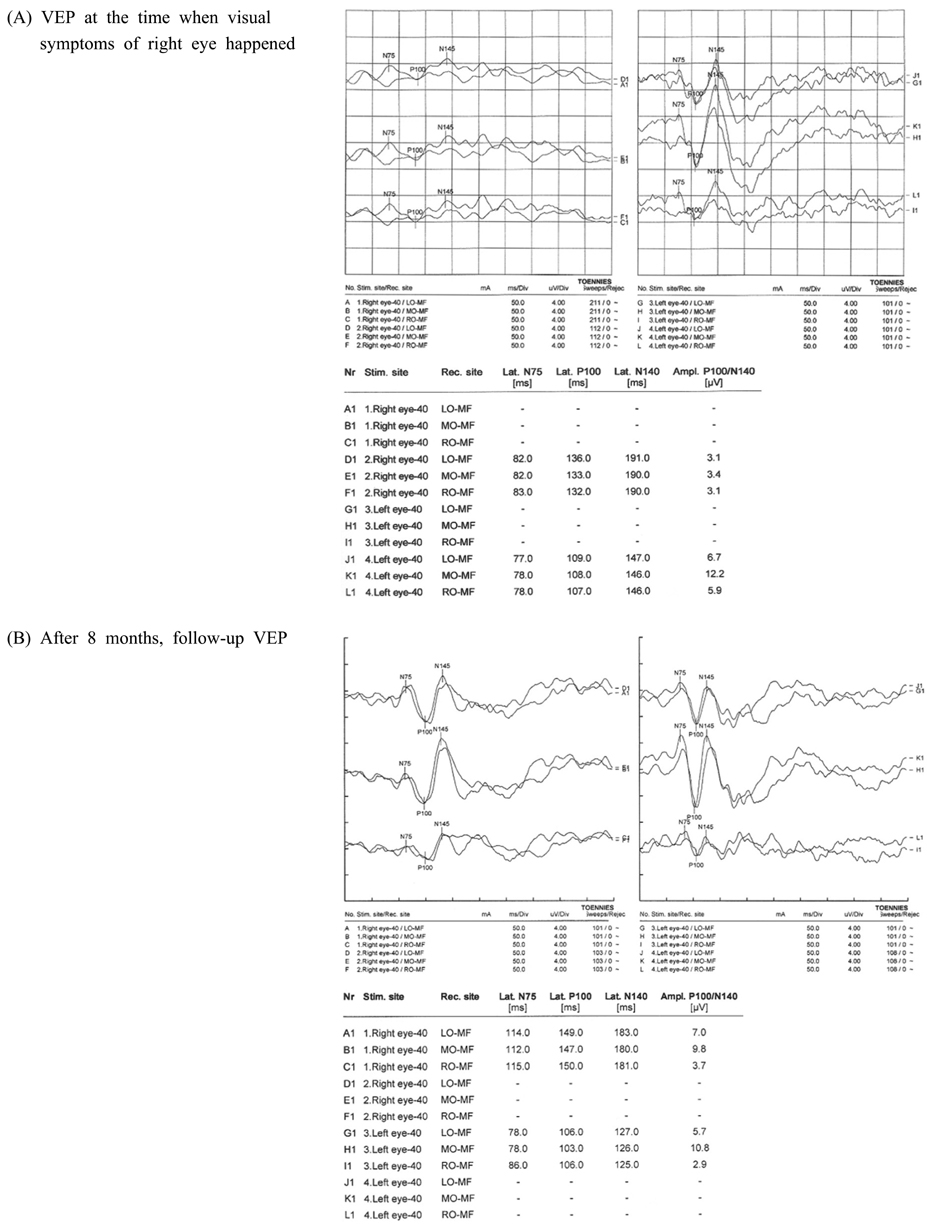
- The co-occurrence of multiple sclerosis and peripheral demyelinating neuropathy is rare. It has been disputed whether these are pathologically related or coincidental findings. We report a 36-year-old woman who presented with diplopia, right facial palsy and left-sided weakness. Brain magnetic resonance imaging showed a lesion indicative of central demyelinating disease. Nerve conduction studies revealed peripheral multifocal demyelinating neuropathies. We suggest that the central and the peripheral lesions may be continua of a demyelinating process.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Concurrence of Multifocal Motor Neuropathy and Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Suk-Won Ahn, Su-Hyun Kim, Byung-Su Park, Jeong-In Cha, Sung-Min Kim, Jung-Joon Sung, Kwang-Woo Lee
J Clin Neurol. 2011;7(3):168-172. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2011.7.3.168.
Reference
-
1. Rosenberg NL, Boudette D. Hypertrophic neuropathy and multiple sclerosis. Neurology (Cleveland). 1983. 33:1361–1364.
Article2. Ro YI, Alexander B, Oh SJ. Multiple sclerosis and hypertrophic demyelinating peripheral neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1983. 6:312–316.
Article3. Poser CM. The peripheral nervous system in multiple sclerosis. A review and pathogenetic hypothesis. J Neurol Sci. 1987. 79:83–90.4. Naganuma M, Shima K, Matsumoto A, Tashiro K. Chronic multifocal demyelinating neuropathy associated with central nervous system demyelination. Muscle Nerve. 1991. 14:953–959.
Article5. Almsaddi M, Bertorini TE, Seltzer WK. Demyelinating neuropathy in a patient with multiple sclerosis and genotypical HMSN-1. Neuromuscul Disord. 1998. 8:87–89.
Article6. Lee CH, Kim BJ, Park KW, Koh SB, Kim HJ, Lee DH. Chronic inflammatory demeylinating polyneuropathy developed during interferon-β therapy in a patient with multiple sclerosis. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2006. 24(5):486–490.7. Matsuse D, Ochi H, Tashiro K, Nomura T, Murai H, Taniwaki T, et al. Exacerbation of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy during interferonβ-1b therapy in a patient with childhood-onset multiple sclerosis. Intern Med. 2005. 44(1):68–72.
Article8. Pollock M, Calder C, Allpress S. Peripheral nerve abnormality in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1977. 2:41–48.
Article9. Ropper AH, Brown RH. Adams and Victor's Principles of neurology. 2005. 8th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;771–796.10. Mendell JR, Kolkin S, Kissel JT, Weiss KL, Chakeres DW, Rammohan KW. Evidence for central nervous system demyelinating in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology. 1987. 37:1291–1294.
Article11. Kim BJ, Lee KH. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2005. 23:143–151.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Tumefactive Lesion: Demyelinating Disease Versus Brain Tumor
- Unilateral Hypoglossal Neuropathy in Multifocal Acquired Demyelinating Sensory and Motor Neuropathy: Differential Diagnosis of Motor Neuron Disease
- Introduction to the Management and Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathies
- A Case of Multiple Sclerosis Presenting with Tumefactive Lesions
- A Case of Multiple Sclerosis Presenting as Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis